POSTCLASSICAL TEST REVIEW 600
advertisement

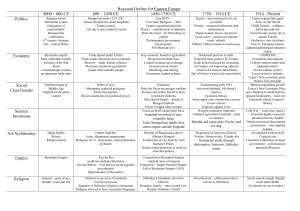
POSTCLASSICAL TEST REVIEW 600-1450 TOPIC/OBJECTIVE 1 2 name _____________________ DESCRIPTION Rise of Islam (reread chapter 9 homework) During the Abbasid period (750-1258), the status of women Abbasid period, slavery existed in decreased due to Persian influence cities and rural areas; typical of unskilled occupations 3* Bedouin religion before Muhammad Bedouins—Arab nomads; combined animism & polytheism 4 Muslim belief system Five pillars of Faith 5 Describe Byzantine resistance to Muslim attacks More effective than Sasanids (Persia),but lost land in Egypt,, Syria, & Palestine 6 Muhammad’s flight to Medina. Impact? Term: hijra (hegira), 622 CE. Many people convert to Islam:+ effect: attracts poor 7 Difference between Islam & Hinduism Islam stresses egalitarianism (equality), Hinduism is based on the caste system. 8 Describe urbanization in the Abbasid period Despite political breakdown (disintegration), towns continued to grow rapidly 9 Crusades. Examples of cultural exchange adopted by Europeans Scientific learning, Arab numbers, military technology, language 10 Seljuk Turk conquest of Baghdad in 1055. Impact? (context: during Abbasid period) Turks restored stability despite challenges posed by Fatimid Egypt & Byzantine empire Africa. West Africa (Ghana, Mali, Songhay) & East African trading cities (reread chapter 15 homework) 11 Weakness of Africa’s commercial economy? Loss of natural resources. They exported gold bullion & raw materials to obtain manufactured goods 12 Who conquered Ghana? When? Impact? Almoravids (Berbers); 1076 spread of Islam to West Africa 13 Reason for Songhay’s downfall. Invasion: well-armed Moroccan Muslim armies seeking gold 14 Impact of slave trade due to Muslim Slavery became diffused & slave trade then developed quickly contact. (Sahara, West Africa) 15 East African towns. Traded with whom? (see Mombasa, Kilwa, Mogadishu, p. 377) Persian Gulf, India, China, markets in the hinterlands west of the urbanized coast 16 African societies NOT associated with a writing system Islam or Christianity lacked … 17 East Africa. Extent of Islam’s penetration? Spread mainly to coastal cities and towns; not much penetration into the interior. Eastern & Western Europe (reread homework to chapters 10, 12) 18 Significance of Byzantine Empire! Answer:Survived almost 1000 years; scholars kept Rome’s cultural achievements alive Constantinople major urban center; culture spread to Russia and throughout Balkans 19 Byzantine’s greatest impact was on … 20 Who conquered the Byzantines? Impact? 21 During the Middle Ages northern regions of eastern and western Europe struggled to establish … 22 Impact of Justinian’s reconquest (circa 565) 23 Impact of Justinian’s code 24 economic result of Byzantine conflict with Arab Muslims Russia: religion, churches (onion domes) & Cyrillic alphabet 1453; Ottoman Turks new water routes for Europeans political identities because unsafe roads decentralized governments Weakened empire’s defenses on Eastern border with the Persians Strengthened & organized Roman law 25 similarity between China & Byzantine In Byzantine Empire, small farmers were weakened by heavy taxes, leading to greater ARISTOCRATIC estates. Elaborate & well-trained bureaucracy 26 greatest concentration of urbanization Italy and the low countries (Netherlands) after the tenth century (hint: Venice, Genoa) 27 main result of the Crusades on Europe Cultural diffusion and economic revival based on trade 28 European intellectual endeavors before 1000? After 1000? Before: limited to copying ancient texts After: synthesis of rationalism & theology (Aquinas) Read about Aquinas on p.408! 29 European women’s roles 30 Hundred Years War. (1337-1453) Impact? The Americas prior to 1492 (ch.12) 31 in 1492, the population of the Americas Were married or were nuns; assisted men; more limitations on roles; involved in local commerce Both England and France emerged as stronger centralized governments Close to that of Europe was … 32 practice common to Aztec and Inca tribute system 33 During the postclassical era (600-1450) Entirely separate from those of the Old World American societies were … 34 civilization that preceded Aztecs? Where? 35 first Aztec form of government Toltecs, central Mexico (memory device: Ol’Teo’ma’Tol’Az) city-states 36 Impact of Aztec expansion and conquest The Aztec clan-based society became more hierarchical East Asia: China, Japan, Korea, Mongols 37 political situation after the fall of the Han 38 name first 7 Chinese dynasties in order 39 reunification of China; When? How? 40 The Tang supported the revival of the 41 During Song Empire, the scholar gentry Period of disunity; ruled by non Chinese nomads; Buddhism eclipsed Confucianism Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, Sui, Tang, Song Sui, 589; with help of nomadic warrior elite Confucian scholar gentry, often at the expense of the aristocracy (why?) Continued its ascent over aristocracy & Buddhists 42 Japan. The Taika reforms were an attempt remake Japanese monarch into an absolutist Chinese Emperor to … 43 Rise of Samurai. Social Impact. Peasants reduced to serf status (bound to the land) 44 Japanese feudal period; memorize KAT Kamakura, Ashikaga, Tokugawa 45 China failed to assimilate Vietnamese. Why? Chinese imports didn’t impact or impress peasants 46 religious preference of the Korean elite? Buddhism, which it spread to Japan in the 600s 47 Russia, at the time of the Mongol invasion? split into small kingdoms located on trading cities It became Russia’s leading political center due 48 Mongol impact on Moscow … to collection of tribute 49 favored military tactic of Chinggis (Genghis) Fake retreat followed by attack from the flanks Khan … 50 How did Mongols weaken centers of Islamic civilization? 51 How the Yuan (Mongols) weakened scholar gentry 52 extent of Timur-i lang’s conquest (a.k.a. Timur, read top of p.336) 53 Song Dynasty trade patterns focused on … 54 In order to expand its economy, the Tang dynasty strengthened its … Cities destroyed from Central Asia to Mediterranean; mosques destroyed They didn’t reinstate the civil service examinations Persia, south Russia, India, Fertile Crescent Trade growth along the Pacific coast and Southeast Asia Infrastructure: waterways, canals, and roads (see bottom of p.280) 55 One reason the economy of Tang China Tributary system (read p.279) prospered was the development of the … 56 The Japanese novel, The Tale of Genji Was significant because … it was among the earliest Japanese literary works (discussed on p.295) Miscellaneous questions 57 another reason why the West began new trade routes after 1400 Technological barriers had been overcome i.e. lateen sails, compass 58 why Italy emerged as Renaissance center Central location on Mediterranean Sea; brought back goods & ideas (contact w/scholars) 59 Renaissance characteristics Humanism, interest in nature & things of this world (temporal) 60 European demographic changes; 1300s, 1400s Urbanization, growth of urban economy, decline of feudalism 61 Ming China’s most famous explorer? Places he traveled to? What he collected? Zheng He; Strait of Malacca, India, East Africa; collected tribute 62 Greatest Muslim empire after Abbasid’s fall & Mongol withdrawal? Ottoman Empire; Constantinople became Istanbul. (see Hagia Sophia) 63 Greatest Ottoman leader? Sulieman the Magnificent. (p.526) POSTCLASSICAL TEST REVIEW 600-1450 TOPIC/OBJECTIVE Rise of Islam 1 Abbasid period, status of women 2 Abbasid period, slavery existed in 3* Bedouin religion before Muhammad name _____________________ DESCRIPTION (reread chapter 9 homework) Bedouins—Arab nomads; combined 4 Muslim belief system 5 Describe Byzantine resistance to Muslim attacks More effective than Sasanids (Persia),but lost land in Egypt,, Syria, & Palestine 6 Muhammad’s flight to Medina. Impact? Term: hijra (hegira), 622 CE. Many people convert to Islam:+ effect: attracts poor 7 Difference between Islam & Hinduism Islam stresses egalitarianism (equality), Hinduism is based on the ____________ 8 Describe urbanization in the Abbasid period Despite political breakdown (disintegration), towns continued to grow rapidly 9 Crusades. Examples of cultural exchange adopted by Europeans 10 Seljuk Turk conquest of Baghdad in 1055. Impact? (context: during Abbasid period) Turks restored stability despite challenges posed by Fatimid Egypt & Byzantine empire Africa. West Africa (Ghana, Mali, Songhay) & East African trading cities (ch.15) 11 Weakness of Africa’s commercial economy? __________________________ They exported gold bullion & raw materials to obtain manufactured goods 12 Who conquered Ghana? When? Impact? 13 Reason for Songhay’s downfall. 14 Impact of slave trade due to Muslim contact. (Sahara, West Africa) 15 East African towns. Traded with whom? (see Mombasa, Kilwa, Mogadishu, p. 377) Persian Gulf, India, China, markets in the hinterlands west of the urbanized coast 16 African societies NOT associated with Islam or Christianity lacked … 17 East Africa. Extent of Islam’s penetration? Spread mainly to coastal cities and towns; not much penetration into the interior. Eastern & Western Europe (reread homework to chapters 10, 12) 18 Significance of Byzantine Empire! Answer: Survived almost 1000 years; Constantinople major urban center; culture spread to Russia and throughout Balkans; 19 Byzantine’s greatest impact was on … 20 Who conquered the Byzantines? Impact? 21 During the Middle Ages northern regions of eastern and western Europe struggled to establish … 22 Impact of Justinian’s reconquest (circa 565) 23 Impact of Justinian’s code 24 economic result of Byzantine conflict with Arab Muslims Weakened empire’s defenses on Eastern border with the Persians In Byzantine Empire, small farmers were weakened by heavy taxes, leading to greater ARISTOCRATIC estates. 25 similarity between China & Byzantine 26 greatest concentration of urbanization Italy and the low countries (Netherlands) after the tenth century (hint: Venice, Genoa) 27 main result of the Crusades on Europe Cultural diffusion and economic revival based on trade 28 European intellectual endeavors before 1000? After 1000? Before: limited to copying ancient texts After: synthesis of rationalism & theology (Aquinas) Read about Aquinas on p.408! 29 European women’s roles 30 Hundred Years War. (1337-1453) Impact? The Americas prior to 1492 (ch.12) 31 in 1492, the population of the Americas Were married or were nuns; assisted men; more limitations on roles; involved in local commerce Both England and France emerged as stronger centralized governments was … 32 practice common to Aztec and Inca 33 During the postclassical era (600-1450) Entirely separate from those of the Old World American societies were … 34 civilization that preceded Aztecs? Where? 35 first Aztec form of government Toltecs, central Mexico (memory device: Ol’Teo’ma’Tol’Az) city-states 36 Impact of Aztec expansion and conquest East Asia: China, Japan, Korea, Mongols 37 political situation after the fall of the Han Period of disunity; ruled by non Chinese nomads; Buddhism eclipsed Confucianism 38 name first 7 Chinese dynasties in order 39 reunification of China; When? How? 40 The Tang supported the revival of the Sui, 589; with help of nomadic warrior elite 41 During Song Empire, the scholar gentry Continued its ascent over aristocracy & Buddhists 42 Japan. The Taika reforms were an attempt remake Japanese monarch into an absolutist Chinese Emperor to … 43 Rise of Samurai. Social Impact. 44 Japanese feudal period; memorize KAT 45 China failed to assimilate Vietnamese. Why? Chinese imports didn’t impact or impress peasants 46 religious preference of the Korean elite? 47 Russia, at the time of the Mongol invasion? split into small kingdoms located on trading cities 48 Mongol impact on Moscow … 49 favored military tactic of Chinggis (Genghis) Fake retreat followed by Khan … 50 How did Mongols weaken centers of Islamic civilization? 51 How the Yuan (Mongols) weakened scholar gentry They didn’t reinstate the 52 extent of Timur-i lang’s conquest (a.k.a. Timur, read top of p.336) 53 Song Dynasty trade patterns focused on … Trade growth along the Pacific coast and Southeast Asia 54 In order to expand its economy, the Tang dynasty strengthened its … (see bottom of p.280) 55 One reason the economy of Tang China prospered was the development of the … 56 The Japanese novel, The Tale of Genji was significant because … (read p.279) it was among the earliest Japanese literary works (discussed on p.295) Miscellaneous questions 57 another reason why the West began new trade routes after 1400 i.e. lateen sails, compass 58 why Italy emerged as Renaissance center 59 Renaissance characteristics 60 European demographic changes; 1300s, 1400s 61 Ming China’s most famous explorer? Places he traveled to? What he collected? 62 Greatest Muslim empire after Abbasid’s fall & Mongol withdrawal? Ottoman Empire; Constantinople became Istanbul. (see Hagia Sophia) 63 Greatest Ottoman leader? Sulieman the Magnificent. (p.526)