Study Guide
advertisement

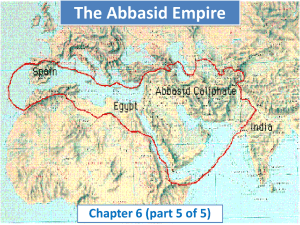
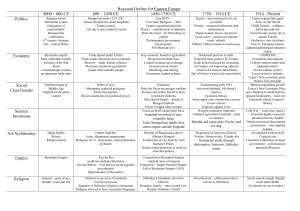
Post-Class: Ch9-10 Study Guide NAME: ____________________________ Divergent Histories in Europe (Ch. 9-10) ...is about a new Christian Europe and the Byzantine Empire’s decreasing ability to continue the tradition of the Eastern Roman Empire while Western Europe gradually made progress by addressing basic concerns following the chaos of Rome’s fall. Overarching Ideas: Humans need to adapt to environments has necessitated technological innovation. Cultures spread through syncretism. Economic conditions and religion are key components in legitimizing or undermining government. Ever intensifying trade is a powerful force for social and political change. Social inequality is source of conflict yet ever-present in civilizations. Objectives: 1. Evaluate the significance of Byzantine Empire on European civilization. 2. Explain how the beliefs of Orthodox Christianity and Catholicism impacted Eastern and Western European societies. 3. Explain the spread of Christianity and its interactions with non-Christian groups. 4. Analyze the causes and effects of social hierarchy during the postclassical period. 5. Compare the social and political evolution of Eastern Europe and Western Europe. 6. Compare the economic and political structures of Western Europe’s early Middle Ages and high Middle Ages. 7. Analyze how conflict aided the exchanges of intensified postclassical networks. 8. Analyze the changes and continuities in the role of cities during the classical and postclassical periods. Key Concepts: Explain the definition, role, and significance of… Caesaropapism Hagia Sophia Icon Eastern Orthodox Cyrillic Russian Orthodox Vladimir Tatars Early Middle Ages High Middle Ages Late Middle Ages Medieval Feudalism Manorialism Norse / Vikings Normans Ghettos Three estates Lords Vassals Serfs Three-field system Clovis Carolingians Charlemagne William the Conqueror Holy Roman Empire Magna Carta Crusades Thomas Aquinas Scholasticism Gothic Hanseatic League Guilds Hundred Years War Black Death Eastern Europe Key Places: Locate on the map… Byzantine Empire in 565 Byzantine Empire b/t 867-1025 Byzantine Empire post-1071 Constantinople Anatolia Balkan Peninsula Scandinavia Dnieper River Kiev Russia Persia Arabia Guided Timeline: Byzantium - E. Europe Dar al-Islam Russia – E. Europe 330 527 – 565 600 Rise & Spread of Islam 600-650 Umayyad & Strengthening Trade Contacts 661-750 600s 597 – 867 Peak of Abbasid 750-1000 864 867 – 1025 980 – 1015 1000 Decline of Abbasid & Growing Muslim Influence in Af, S/SE Asia 1000-1250 Fall of Abbasid 1258 Peak of Muslim Trade & Influence 1250-1450 1450 1054 1019 – 1054 1100 – 1237 1100 – 1453 1237 – 1480 Western Europe Key Places: Locate on the map… Carolingian Empire Rome Atlantic Ocean North Sea Baltic Sea England Holy Roman Empire Pyrenees Mountains Mediterranean Sea Black Sea Constantinople Jerusalem Scandinavia Normandy Islamic caliphates Guided Timeline: Dar al-Islam 600 E. Europe Eastern Roman Empire 330 - 565 Western Europe Rise & Spread of Islam 600-650 Umayyad & Strengthening Trade Contacts 661-750 Byzantine losses & Russian origins 597 – 867 500 – 900 800-814 Peak of Abbasid 750-1000 Peak & Spread of Orthodoxy 864 – 1054 1000 900 – 1100 Decline of Abbasid & Growing Muslim Influence in Af, S/SE Asia 1000-1250 Fall of Abbasid 1258 Peak of Muslim Trade & Influence 1250-1450 1450 1096 - Decline from Turk & Mongol wars 1100 – 1453 1100 – 1338 1338 1450 Guided Timeline: Dar al-Islam Byzantium - E. Europe Russia – E. Europe Western Europe 330 527 – 565 600 Rise & Spread of Islam 600-650 Umayyad & Strengthening Trade Contacts 661-750 600s 597 – 867 500 – 900 800-814 Peak of Abbasid 750-1000 864 867 – 1025 980 – 1015 900 – 1100 1000 Decline of Abbasid & Growing Muslim Influence in Af, S/SE Asia 1000-1250 Fall of Abbasid 1258 Peak of Muslim Trade & Influence 1250-1450 1450 1054 1019 – 1054 1096 - 1100 – 1237 1100 – 1338 1100 – 1453 1237 – 1480 1338 1450