Unit 2 Expanding Zones of Exchange
advertisement

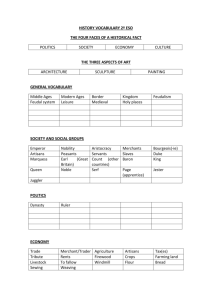
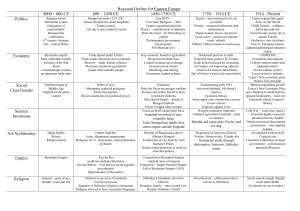
Unit 2 Expanding Zones of Exchange (500-1200) Global History II Review 1 Gupta Empire (320-550) • Hinduism strongly influenced people • Efficient government (bureaucracy) • Caste System organized society – Untouchables were at the bottom (outcasts) • Scientific Contributions – Mathematics: Concept of Zero, Numbers – Medicine – Architecture – Literature 2 Tang and Song Dynasties • Chinese Dynasties (618-907) (960-1279) – Conquered territory and made tributary states – Highly educated ruling class – Social Structure:Gentry, Peasants, Merchants – Expanded trade – Built Canals to encourage trade and transp. – Literature and Arts developed – Huge influence on Japan 3 Byzantine Empire and Russia • Byzantine Empire (565-1453) – Preserved and spread Greco-Roman culture – Justinian’s Code (updated Roman laws) – Engineering and Architectural achievements • Used Roman engineering knowledge • Built large churches – Art: Mosaics and Icons – Orthodox Christian Church • Split from the Roman Catholic Church 4 Byzantine Empire and Russia • Russia (800s- present) – Early trade center of Kiev emerged – Written language developed by Christian Byzantine missionaries – Developed Orthodox Christianity – Autocratic government (Czars= Caesars) – Adopted much from the Byzantine Empire 5 Islamic Civilization • Spread of Islam – Caliph is a successor to Muhammad – Middle East, North Africa, Spain, Sicily, India and Southeast Asia – Trade networks and conquest • Islamic Law – Sharia is law regulating all aspects of life – Sunni and Shi’a split over disagreement on caliph’s authority 6 Islamic Civilization • Society – Permitted social mobility – Tolerant of other religions in conquered lands – Women enjoyed more freedoms than Europe • Islam’s Golden Age – Preserved Greco-Roman culture – Encouraged Education – Art, Literature, and Medicine flourished 7 Islamic Civilization • Mathematics and Science – Development of Algebra and Astronomy • Christian Europe – Islam expanded to Spain and Sicily – Crusades fought between Christians and Muslims over the Holy Lands (Jerusalem) 8 Medieval Europe • Middle Ages (500-1450s) – Emerged as small independent kingdoms after the fall of the Roman Empire • Franks – Germanic empire developed in (France) – Charlemagne became Holy Roman Emperor – Encouraged learning 9 Medieval Europe • Feudalism – Political system using land for loyalty – Social Structure • King, Nobles, Knights, Peasants – Knights lived by a code of Chivalry (loyalty) • Manorialism – Economic system structured around lord’s manor or estate – Peasants (serfs) work the land, lord protects 10 Medieval Europe • Church in Medieval Life – Church hierarchy similar to feudal society – Church was most important thing in life – Church had more power than kings • Cultural Achievements – Literature developed – Gothic architecture developed 11 Crusades • Causes – Byzantine Empire was fighting Muslim Turks – Pope wanted to increase power – Nobles wanted to gain wealth and land – Serfs hoped to escape feudal oppression • Effects – Increased trade between Europe and Asia – Expanded learning of Greco-Roman culture – Power of the Church decreased 12