A. Humerus- (2 Total)
advertisement

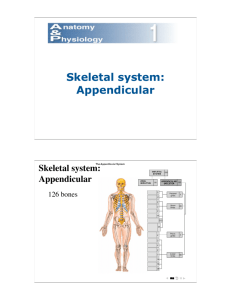
Appendicular Skeleton Outline Contains the bones that lie outside of the mid-ventral axis. Primarily the appendages 1.Pectoral Girdle Provides connection between the axial skeleton and upper limbs. Each girdle contains a Clavicle and a Scapula. Together they Support the arms and are the point of Attachment for the muscles that move the arms. o Clavicle(2) Slender rod like bone. Extends Horizontal between the Sternum and the scapula at the base of the neck. Meets with the scapula to form the Acromioclavicular joint which helps hold the Shoulder in place during movement. o Scapula Triangular in shape, with a thin broad surface and two prominent processes. Acromion process: unites with the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint. Coracoid process anterior to the Acromion process, it provides a place for muscles of the Chest to attach. Glenoid cavity if the oval depression on the Lateral Edge of the scapula, it receives the head of the Humerus. Forms the second joint of the shoulder called the Glenohumeral joint. 2.Upper Limbs Contains a total of 64 bones Supports the arms, wrists, hands, fingers of each side of the body. Each limb contains: o (1)Humerus- Bone of the upper arm, runs from shoulder to elbow (aka the funny bone) o (1)Radius & (1)Ulna- Bones of the lower arm (forearm) run from the elbow to the wrist, Radius(always thumb side) allows you to roll your wrist, Ulna allows you to bend your elbow o Metacarpals- (5) Bones of the hand/palm o Carpals- (8) Bones of the wrist: Scaphiod, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate o Phalanges- (14)Bones of the finger two in the thumb three in every other finger. *Total bones per appendage is (30) x (2) = 60 + (2) Clavicle + (2) Scapula= 64 Total Bones. A. Humerus- (2 Total) a. Prominent Long bone of the arm. b. Extends from the Shoulder to the Elbow. c. The proximal end of the Humerus is known as the Head. d. At the distal end are two processes that articulate with the Ulna and the Radius to form the Elbow joint. i. Capitulum: Articulates with the radius ii. Trochlea: Articulates with the ulna B. Radius- (2 Total) a. Lateral bone of the forearm. b. Always in-line with the Thumb. c. The Head of the radius articulates with the Capitulum of the humerus. d. Styloid process: projection at the distal end that articulates with the processes of the Wrist. C. Ulna- (2 Total) a. Located medial to the radius. b. Coranoid (anterior), Olecronon (posterior) process: projection on the Proximal end, that articulates with the Humerus. i. Forms pointy end of the elbow. ii. Also contains a Styloid process that articulates with the wrist bones. D. Handa. Contains Carpals, Metacarpals, and Phalanges. i. Carpals(16)1. 8 small bones that form the wrist. 2. Bound together by Ligaments. 3. Articulate with the Ulna and the Radius of the arm and the Metacarpals of the hand. 4. Hamate, Capitate, Trapezoid, and Trapezium articulate with the Metacarpals. 5. Pisiform, Triquetrum, Lunate and Scaphoid articulate with the Arm. ii. Metacarpals(10)1. 5 bones which form the Palm of the hand. 2. Contains a flattened base, elongated shaft and rounded distal head. 3. They are numbered 1-5 beginning with the thumb. iii. Phalanges(28)1. 14 bones in each hand. 2. Form the fingers or “Digits” of the hand. 3. Contains three sections (Proximal, Middle, Distal, Phalany) in four fingers. 4. Contain only proximal and distal in the thumb. 3.Pelvic Girdle Forms a strong frame that supports the lower limbs. Consists of two large Coxal bones. Unite Anterior to each other and Posterior to the sacrum. Form a ring structure called the Pelvis. The Pelvis of males and females differ due to the function of childbearing in females. The superior opening of the Pelvis is called the Pelvic Inlet. o Coxae Bones In a newborn consist of three different bones. These bones later fuse. Acetabulum Located on the lateral side of each coxal bone. Forms the socket for the head of the Femur. Three Bones of the Coxae Ilium Largest of the three bones Forms the bone ridge of the hip called the Iliac Crest. Unites with the Sacrum to form the Sacroiliac joint. Has many processes for muscle attachment. Ischium- Forms the inferior and posterior portion of the coxae bone. Pubis Forms the inferior and anterior portion of the coxal bones. Meets with the other pubis bone to form the joint called the Symphysis Pubis. Also forms the Pelvic arch. 4.Lower Limbs Supports the thigh, leg, ankle, and foot. Contains a total of 60 bones. Made up of the Femur, Patella, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsals, Metatarsals, and Phalanges. o Femur (2 Total) Longest and heaviest bone in the body. The Proximal end is the head it projects medially to fit into the Acetabulum of the coxal bone. The distal end of the femur contains two rounded processes that articulate with the Tibia of the posterior side. These processes are called the Lateral and Medial condyles. Articulate with a separate bone on the distal end anterior side, called the Patella. o Patella (2 Total) Also known as the knee cap Located within a large tendon that wraps over the anterior side of the knee o Tibia (2 Total) Larger of the two bones that support the legs. Located on the Medial side of the leg. Also contains Lateral and Medial condyles on the proximal end. Distal end contains pointed processes called Medial Malleolus Forms pointy medial side of the ankle. Articulates with the Talus bone on the distal end o Fibula (2 Total) Thin twisted bone located lateral to the tibia. The proximal end contains the head which articulates with the lateral condyles of the tibia. Distal end contains the processes called the lateral Malleolus Forms the bump on the lateral side of the ankle. Distal end also articulates with the talus o Foot (26 Bones) Made up of the Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges. Tarsals(7) Most prominent are the talus and the calcaneous. o Talus- Articulate with the Tibia and the Fibula. Supports most of the body weight before shifting it to other bones. o Calcaneus- Heel bone, Below Talus, The largest and strongest of the foot bones. o Navicular,Cuboid, Lateral Cuneiform, Intermediate Cuneiform, Medial Cuneiform Form remaining five tarsals. Metatarsals(5) o Numbered 1-5 starting with the big toe. o Contains proximal base, elongated shaft and distal head o Distal head forms the ball of the foot. o Between the calcaneus and the ball is the arch of the foot. Phalanges (14) o The big toe contains two bones (proximal and distal Phalany). o Remaining 4 toes contain 3 bones (Proximal, Distal, Middle).