Notes filled
advertisement

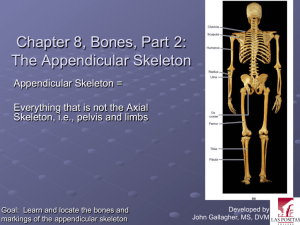
Skeletal system: Appendicular Skeletal system: Appendicular 126 bones Pectoral girdles A set of bones that attach the arms to the axial skeleton. Clavical and scapula. clavicles 2 Collar bones: anterior bone of the pectoral girdle. sternal extremity The end that joins the sternum: medial acromial extremity The end that joins the scapula; lateral scapulae 2 Shoulder blade: posterior. Acromion Process that joins with the acromial end of the clavicle. glenoid cavity The cup-like space on the lateral side of the bone that forms a joint with the humerus. supraspinous fossa A shallow depression on the body of the scapula where the supraspinous muscle orginiates. Upper extremities (arms) 60 bones Humerus 2 The upper arm bone. Head A large rounded condyle that fits into the glenoid cavity. deltoid tuberosity A roughened area on the lateral side of the humerus that serves as an attachment site for the deltoid muscle. Capitulum A condyle on the distal, anterior surface of the humerus: articulates with the radius. olecranon fossa A fossa on the distal, posterior surface of the humerus: The olecranon process of the ulna fits here when the forearm is extended. medial and lateral epicondyle Muscle attachment sites near the distal end. Ulna 2 The medial bone is the forearm olecranon process The point of the elbow, fits into the fossa on the humerus. trochlear notch A c-shaped notch that covers the trochlea on the humerus; part of a joint between the humerus and ulna Radius 2 The lateral bone in the forearm radial tuberosity A rough area that is the attachment site for the biceps muscle Carpals 8/side Bones that form the wrist and part of the palm. Lunate Forms joint with the ulna. scaphoid Forms joint with the radius. Metacarpals 5 Form part of the palm: consist of 5 bones, I-V from thumb side to the little finger side. Phalanges Fingers or digits. The 4 fingers have the following: Proximal Nearest the metacarpals. Middle distal The most distal phalanges. The thumb has only the proximal and distal. Pelvic gridle Pelvis The set of bones that attaches the lower extremities to the axial skeleton. A name used to designate the collection of bones that form both pelvic girdles. coxal bones Sacrum coccyx An alternate term used to name each pelvic bone Part of the vertebral column, and not directly part of the girdle, but found in this region. Tail bone and part of the vertebral column. coxal bones A pelvic girdle; made of 3 bones. Illium Most superior bone. Pubis Anterior and inferior. Ischium Posterior and inferior. ! acetabulum A deep fossa formed by all three coxal bones; femur articulates here. Ilium iliac crest A ridge along the superior border of the ilium. Attachment site for muscles. auricular surface On the lateral surface; a rough area the forms the lateral side of the sacroiliac joint. Ischium obuturator foramen A large foramen formed by the ischium and pubic bones. Pubis symphysis pubis The flat area between the right and left pubic bones is attached to a fibrocartilage disc called the pubic symphysis. Lower extremities" Femur 2 Thigh bone. Head Large round condyle which articulates with the acetabulum of the coxal bones. greater and lesser trochanter Large processes near the proximal end of the bone that serve as muscle attachment sites medial and lateral condyle Large smooth condyles at the distal end of the bone that articulate with the tibia. patellar surface/groove Smooth area on the distal, anterior surface of the femur, between the condyles, that articulates with the patella; knee cap. Patella 2 The knee cap. A sesamoid bone found embedded within the tendon of the quadriceps (or patellar ligament.) Tibia 2 The larger, medical of the two bones of the lower leg. Support 90% of the forces transmitted through the lower leg. tibial tuberosity A large rough area on the anterior, proximal surface of the tibia; the patellar ligament attaches here. medial malleolus A large “epicondyle” on the medial, distal surface of the tibia; forms the medial side of the so called “ankle bone.” Fibula 2 The smaller, lateral of the two bones of the lower leg. These bones cannot rotate around each other; they are fixed. lateral malleolus A large epicondyle on the lateral, distal surface of the tibia; forms the lateral side of the ankle. Tarsals 7/side The bones that form the ankle joint and the posterior part of the foot. Talus The bone that articulates with the tibia and fibula. calcaneus The heel bone. Contains the calcaneal tuberosity, that is the attachment point for the gastrocnemius. Metatarsals Forms the anterior part of the arch of the foot. Same number and organization as the palm. Phalanges Similar organization as the foot.