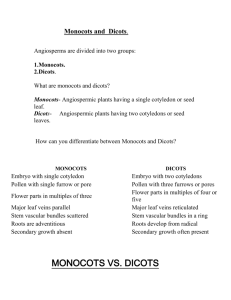
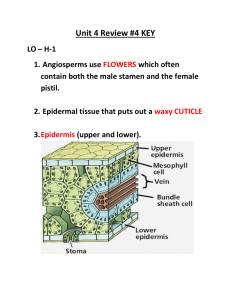
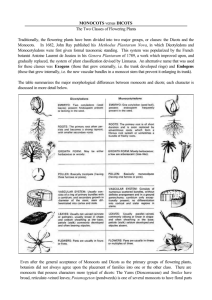
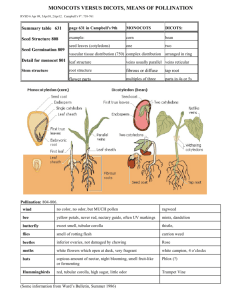
Key to the Families (pages 92 and 93) Modified with permission by
advertisement

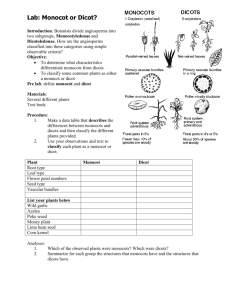
Key to the Families (pages 92 and 93) Modified with permission by Marion Lobstein 4-18-14 1 Plant minute, consisting of filaments or thalli (not differentiated into leaves, stems, and roots)……Key A1. Pteridophytes reduced to thalloid or filamentous, free-living gametophytes 1 Plant more complex, with stems (rhizomes), leaves, and roots [lycophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, monocots, dicots (basal angiosperms, and eudicots)]. 2 Plants floating aquatics, never rooted to the substrate ............................. Key C1. Floating aquatics 2 Plants terrestrial, wetland, or aquatic, normally rooted to the substrate 3 Plants woody, trees, shrubs, lianas (woody vines), subshrubs, or rosette shrubs 4 Stems fleshy and flattened, green and photosynthetic, often spines; leaves lacking……..Key D.Cacti 4 Stems not fleshy and flattened, usually brown, gray, or tan (sometimes green and photosynthetic), lacking glochidia (sometimes bearing spines, prickles, or thorns); leaves present 5 Plants rosette shrubs or rosette subshrubs, the leaves strongly basally disposed, leaf arrangement alternate (but often with very short internodes). 6 Leaves fernlike, 1-pinnate-pinnatifid or more divided, deciduous; plants lacking both flowers and seeds, reproducing by spores [pteridophytes ………Key A7. Medium to large terrestrial pteridophytes 6 Leaves simple or 3-foliate; plants bearing seeds, with flowers [monocots and dicots….…................................................................................. ………Key E. Angiosperm shrubs and subshrubs with basal leaves 5 Plants trees, shrubs, or lianas, the leaves usually many and cauline (borne along the stemleaf arrangement alternate, opposite, or whorled. 7 Leaves stiff, needle- or scalelike, reproductive structures are cones (the cone sometimes modified and fleshy and berrylike) or the seed solitary and mostly or completely enclosed in a fleshy or leathery aril or receptacle [gymnosperms]……….. Key B. Gymnosperms 7 Leaves generally not stiff (some exceptions), usually broader and with well-developed blades, reproductive structures are flowers [dicots and monocots]. 8 Leaves alternate [dicots and monocots]. 9 Leaves compound [dicots and monocots]….Key F. Woody angiosperms with alternate, compound leaves 9 Leaves simple [dicots and monocots]……....Key G. Woody angiosperms with alternate, simple leaves 8 Leaves opposite or whorled [dicots]. 10 Leaves whorled ....... Key H. Woody angiosperms with whorled leaves 10 Leaves opposite. 11 Leaves compound…….Key I. Woody angiosperms with opposite, compound leaves 11 Leaves simple…………Key J. Woody angiosperms with opposite, simple leaves 3 Plants herbaceous, herbs, or herbaceous vines 12 Plants aquatics, all of the plant typically submerged or suspended in water or floating on its surface…….Key C. Aquatics 12 Plants terrestrial or amphibious, all or most of the plant, normally borne in the air, emergent plants may have their bases permanently submerged, 13 Plants lacking chlorophyll (white, pink, orange, tan, red), strictly parasitic or mycotrophic [dicots and monocots] Key K. Holoparasites and holomycotrophs 13 Plants with chlorophyll (usually all or partly green, the green pigment sometimes wholly or partly masked by nongreen pigments), at least in part autotrophic (many partly mycotrophic or partly parasitic). 14 Plant reproducing by spores [lycophytes and pteridophytes]………Key A. Lycophytes and pteridophytes 14 Plant reproducing by seeds, developing in fruits derived from flowers [eudicots, basal angiosperms, and monocots]. 15 Plants epiphytic, normally growing attached to plants and not rooting in soil……Key L. Epiphytic angiosperms 15 Plants terrestrial, rooted in soil (sometimes on logs or in tree knotholes, hollows, or treelimb crotches where soil has accumulated, but not truly epiphytic). 16 [monocots; flower parts usually in 3’s, veins in leaves usually parallel……..Key M. Monocots 16 [eudicots and basal angiosperms treated as dicots; flower parts usually in 4’s or 5’s, veins in leaves usually netted] 17 Leaves strictly basal or strongly basally disposed (the basal leaves the largest, and usually persistent for most of the growing season)…………………Key N. Herbaceous dicots with mainly basal leaves 17 Leaves cauline (if plant has basal leaves, they are not noticeably the largest, often senescing early). 18 Leaves alternate. 19 Leaves compound…………Key O. Herbaceous dicots with alternate, compound leaves 19 Leaves simple……………...Key P. Herbaceous dicots with alternate, simple leaves 18 Leaves opposite or whorled or appearing whorled (a few plants have leaves or leaflike structures that appear whorled but anatomically are opposite or alternate with leaflets divided to the stem). 20 Leaves whorled (some taxa normally having opposite leaves can have occasional developmental errors that result in an individual plant with 3-whorled leaves; these are not accommodated in the key as whorled. [If a plant does not key readily as whorled, try it as opposite]) or appearing so…………Key Q. Herbaceous dicots with whorled leaves on the stem 20 Leaves opposite. 21 Leaves compound……..Key R. Herbaceous dicots with opposite, compound leaves on the stem 21 Leaves simple………….Key S. Herbaceous dicots with opposite, simple leaves on the stem