Review
advertisement

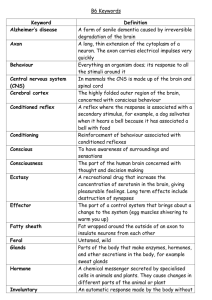
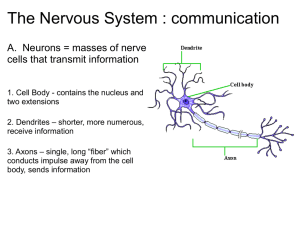
Unit IV Review What is a nerve? What is it composed of? What are the 3 functional classes of neurons? What are the functions of each functional class of neuron? What are the structures of a neuron and what do they do? Based on the processes coming off a soma, what are the 4 classes of neurons? Which structural class is most common? Which type of cells out number neurons in the nervous system? What does each type of neuroglial cell do and which subdivision of the nervous system is it found? What 2 things affect the rate at which a signal is transmitted? What would an axon look like to send a fast signal? Slow signal? Which nerve fibers exhibit regeneration? Why not nerves of the other subdivision? How does regeneration of a nerve occur? What are the properties of a reflex? Define reflex arc. What is the pathway of a reflex arc? What type of reflex maintains equilibrium and posture on a day to day basis? This type of reflex depends on _____________ to prevent muscles from working against each other. What is an example of a tendon reflex? Why are they so quick? What 2 reflexes happen simultaneously due to a pain stimulus? What happens with each? What 2 things does the Golgi Tendon Reflex do? What structures make up the central nervous system? What does the Cerebrospinal Fluid do? What does the blood-brain barrier do? What are the Circumventricular organs? Spinal Cord What do the central pattern generators do? Which part of the central nervous system mediates reflexes? Where is the spinal cord located? How are spinal nerves named? What do the meninges do? Know their order. The spinal cord and brain (Forebrain) both contain white and gray matter. How do their locations differ? Gray matter is composed mostly of (which structure of a neuron) and so has (little or a lot) of myelin. White matter consists mainly of (which structure of a neuron) and so has (little or a lot) of myelin. Sensory neurons enter the spinal cord through the _____ horns and leaves either through the _____ horns if somatic motor nerve fibers or the ____ horns if sympathetic motor nerve fibers. Which part of the spinal cord is lined with ependymal cells and so contains CSF? Define white matter reflex arcs: Contralateral (ex: crossed extensor reflex); Ipsalateral (ex: withdrawal reflex); Decussation (ex: optic nerves) Brain Know which direction is rostral and caudal. Which part of the brain contains the most neurons (50%)? These are the major functions for each part of the brain that you should know: Hindbrain Medulla Oblongata: controls cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory centers Pons: breathing, facial expression and sensation, swallowing Cerebellum: muscular coordination Midbrain Cerebral peduncles: corticospinal tracts involved in fine motor movements Tegmentum: collaborates with cerebellum in fine motor control Substantia nigra: inhibitory (stop) signals to basal nuclei and thalamus (motor controls) (Parkinson's disease) Central gray matter: pain awareness Tectum: superior colliculi – vision reflexs (attention, tracking moving objects) inferior colliculi – hearing reflexes Reticular formation: habituation, sleep, consciousness (irreversible coma), pain modulation Forebrain (diencephalon) Thalamus: sensory input to cerebrum (gateway to cerebral cortex), key role in motor control (connects cerebrum → cerebellum), emotion and memory (limbic system) Hypothalamus: generally controls endocrine system (hormone production) and autonomic nervous system (involuntary processes), monitors blood temp, blood glucose and amino acids levels (hunger) Epithalamus: pineal gland (endocrine)-circadian rhythms, habenula – connects limbic to cerebrum Forebrain (telencephalon) Cerebrum: general – thinking, memory, problem solving, language left hemisphere – words, logic, numbers, language right hemisphere – graphics, pictures, intuition, emotion -identify gyri and sulci (hills and grooves) – what do they allow for? -Know the functions of the 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal -White matter in the cerebrum consists of 3 types of neural tracts. What areas do they allow to communicate? -Gray matter is found in 3 places of the cerebrum. Which place has the most gray matter? Basal nuclei: where is it located? Involved in motor control. Limbic system: involved in emotion and learning. Motivational area. Higher brain functions are mostly associated with what part of the brain? What is the best way to study which part of the brain is most active during a particular action? What structures are included in the peripheral nervous system? What characteristics does a nerve cell posses in the resting membrane potential? How is a nerve impulse sent along the axon? What is the refractory period? What are the 3 properties of an action potential? What is saltatory propagation? Know the steps to transmission of an impulse from one neuron to another at a chemical synapse. What is the synaptic delay? What are the 3 main types of neurotransmitters? What are the 3 types of chemical synapses? How do they differ? What is the advantage of Excitatory Adrenergic Synapses? How is a signal stopped? What does “summation” refer to with postsynaptic potentials? What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system? How are the autonomic and somatic reflex arcs different? How are the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system different? Know what the accessory vision structures do. Which eye structures refract and focus light? These are known as ____. Which structures receive and transmit the signal? These are known as ____. How is an image formed? What is the projection pathway? What are the differences between a rod and a cone photoreceptor? What is the duplicity theory? What allows for depth perception? Have a basic understanding of the abnormalities. What is pitch and loudness? Know what the various parts of the ear do. Equilibrium is sensed in the _____, while sound receptors are in the ____. In general, how does equilibrium and hearing produce a stimulus? What is the projection pathway for hearing? Which hair cells do all of the hearing? What types of information about a stimulus can a sensory receptor transmit to the CNS? How is it encoded? Give an example of a receptor named for its: modality. Origin of stimulus. Distribution. What is the difference between unencapsulated and encapsulated receptors? What do free nerve endings sense? Receptors for light touch (meissner) are located ____; whereas, receptors for pressure (pacinian) are located ____. What is the pathway for a somesthetic impulse? What is a pain receptor known as? Where is the only place they are not located? What is the most potent pain stimulus? What are the two types of pain? What are the two main pathways for pain impulses? What is referred pain? What are endogenous opioids? What type of papillae contain the most taste buds? How are taste buds protected? In order for foods to be tasted, what must happen to the molecules? What are the 5 primary taste sensations and what chemicals produce them? What neurons are the only ones exposed to the external environment? How do we smell?