Chapter 1: Introduction to Psychology (pages 17– 38)
advertisement

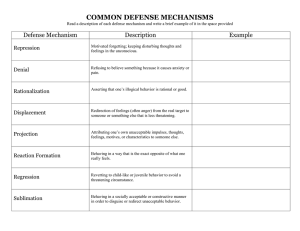
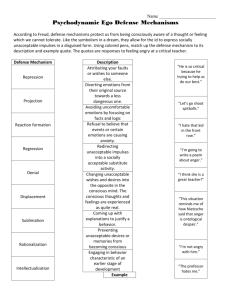
Chapter 12: Personality (pages 225-241) 1. Define personality. 2. List the four theories of personality dominant to the 20th century. 3. Define objective personality tests and give examples. 4. Define projective personality tests and give examples. 5. List three reasons personality tests are used. 6. Define defense mechanisms. 7. List five characteristics of defense mechanisms. 8. Match the following defense mechanisms to the appropriate definition or example below. ____1. reaction formation ____10. repression ____2. fixation ____11. regression ____3. identification ____12. compartmentalization ____4. substitution ____13. undoing ____5. compensation ____14. overcompensation ____6. denial ____15. projection ____7. sublimation ____16. rationalization ____8. isolation ____17. intellectualization ____9. displacement a. Instead of regressing, a person who encounters trauma remains at that level of emotional development present during the trauma. b. Thoughts, feelings, wishes, or motives are denied access to consciousness. c. The adoption of attitudes and behavior contrary to an individual’s true feelings or unconscious impulses. d. A person models their values, behavior and attitudes after another person’s without knowing that they are doing so. e. An unconscious striving to make up for inferiority feelings resulting from lack of acceptance of the way God made us. f. There is a denial of true desires and an acceptance of partial or modified fulfillment of those desires. g. Used to hide ideas and impulses from awareness, the primary defense mechanism upon which all others are based. h. A channeling of unacceptable drives into constructive behavior without a conscious awareness that those drives exist. i. Experiencing attitudes as if they were unconnected and unrelated, like they are separated, in different parts of the brain. j. Current conflicts provoke a return to an earlier stage of emotional immaturity where there is more of a feeling of protection from life stresses. k. Unacceptable emotions are split off from conscious thought, isolated from conscious awareness; i.e. all anger is sin, so anger must be isolated to relieve false guilt. l. The transferring of an emotion to a more acceptable substitute, such as a man angry at his boss, upon arriving at home, yells at his wife. m. Attributing one’s wishes or impulses to someone else. n. Excessive use of intellectual vocabulary, thinking, discussions, and philosophies to avoid feelings. o. Justification of unacceptable attitudes, beliefs, or behavior by the misapplication of viable reasons or by the invention of false reasons. p. A socially acceptable way of making up for weaknesses. q. The unconscious carrying out of behavior or verbal communication to negate a previous mistake, as though the mistake never occurred. 9. List alternatives to defense mechanisms?