Methods of Satisfying Human Needs: Defense Mechanisms
advertisement

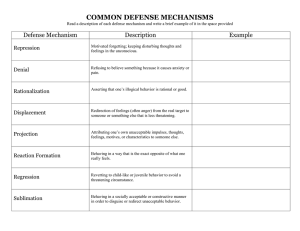
METHODS OF SATISFYING HUMAN NEEDS DIRECT METHODS •Meeting the need •Obtaining satisfaction •Hard work •Realistic goals •Situation evaluation •Cooperation with others INDIRECT METHODS •Reduce need •Relieve tension created by unmet need •Defense Mechanisms INDIRECT METHODS •Defense mechanisms •Help a person deal with an unpleasant situation •Provide methods for maintaining selfesteem and relieving discomfort •Can be unhealthy if used all the time RATIONALIZATION Using an ‘acceptable’ explanation for behavior in order to avoid the real reason or true motivation PROJECTION Placing blame on someone else or on circumstances rather than accepting responsibility DISPLACEMENT Transferring feelings about one person to someone else COMPENSATION The substitution of one goal for another in order to achieve success DAYDREAMING Provides a means of escape when a person is not satisfied with reality REPRESSION The transfer of unacceptable or painful ideas, feelings into the unconscious mind. Individual is NOT aware that this is occurring. SUPPRESSION Similar to repression but individual IS aware and refuses to deal with feelings DENIAL Disbelief of an event or idea that is too frightening or shocking to cope with WITHDRAWAL Cease to communicate or physically remove themselves from a situation