Pure Competition Exam: Economics Questions & Problems
advertisement

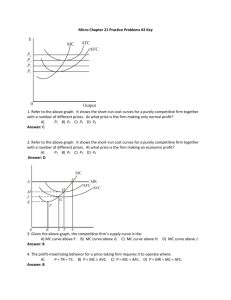
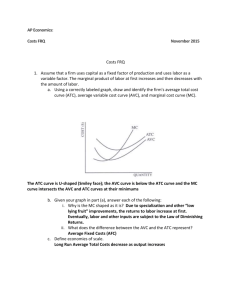
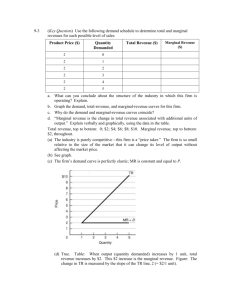
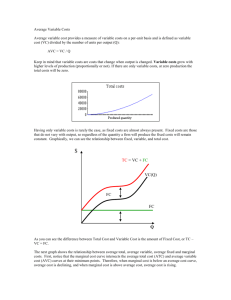
Pure Competition True or false : 1) Along the purely competitive firm's demand curve, average revenue is equal to marginal revenue. 2) In pure competition, the industry demand curve is infinitely price elastic. 3) The break-even point means that the firm is realizing economic profits. 4) In the short run, a competitive firm will not produce unless price is equal to average total costs. 5) In the short run, fixed costs are irrelevant in determining a firm's optimal level of output. 6) In short-run equilibrium, a competitive firm cannot earn economic profits. 7) If MR > MC for a competitive firm, it should raise its price and increase its level of output. 8) In long-run equilibrium, a competitive firm produces where P = MR = MC = minimum ATC and earns normal economic profits. 9) When firms in a purely competitive industry are earning profits that are greater than normal, the supply of the product will tend to decrease in the long run. 10) Productive efficiency refers to long-run market conditions where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue. 11) In pure competition, resources are optimally allocated when production occurs at the output level where P=MC. 12) In pure competition, a firm earns economic profits as long as MR = MC . 13) In the short run, a competitive firm shuts down production when TR < TC . 52 Multiple choice : (1) Which market model has the least number of firms ? A) monopolistic competition B) pure competition C) pure monopoly D) oligopoly (2) Which idea is inconsistent with pure competition ? A) short-run losses B) product differentiation C) freedom of entry or exit for firms D) a large number of buyers and sellers (3) Which characteristic would best be associated with pure competition ? A) few sellers B) price taker C) nonprice competition D) product differentiation (4) Which is a reason why there is no advertising by individual firms under pure competition ? A) Firms produce a homogeneous product . B) The quantity of the product demanded is very large . C) The market demand curve cannot be increased . D) Firms do not make long-run profits. (5) The demand curve faced by a purely competitive firm : A) has unitary elasticity . B) yields constant total revenue . C) is identical to the market demand curve . D) is one where average revenue equals marginal revenue. (6) In the standard model of pure competition, a profit-maximizing entrepreneur will shut down in the short run if : A) B) C) D) 53 marginal cost is greater than average revenue . average cost is greater than average revenue . average fixed cost is greater than average revenue . total revenue is less than total variable costs. (7 ) Let us suppose that Happy Shrimps cafe has the following revenue and cost structure: total revenue 3,000 k.d per week total variable cost 2,000 k.d per week total fixed costs 2,000 k.d per week A) B) C) D) Happy Shrimps should stay open in the long run . Happy Shrimps should shut down in the short run . Happy Shrimps should stay open in the short run . Happy Shrimps should shut down in the short run but reopen in the long run. (8) In a typical graph for a purely competitive firm, where the total cost and total revenue curves intersect there is a(n): A) economic profit. B) economic loss. C) normal profit. D) zero level of output. (9) A profit-maximizing firm in the short run will expand output : A) until marginal cost begins to rise . B) until total revenue equals total cost . C) until marginal cost equals average variable cost . D) as long as marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost. (10) A firm sells a product in a purely competitive market. The marginal cost of the product at the current output of 1,000 units is k.d 2.50. The minimum possible average variable cost is k.d 2.00. The market price of the product is k.d 2.50. To maximize profit or minimize losses, the firm should: A) continue producing 1,000 units. B) produce less than 1,000 units. C) produce more than 1,000 units. D) shut down. (11) A firm sells a product in a purely competitive market. The marginal cost of the product at the current output of 800 units is k.d 3.50. The minimum possible average variable cost is k.d 3.00. The market price of the product is k.d 4.00. To maximize profit or minimize losses, the firm should: A) continue producing 800 units. B) produce less than 800 units. C) produce more than 800 units. D) shut down. 54 (12) A firm sells a product in a purely competitive market. The marginal cost of the product at the current output of 500 units is k.d 1.50. The minimum possible average variable cost is k.d 1.00. The market price of the product is k.d 1.25. To maximize profit or minimize losses, the firm should: A) continue producing 500 units. B) produce less than 500 units. C) produce more than 500 units. D) shut down. (13) A firm sells a product in a purely competitive market. The marginal cost of the product at the current output of 200 units is k.d 4.00. The minimum possible average variable cost is k.d 3.50. The market price of the product is k.d 3.00. To maximize profit or minimize losses, the firm should: A) continue to produce 500 units. B) produce less than 500 units. C) produce more than 500 units. D) shut down. (14) Consider the cost chart below for a purely competitive firm. The lowest output level on this firm's short-run supply curve is: Output 10 12 14 16 20 A) C) 10 16 AVC 5 4 4.75 5.75 9 ATC 15 13 11.5 9 12 MC 3 4 6 9 14 B) D) 12 20 (15) The individual firm's short-run supply curve is that part of its: A) average total cost curve that is upsloping. B) average variable cost curve that is upsloping. C) marginal-cost curve lying above its average variable-cost curve. D) marginal-cost curve lying above its average total-cost curve. (16) A purely competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium and its MC exceeds its ATC. It can be concluded that : A) firms will leave the industry in the long run . B) the firm is realizing an economic profit . C) the firm is realizing a loss . D) this is an increasing-cost industry. 55 (17) The profit-maximizing level of output for the firm shown in the diagram below is : A) B) C) D) OC OB OA OK (18) Consider the purely competitive firm in the graph . The firm is earning : A) normal profits, since its price is above AVC . B) C) D) economic profits, since its price is above AVC . normal profits, since its price just covers ATC . losses, since it is operating at the shutdown point. (19) The graph below shows the short-run cost curves for a purely competitive firm together with a number of different prices. At what price is the firm making only normal profit ? A) B) C) D) 56 P1 P2 P3 P4 (20) Based on the graph, the firm is earning : A) B) C) D) zero normal profits . zero economic profits . zero accounting profits . Information not sufficient . (21) The purely competitive firm as shown in the graph will : A) B) shut down . produce with short-run losses . C) D) produce with long-run economic profits . produce with short-run economic profits. (22) A firm should produce as long as : A) B) C) D) Short run: P > = ATC Short run: P > AVC Short run: P > = ATC Short run: P > = minimum AVC Long run: P > = AVC Long run: P > AVC Long run: P > = MC Long run: P = minimum ATC (23) Productive efficiency refers to : A) cost minimization, where P = minimum ATC . B) production, where P = MC . C) maximizing profits by producing where MR = MC . D) setting TR = TC. (24) Resources are efficiently allocated when production occurs at that output at which : A) C) 57 P equals MR. P exceeds MR. B) D) P equals AVC. P equals MC. Problem sets : (1) A single firm operating in a perfectly competitive market has the following cost schedule : Output MC (k.d) 1 7 2 6 3 5 4 6 5 7 6 8 7 9 8 10 9 11 10 12 11 13 (a) What is the equilibrium output level given that the market price is k.d 8 . (b) Calculate VC at equilibrium . (c) Calculate the firm’s profits ( losses ) at equilibrium given that FC equal k.d 11 . (d) Determine the minimum price for the firm to remain in production. What is the level of production at that price ? 58 (2) Assume a single firm in a purely competitive industry has variable costs as indicated in the following table in column 2. Complete the table and answer the questions. (1) Total product 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 (2) Total var. cost 0 55 75 90 110 135 170 220 290 (3) Total cost 40 _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ (4) (5) (6) (7) AFC _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ AVC _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ ATC _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ MC _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ (a) At a product price of k.d 52, will this firm produce in the short run? Explain. What will its profit or loss be? (b) At a product price of k.d 28, will this firm produce in the short run? Explain. What will its profit or loss be? (c) At a product price of k.d 22, will this firm produce in the short run? Explain. What will its profit or loss be? (e) Complete the following short-run supply schedule for this firm. Product price k.d 72 52 45 28 22 15 Quantity supplied _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Profit (+) or loss (–) _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Assume there are 500 identical firms in this industry, that they have identical cost data as the firm above, and that the industry demand schedule is as follows: Price k.d 72 52 45 28 22 15 Quantity demanded 2,500 3,500 4,000 5,200 5,900 6,700 (e) What will the equilibrium price be? (f) What will the equilibrium output for each firm be? (g) What will profit or loss be per unit? (h) What will profit or loss be per firm? 59 (3) Assume that a purely competitive firm has the schedule of average and marginal costs given in the table below. Output 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 AFC AVC ATC MC 600 300 200 150 120 100 86 76 66 60 200 150 140 145 160 180 205 232 276 320 800 450 340 295 280 280 291 314 342 380 200 100 120 160 220 280 360 460 580 720 (a) In the table below, complete the supply schedule for the competitive firm and state what the economic profit will be at each price. Price k.d 580 460 360 280 220 160 120 Quantity supplied _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Profit (+) or loss (–) _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ (b) If there are 100 firms in the industry and all have the same cost schedule, complete the market supply schedule in the table below. Quantity demanded 500 600 700 800 900 1,000 1,100 Price k.d 580 460 360 280 220 160 120 Quantity supplied _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Answer the following questions: (1) What will the equilibrium price and quantity of the product be? (2) What will the profits of each firm be? (3) Will firms tend to enter or leave the industry in the long run? Explain. 60 Essay Questions : Consider the two diagrams below. Diagram A represents a typical firm in a purely competitive industry. Diagram B represents the supply and demand conditions in that industry. (a) Describe the price, output, and profit situation for the individual firm in the short run. (b) Describe what will happen to the individual firm and the industry in the long run. Show the changes on diagrams A and B. 61 What are four characteristics of pure competition? How would you describe the demand curve for the purely competitive firm? For the industry? Explain the marginal revenue and marginal cost approach to profit maximization and use it to describe profit, loss, and shut down situations for the purely competitive firm. Draw a graph of the short-run cost curves for a purely competitive firm that shows a short-run supply curve for the individual firm. Identify the shutdown point, the break-even point, the profit-maximizing point, and the levels of output associated with those points.