Microeconomics Practice Problems: Chapter 21 Key
advertisement
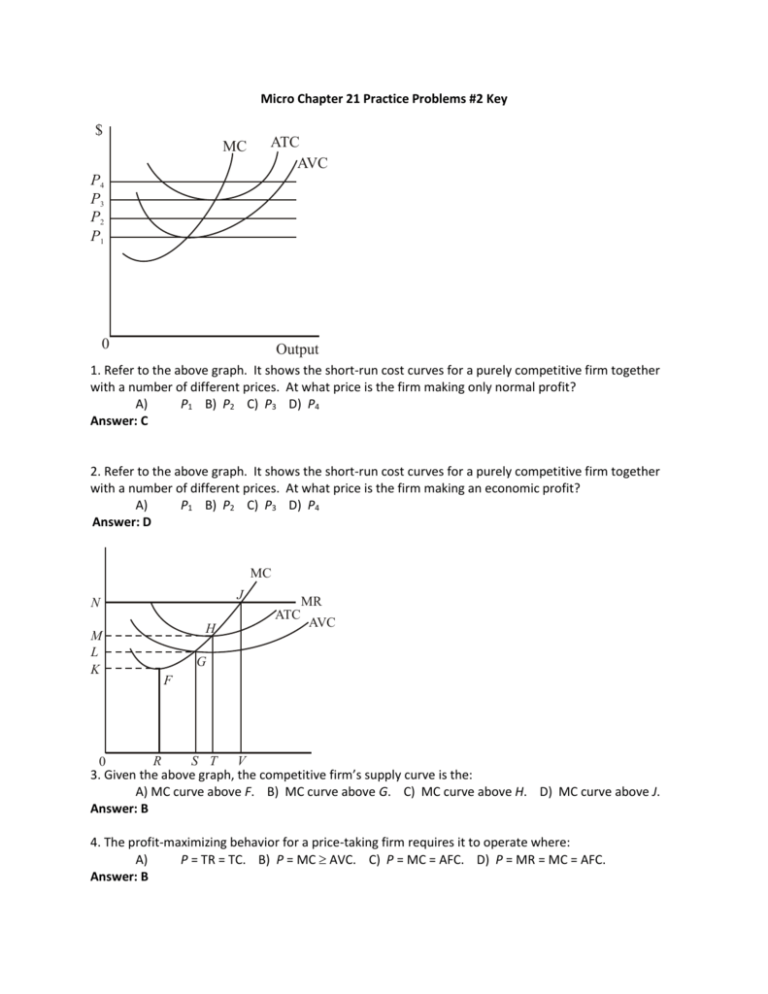
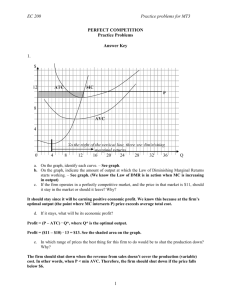
Micro Chapter 21 Practice Problems #2 Key $ MC ATC AVC P4 P3 P2 P1 0 Output 1. Refer to the above graph. It shows the short-run cost curves for a purely competitive firm together with a number of different prices. At what price is the firm making only normal profit? A) P1 B) P2 C) P3 D) P4 Answer: C 2. Refer to the above graph. It shows the short-run cost curves for a purely competitive firm together with a number of different prices. At what price is the firm making an economic profit? A) P1 B) P2 C) P3 D) P4 Answer: D MC J N M L K MR ATC H AVC G F S T V R 0 3. Given the above graph, the competitive firm’s supply curve is the: A) MC curve above F. B) MC curve above G. C) MC curve above H. D) MC curve above J. Answer: B 4. The profit-maximizing behavior for a price-taking firm requires it to operate where: A) P = TR = TC. B) P = MC AVC. C) P = MC = AFC. D) P = MR = MC = AFC. Answer: B 5. Resource costs increase in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a(n): A) increase in average fixed cost for a firm in the industry. B) decrease in average variable cost for a firm in the industry. C) decrease in the marginal cost curve for a firm in the industry. D) decrease in the short-run supply curve for a firm in the industry. Answer: D 6. Assume the market for ball bearings is purely competitive. Currently, each of the firms in this market is making a positive level of economic profits. In the long run, we can expect the market: A) supply curve to increase. C) supply curve to decrease. B) demand curve to increase. D) demand curve to decrease. Answer: A 7. Which of the following is characteristic of a perfectly competitive firm’s demand curve? A. average revenue is less than price at all levels of output B. marginal revenue is equal to marginal costs at all levels of output C. price and marginal revenue are equal at all levels of output D. it is the same as the market demand curve E. demand is inelastic at all levels of output Answer: C 8. The owner of a competitive firm making zero economic profit A. should consider shutting down because she could make more elsewhere B. is making less than normal profits C. is making exactly what she would make in her next best alternative job D. will most likely make more profits in the long run E. is making serious resource allocation errors Answer: C 9. Refer to the above graph. The level of output at which this firm will produce is: A) 0A. B) 0B. C) 0C. D) 0K. Answer: C 10. Refer to the above graph. The level of output at which this firm will shut down is: A) 0A. B) 0B. C) 0C. D) 0K. Answer: A 11. Refer to the above graph. The level of output at which this firm is maximizing an economic profit is: A) 0A. B) 0B. C) 0C. D) 0K. Answer: C Output 10 12 14 16 20 Average variable cost 5.00 4.00 4.75 5.75 9.00 Average total cost 15.00 13.00 11.50 9.00 12.00 Marginal cost 3 4 6 9 14 12. Refer to the above cost chart. The lowest output level on this firm's short-run supply curve is: A) 10. B) 12. C) 16. D) 20. Answer: B 13. Refer to the above cost chart. If the marginal revenue is $6, what output level will the firm produce? A) 10 B) 12 C) 14 D) 20 Answer: C 14. Refer to the above cost chart. Which output level will the firm NOT produce? A) 10 B) 12 C) 16 D) 20 Answer: A Refer to the table below. It shows cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. Output 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 AFC $300 150 100 75 60 50 43 38 33 30 AVC $100 75 70 73 80 90 103 119 138 160 ATC $400 225 170 148 140 140 146 156 171 190 MC $100 50 60 80 110 140 180 230 290 360 15. Refer to the above table. If the market price for the firm's product is $50, the competitive firm will: A) produce 1 unit. B) produce 2 units. C) produce 3 units. D) shut down. Answer: D 16. Refer to the above table. If the market price for the firm's product is $70, the competitive firm will: A) produce 1 unit. B) produce 2 units. C) produce 3 units. D) shut down. Answer: C 17. Refer to the above table. If the market price for the firm's product is $180, the competitive firm will produce: A) 5 units at an economic profit of $100. C) 7 units at an economic profit of $238. B) 6 units at an economic profit of $120. D) 8 units at an economic profit of $278. Answer: C 18. Refer to the above table. If the product price is $290, the per-unit economic profit at the profit-maximizing output is: A) $33. B) $76. C) $119. D) $152. Answer: C 19. Refer to the above graph. To maximize profits, this firm would produce: A) 0D units, which will result in a loss equal to ABGH. B) 0E units, which will result in a loss equal to ALFH. C) 0D units, which will result in economic profits equal to BCFG. D) 0E units, which will result in economic profits equal to ABGH. Answer: D 20. A purely competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium and its MC exceeds its ATC. It can be concluded that: A) firms will leave the industry in the long run. C) the firm is realizing a loss. B) the firm is realizing an economic profit. D) this is an increasing-cost industry. Answer: B PX MC ATC D AVC 0 A B C K Q 21. Refer to the above graph. The profit-maximizing level of output for the firm is: A) 0A. B) 0B. C) 0C. D) 0K. Answer: C 22. Refer to the above graph. At what level of output will the firm shut down? A) 0A B) 0B C) 0C D) 0K Answer: A $ MC ATC AVC D = MR P 0 Q Q 23. Consider the purely competitive firm pictured above. The firm is earning: A) normal profits, since its price is above AVC. B) economic profits, since its price is above AVC. C) normal profits, since its price just covers ATC. D) losses, since it is operating at the shutdown point. Answer: C 24. When a firm produces less output, it can reduce: A) its fixed costs but not its variable costs. B) its variable costs but not its fixed costs. Answer: B C) D) average fixed cost. marginal revenue. 25. Refer to the above graph. It represents a profit-maximizing firm producing under conditions of pure competition. When the firm is in equilibrium in the short run, its average fixed cost is: A) EH. B) DE. C) DH. D) DB. Answer: B 26. The purely competitive firm above will: A) shut down. C) produce with long-run economic profits. B) produce with short-run losses. D) produce with short-run economic profits. Answer: B 27. A purely competitive firm will be willing to produce at a loss in the short run provided: A) the loss is no greater than its total variable costs. B) the loss is no greater than its marginal costs. C) the loss is no greater than its total fixed costs. D) price exceeds marginal costs. Answer: C 28. In general, the supply curve of a purely competitive firm is: A) identical to the marginal-cost curve. B) a horizontal line equal to the market price. C) the rising portion of the average-total-cost (ATC) curve. D) the rising portion of the marginal-cost curve above the AVC curve. Answer: D