AP Economics: Perfect Competition FRQ Review
advertisement

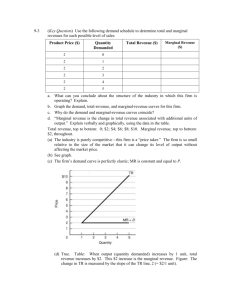
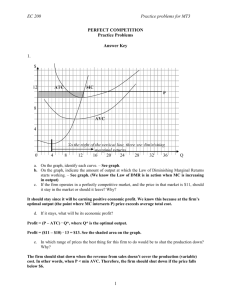
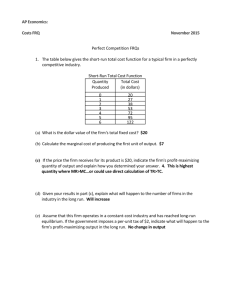
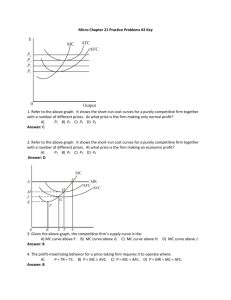
AP Economics: Perfect Competition Review FRQs April 27, 2015 Perfect Competition FRQs 1. The graph above shows the short-run cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. a) Identify the cost curves that are denoted by each of the following labels: i) Curve 1 Marginal Cost ii) Curve 2 Average Total Cost iii) Curve 3 Average Variable Cost b) Explain why Curve 1 does each of the following as output increases: i) Initially decreases Specialization or Economies of Scale ii) Finally increases Diminishing Returns of Inputs c) What measure of cost is represented by the vertical distance between Curve 2 and Curve 3? Average Fixed Cost d) Explain why the vertical distance between Curve 2 and Curve 3 decreases as output increases. Spreading Effect – fixed costs are spread over more units e) Using the letters on the graph, identify 2 points on the firm’s short-run supply curve. K and L 2. Assume that initially a perfectly competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium. a) For the typical profit-maximizing firm in this industry, explain the following: i) how the firm determines its level of output Where Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost (= Price) ii) what the level of profit is and why it is at that level Zero Economic profit because any short-term economic profits would attract new entrants to the industry, shifting the industry supply curve to the right, reducing prices and profits, and if economic profits are negative, firms would exit the industry, shifting the supply curve to the left, raising prices and profits. b) A change occurs that reduces the variable costs of production for all firms in this industry. Explain how and why this decrease in variable costs affects each of the following in the short-run: i) the typical firm’s level of output Increases. Firm’s marginal costs fall, (shift to the right) intersecting marginal revenue at higher output ii) the industry price and level of output Prices fall and output increases. Fall in marginal costs cause industry supply curve to shift to the right, increasing output and reducing price. 3. Assume that in a perfectly competitive market, a firm’s costs and revenues are marginal cost = average variable cost at $20 marginal cost = average total cost at $30 marginal cost = average revenue at $25 a) How will this firm determine the profit-maximizing level of output? The output level where MR = MC at P = $25 b) What price will the firm charge? Explain how you determined this price? $25. At optimal output, MC = MR, which = P. Price is determined by marketplace in perfectly competitive market, and the firm is a price taker. c) Should this firm produce in the short-run? Why or why not? Yes, P > AVC ($25 > $20) d) Will this firm earn a profit or incur a loss? Why? Incur a loss. P < ATC. We know this because MC intersects ATC at its minimum, given as $30. Price is only $25, so the firm is losing at least $5 per unit. 4. Suppose that roses are produced in a perfectly competitive, increasing-cost industry in long-run equilibrium with identical firms. a) Draw correctly labeled side-by-side graphs for the rose industry and a typical firm and show each of the following. i) Industry equilibrium price and quantity, labeled Pm and Qm, respectively ii) The firm’s equilibrium price and quantity, labeled Pf and Qf, respectively Graph 1: Correct labels; downward sloping D and upward sloping S; Q and P identified. Graph 2: Correct labels; horizontal D = MR = P; profit-maximizing equilibrium where MR=MC. MC intersects ATC at its minimum. ATC tangent to D at profitmaximizing equilibrium. b) Is Pm larger than, smaller than, or equal to Pf? equal c) Assume that there is an increase in the demand for roses. On your graphs in part (a), show each of the following. i) The new short-run industry equilibrium price and quantity, labeled Pm2 and Qm2, respectively see above graph; D shifts right, raising P and Q ii) The new short-run profit-maximizing price and quantity for the typical firm, labeled Pf2 and Qf2, respectively see above graph; D shifts up, raising P and Q d) As the industry adjusts to a new long-run equilibrium, i) what will happen to the number of firms in the industry? Explain. Increase. Short-run economic profits will attract new entrants. ii) will the firm’s average total cost curve shift upward, shift downward, or remain unchanged? ATC shifts up e) In the long run, compare the firm’s profit-maximizing price to each of the following. i) Pf in part a) ii) Higher than Pf ii) Pf2 in part c) ii) Lower than Pf2