Unit 1 topic 8 respiration
advertisement

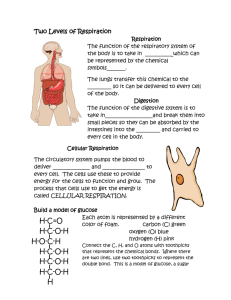
National 5 Biology Unit 1 1.4 Respiration Pupil Course Notes Topic 8 Pupil Notes Respiration Respiration is a series of enzyme controlled reactions by which energy from food is released. The word equation below summarises aerobic respiration (breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen). Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water ATP production The energy released from glucose is stored in a molecule called ATP. ATP is produced when a molecule of ADP is joined to a molecule of Pi (inorganic phosphate). When the energy is required for a cellular process, such as muscle contraction or protein synthesis, the ATP is broken down to for ADP and Pi releasing the stored energy. Glucose + Oxygen ADP + Pi Cellular Processes, e.g. protein synthesis Respiration Carbon Dioxide + Water North Lanarkshire Council Protein ATP Amino Acids Page 1 of 3 National 5 Biology 1.4 Respiration Pupil Course Notes Processes in cells and organisms that require energy These are examples of processes in cells and organisms that require energy Protein synthesis Cell division Active transport Muscle contraction Transmission of nerve impulses Respiration reactions The first stage of respiration occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves the breakdown of glucose to form pyruvate (pyruvic acid). (This stage is called glycolysis) Glucose Pyruvate This stage does not require oxygen and it occurs in both aerobic respiration and fermentation The second stage of respiration requires oxygen. It takes place in the mitochondria and only occurs in aerobic respiration. Carbon dioxide and water are produced from pyruvate by these reactions Mitochondria The diagram shows a mitochondrion Cells that need to use a lot of energy, like muscle cells, sperm cells and neurones (nerve cells) have a lot of mitochondria. North Lanarkshire Council Page 2 of 3 National 5 Biology 1.4 Respiration Pupil Course Notes Fermentation Fermentation is the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen. Fermentation in yeast cells and plant cells produces ethanol and carbon dioxide The summary equation for fermentation in yeast and plant cells is: glucose ethanol + carbon dioxide Fermentation in animal cells (including human muscle cells) produces lactic acid. The summary equation for fermentation in animal cells is: glucose lactic acid Production of ATP Aerobic respiration produces 38 molecules of ATP for each glucose molecule broken down. Fermentation produces 2 molecules of ATP for each glucose molecule broken down. Comparison of aerobic respiration and fermentation Type of Aerobic Fermentation in Fermentation in Respiration Respiration Animals Plants and Yeast Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Location(s) Cytoplasm and Mitochondria Final Carbon Dioxide Products and Water ATP Yield 38 molecules North Lanarkshire Council Lactic Acid 2 molecules Ethanol and Carbon Dioxide 2 molecules Page 3 of 3