Metabolism Quiz
advertisement

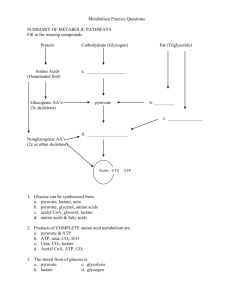
Practice Quiz: Metabolism Nutrition 12 1. Identify each of the following chemical reactions as being either catabolic (write C in the blank) or anabolic (write A in the blank): ___A glucose molecule is converted to 2 pyruvate molecules. ___Amino acids are attached to make a protein. ___Glycogen breaks down to individual glucose molecules. ___A fatty acid forms acetyl CoA molecules. ___Glycerol and fatty acids are joined to form a triglyceride. ___An ATP molecule splits into ADP and a free phosphate. 2. "Energy" is released during 3. ATP is a source of: a. chemical energy a. anabolic reactions b. mechanical energy b. catabolic reactions c. solar energy d. electrical energy 4. Most ATP is synthesized during ______ in this region of the cell _________: a. glycolysis a. cytoplasm b. TCA (Krebs) cycle b. mitochondria c. electron transport c. nucleus 5. The coenzyme NAD contains the vitamin: a. riboflavin b. biotin c. niacin d. thiamin 6. Which vitamin is within the FAD structure? ______ Which is within CoA? _________ a. riboflavin b. pantothenic acid c. niacin d. thiamin e. biotin 7. The role of NAD and FAD during energy metabolism: a. carry hydrogen ions in cells c. carry carbon dioxide b. carry oxygen in bloodstream d. carry carbon groups 8. During which step(s) in energy metabolism does oxygen directly participate? a. glycolysis b. Krebs cycle c. electron transport d. all three 9. How many ATP are usually made during glycolysis?_____ when a glucose molecule is fully oxidized?_____ About how many ATP are made 10. Fatty acids break down to form this molecule when entering the energy metabolism pathways: a. acetyl CoA b. pyruvate c. oxaloacetic acid 11. Which amino acids are able to make glucose: a. lipogenic (ketogenic) amino acids b. glucogenic amino acids c. both types 12. Lipogenic (ketogenic) amino acids usually enter the metabolic pathways as: a. glucose b. acetyl CoA c. oxaloacetic acid 13. Lipogenic (ketogenic) amino acids and fatty acids cannot make glucose because they enter the metabolic pathways as_____________; this molecule cannot be converted into_________, which is the usual precursor for glucose production. 14. When glucose is oxidized to make ATP, these two byproducts are also formed: a. carbon dioxide b. oxygen c. water d. urea e. biotin 15. Glycolysis occurs in this part of the cell:___________, whereas the TCA (Krebs) cycle occurs here:____________. 16. Which pathway is considered 'anaerobic'? a. glycolysis b. TCA (Krebs) cycle 17. Which pathways are "aerobic"? 18. Glucose can be metabolized a. glycolysis c. electron transport b. TCA (Krebs) cycle a. anaerobically c. electron transport b. aerobically c. both a and b 19. Which reaction is absolutely irreversible in our cells? a. glycogen glucose b. protein amino acids c. glucose pyruvate d. pyruvate acetyl CoA e. fatty acids acetyl CoA 20. Lactic acid builds up from ______during _______when______ is/are limited: a. pyruvate a. anaerobic metabolism a. mitochondria/ oxygen supply) b. acetyl CoA b. aerobic metabolism b. carbon dioxide c. fatty acids c. water d. ketone bodies d. carbohydrate 21. Where does lactic acid go, to be eventually converted into glucose: a. liver b. kidney c. brain d. muscle 22. Ketone bodies build up from_____ when______ is limited: a. pyruvate a. oxygen b. acetyl CoA b. carbohydrate c. amino acids c. carbon dioxide d. glycerol d. water 23. Ketone bodies are produced in high amounts when an individual: (circle 4) a. has Type 1 diabetes d. studies too hard g. starts an Atkins diet b. diets or fasts e. runs a marathon h. overeats c. eats too much carbohydrate f. has a vitamin B deficiency 24. A weight lifter's muscles primarily use this fuel during exercise: a. glucose b. fat c. some amino acids 25. A marathon runner uses these fuels (circle all that apply): a. glucose b. fat c. some amino acids 26. A very high intensity exercise is considered: a. anaerobic b. aerobic 27. As an activity continues long-term, the muscles use this fuel in greater and greater amounts: a. carbohydrate b. fat 28. Like ATP, creatine phosphate is a high energy compound, found in MUSCLE. It is usually used: a. in the initial seconds of a high intensity exercise b. during the latter part of a low intensity exercise c. continuously during any type of exercise d. after activity ceases and muscles are resting Matching question: match the following terms with the phrase in the right-hand column. Answers can be used more than once. ____acetyl CoA a. a process that requires ATP ____ definition of aerobic ____ ATP b. pathway that breaks down acetyl CoA to CO2 (and also releases H to power ATP production) c. pathway that breaks down glucose to pyruvate ____ muscle contraction d. 6-carbon carbohydrate molecule ____electron transport ____ active transport e. metabolic process powered by electron/hydrogen transport to attach phosphorus to ADP f. 3-carbon molecule produced during glycolysis ____lactic acid g. molecule that provides energy for cellular reactions ____glycolysis h. molecule that is broken down in TCA cycle ____pyruvate i. requires the presence of oxygen ____TCA cycle j. coenzyme that contains the vitamin pantothenic acid ____ CoA k. 3-carbon molecule produced during anaerobic activity ____glucose