Metabolism Practice Questions
advertisement
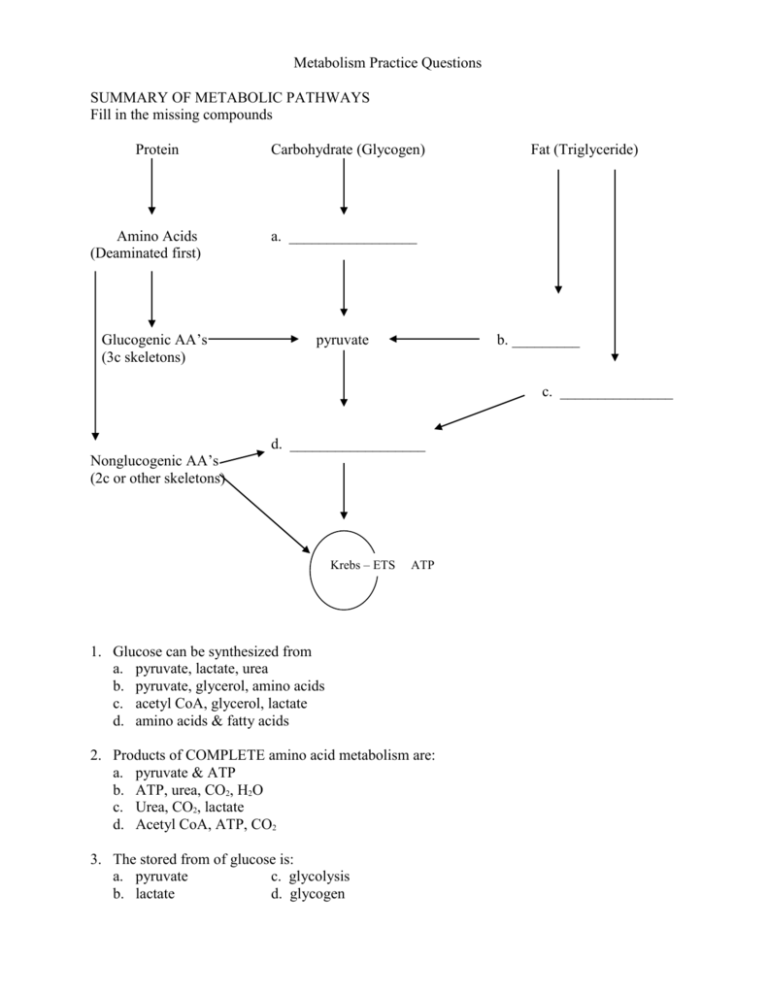
Metabolism Practice Questions SUMMARY OF METABOLIC PATHWAYS Fill in the missing compounds Protein Amino Acids (Deaminated first) Glucogenic AA’s (3c skeletons) Carbohydrate (Glycogen) Fat (Triglyceride) a. _________________ pyruvate b. _________ c. _______________ d. __________________ Nonglucogenic AA’s (2c or other skeletons) Krebs – ETS ATP 1. Glucose can be synthesized from a. pyruvate, lactate, urea b. pyruvate, glycerol, amino acids c. acetyl CoA, glycerol, lactate d. amino acids & fatty acids 2. Products of COMPLETE amino acid metabolism are: a. pyruvate & ATP b. ATP, urea, CO2, H2O c. Urea, CO2, lactate d. Acetyl CoA, ATP, CO2 3. The stored from of glucose is: a. pyruvate c. glycolysis b. lactate d. glycogen 4. The Krebs cycle is primarily a(n) a. anabolic pathway b. catabolic pathway c. glucogenic pathway 5. The two components of triglyceride molecules are: a. acetyl CoA and fatty acids c. fatty acids and glycerol b. glycerol and amino acids d. fatty acids and pyruvate 6. “Incomplete oxidation” is another way to describe: a. Krebs cycle b. electron transport system c. deamination d. glycolysis 7. Fatty acids must be converted to ____ before entering the Krebs cycle. a. pyruvate b. acetyl CoA c. triglyceride molecules d. ATP 8. The complete oxidation of triglyceride yields: a. ATP, H2O, & CO2 b. ATP, CO2, and urea c. Acetyl CoA, CO2, & H2O d. Glycerol, CO2, ATP, & H2O 9. Urea is the product of amino acid deamination a. true b. false 10. The compound from which ketone bodies are synthesized is: a. lactic acid b. acetyl CoA c. triglyceride d. amino acids Match the terms on the left with the appropriate phrase or term on the right. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. reconversion of lactate into glucose hydrogen reservoir anaerobic metabolic pathway urea production high levels occur with fasting from within the body a catabolic pathway metabolic equilibrium cellular location of glycolysis molecule linking glycolysis & Krebs cycle 3-carbon amino acids enters ATP-producing pathway at Acetyl CoA an anabolic pathway ___ glycolysis ___ glycerol ___ acetyl CoA ___ glucogenic compound ___ lactate ___ Krebs cycle ___ mitochondria ___ cytosol ___ homeostasis ___ ketone bodies ___ Cori cycle ___ gluconeogenesis ___ fatty acid 24. The ATP producing power house of the cell 25. Component of TG used for glucose synthesis ___ endogenous ___ deamination