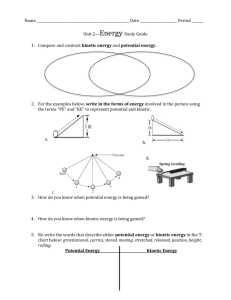
Name: Date: Period:______ Chapter 12 Study Guide _Energy_ is
advertisement

Name:_______________________________ Date:___________________ Period:______ Chapter 12 Study Guide 1. _Energy_ is the ability to cause change. 2. What happens when you add heat to matter? When you take it away? _When you add heat to matter the atoms move faster. When you take away the heat the atoms will move slower 3. What is kinetic energy? What is an example? Kinetic energy is energy due to motion. Examples: moving car, person running, 4. What two things does kinetic energy depend upon? Mass and speed 5. What is potential energy? Energy that is stored due to the interaction between objects or particles. 6. If an object is on top of a hill or in a position off the ground, what type of energy does it have? Gravitational potential energy 7. What two things does gravitational potential energy depend on? The mass of the objects and the distance the object is from Earth 8. What is thermal energy? Give an example. the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of the particles that make up the object. Example: rubbing your hands together to warm them, hugging someone 9. What is mechanical energy? Examples? The sum of the kinetic and potential energy in a system. Examples: weight lifted above your head, pistons in an engine, walking 10. What is sound energy? Examples? Energy carried by sound waves. Examples: bee buzzing, bell ringing, screaming and yelling 11. What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state? Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. 12. __Thermal__ energy is transformed in every energy transformation. 13. What is radiant energy and give an example. Energy carried by electromagnetic waves. Examples: radio waves, sunlight, xrays, fluorescent light bulb 14. What is nuclear energy and give examples. Energy stored in and released from the nucleus of an atom. Examples: atoms splitting, power plant 15. What are renewable energy resources? Examples? an energy resource that is replaced as fast as, or faster than it is used; Examples: solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass 16. What are non renewable energy resources and list some examples? An energy resource that is available in limited amounts or that is used faster than it can be replaced in nature. Examples: Fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, propane, and coal) Nuclear energy 17. Swimmers have to eat well before a meet because the food has which type of energy? Chemical energy 18. What is an open system? Closed system? Open system is a system that exchanges matter or energy with the environment. A closed system is a system that does not exchange matter or energy with the environment. 19. What is electric energy? Examples? Energy in an electric current. Examples: cell phone battery, television ESSAYS: 1. Sunlight is absorbed by a solar panel on a house. The energy collected by the solar panel is used to run a blender that chops apples. The apples are part of a recipe that is cooked in the oven. Explain the forms of energy that are used and how they are used. Sunlight is radiant energy, it is transformed into electric energy in the solar panel. The blender transforms that electrical energy into mechanical energy to chop the apples. The oven transfers thermal energy to the apples. 2. Define kinetic and potential energy. Explain why an airplane flying from Newark to Los Angeles has both kinetic and potential energy. Kinetic energy is energy an object has due to its motion. Potential energy is energy that is stored due to an object’s position. An airplane flying has both because it is in motion and it has height above the Earth’s surface so it also has gravitational potential energy.