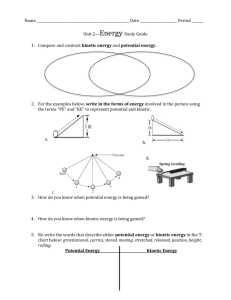
1) An example of kinetic energy is a:
advertisement

Name _______________________________ Date __________________ SOL PS.6 1. An example of kinetic energy is a: A B C D compressed spring. boulder perched on a cliff. stretched rubber band. car stopping by its brakes. 2. Which of these is an example of potential energy being changed into kinetic energy? A B C D compressing a spring a planet orbiting the sun sliding down a hill on a sled stretching a rubber band 5. Which of the following illustrates the concept of potential energy? A B C D water at the bottom of a waterfall an automobile accelerating a fully expanded spring a fully-charged battery 6. Which of the following illustrates the concept of kinetic energy? A B C D a boulder falling off a cliff a spring compressed by a weight a satillite in a geosynchronous orbit the battery of a turned-off portable radio 3. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy: 7. What form does the "wasted energy" in energy transformations usually take? A B C D A B C D cannot be lost by a system. can be gained by a system. cannot be changed within a system. cannot be created or destroyed. 4. An implication of the Second Law of Thermodynamics is that: A some energy is always wasted as heat. B machines can be 100 percent efficient. C all energy can be used to do work. D energy is usually changed into matter. sound waves light chemical energy heat 8. Which of the following is NOT true? A kinetic energy can be changed into potential energy B potential energy can be changed into kinetic energy C heat energy is always potential energy D electrical energy can be potential energy _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright©1999,2000 S.S. Flanagan & D.E. Mott 13 Do not reproduce without permission. 07-15-00 Name _______________________________ Date __________________ SOL PS.6 9. In a thunderstorm, the static electrical energy stored in clouds and the earth is released. What form does it take? A B C D heat, light, and sound heat and light only heat, chemical, and light It just changes from potential to chemical energy. 10. The Second Law of Thermodynamics explicitly says: A Heat spontaneously (naturally) flows from an area of higher temperature to an area of lower temperature. B Heat spontaneously (naturally) flows from an area of lower temperature to an area of higher temperature. C No heat can flow in a vacuum. D Heat cannot be changed into other forms of energy. 11. Sound is really a special type of what energy? A B C D light energy heat energy mechanical energy chemical energy 12. Light energy is a form of: A B C D chemical energy. potential energy. heat energy. electromagnetic energy. 13. Albert Einstein's famous equation: E = mc2; really means what? A Electrical energy equals mass times the square of the charge. B The electric charge on the electron equals its mass times the speed of light squared. C Energy and matter are really two different forms of the same thing. D A great amount of mass can be converted into a very small amount of energy. 14. Energy possessed by an object due to its motion is called: A B C D potential or chemical energy. electromechanical energy. kinetic or mechanical energy. thermoelectric energy. 15. The kinetic energy possessed by an object in motion is determined by what? A B C D The object's acceleration and mass the object's potential energy the work done on the object the object's mass and velocity _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ Copyright©1999,2000 S.S. Flanagan & D.E. Mott 14 Do not reproduce without permission. 07-15-00