UbD Conservation of Energy - Richter
advertisement

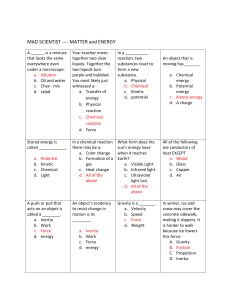
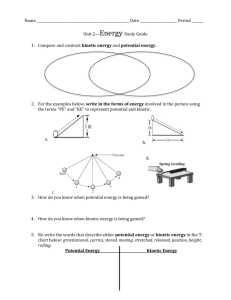
UbD Template 2.0 Stage 1 Desired Results ESTABLISHED GOALS Transfer G ○ 2.1 In MASTE-IP 2.1 Interpret and provide examples that illustrate the law of conservation of energy. MASTE-IP 2.2 Interpret and provide examples of how energy can be converted from gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy and vice versa. Students will be able to independently use their learning to… T ○ Describe the changes in energy in everyday actions and make estimate calculations of energy and changes in energy of everyday actions. Meaning UNDERSTANDINGS U ○ ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Q ○ Students will understand that… What does it mean to say that energy is Energy is conserved. wasted? Potential energy is directly proportional to What does it mean for a machine/process to mass and height difference. be efficient? Kinetic energy is directly proportional mass and the square of velocity. Efficiency is a measure of the ratio of input energy to output energy. (A Joule is equal to a Newton-meter?) Acquisition Students will know… K ○ The definition of energy. The definitions of potential and kinetic energy. The Law of Conservation of Energy. The units of energy are Joules. The definition of efficiency. Students will be skilled at… S ○ Calculating potential energy given mass and height difference. Calculating kinetic energy given mass and velocity. Calculate potential and kinetic energy from measured data. Performing calculations in which known potential energy (height) is converted to unknown kinetic energy (velocity) and vice versa. Calculating the efficiency of energy transfer. Stage 2 - Evidence Evaluative Criteria <type here> Assessment Evidence TRANSFER TASK(S): TT ○ <type here> <type here> OTHER EVIDENCE: <type here> Stage 3 – Learning Plan Summary of Key Learning Events and Instruction <type here> OE ○