137Lab1Handout
advertisement

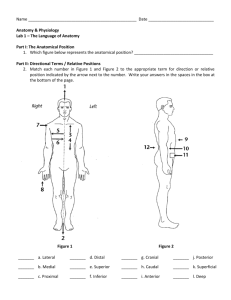
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I – Laboratory LAB EXERCISE I: ORGANS, SYSTEMS, AND ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY (Pages 1 – 11 in your lab manual) 1. Organ Systems (pages 1 – 3) Know each major organ system and the listed organs in each system. Be able to identify the organs on the lab models and/or diagrams. Integumentary System Epidermis Dermis Hypodermis Skeletal System Bone Cartilage Muscular System Muscles Hair Sebaceous gland Sweat gland Ligament Tendons Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Nerves Endocrine System Pineal gland Pituitary gland Thyroid Thymus Parathyroid glands Pancreas Adrenal gland Ovary Testes Cardiovascular System Heart Aorta Arteries Veins Lymphatic System Lymph nodes Lymph vessels Spleen Thymus gland Respiratory System Larynx Trachea Bronchi Lung Digestive System Teeth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine (ascending, transverse, and descending) Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Urinary System Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Urethra Male Reproductive System Testes Epididymis Scrotum Seminal vesicle Penis Vas deferens Prostate gland Female Reproductive System Uterus Fallopian tubes Ovary Vagina 2. Anatomic Position (page 3) Describe the anatomic position. 3. Directional Terms (pages 3 – 4 and Table 1.1) Know the following directional terms: Superior/Inferior Dorsal/Ventral Anterior/Posterior Proximal/Distal Medial/Lateral Superficial/Deep Cranial/Caudal Ipsilateral/Contralateral (not in lab manual – lab instructor will explain) Be able to use these terms when comparing two body parts. For example, the heart is superior to the stomach. The stomach is inferior to the heart. 4. Planes of Sectioning (pages 4 – 5) Know these planes of the body: Frontal (Coronal) Plane Sagittal Plane Midsagittal (Median) Plane Parasagittal Plane Transverse (Horizontal) Plane (Cross-section) If shown a section of the body, organ, or picture on a diagram, you should be able to identify along which plane the section was made. 5. Major Body Cavities (pages 5 – 6) Know the major body cavities and the divisions of each. Also, know which organs lie in each body cavity. Be able to identify the body cavities on a diagram or torso model. Dorsal Cavity Cranial Cavity Vertebral Cavity Ventral Cavity Thoracic Cavity Pleural Cavity Pericardial Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity 6. Regions of the Body (Surface Terminology) (pages 6 – 7) Locate all of the anterior and posterior surface region landmarks that are listed in your lab manual. Be able to locate these landmarks on the baby doll in lab. Cephalic/Cranial (head) Frontal (forehead) Orbital (eye) Nasal (nose) Buccal (cheek) Oral (mouth) Mental (chin) Cervical (neck) Nuchal (back of neck) Trunk Thoracic (chest) Pectoral (chest muscle) Sternal (breastbone) Clavicular (collarbone) Acromial (shoulder) Abdominal (belly) Umbilical (belly button) Inguinal (groin) Pubic (genital) Coxal (hip) Scapular (shoulder blade) Vertebral (spine) Lumbar (small of back) Sacral (sacrum) Gluteal (buttock) Upper extremity (arm and hand) Axillary (armpit) Brachial (upper arm) Cubital (elbow) Antebrachial (forearm) Carpal (wrist) Manual (hand) Dorsum (back of hand) Digital (fingers) Lower extremity (leg and foot) Femoral (thigh) Patellar (kneecap) Popliteal (back of knee) Crural (leg) Tarsal (ankle) Pedal (foot) Digital (toes) Calcaneal (heel) 7. Abdominal Regions (pages 7 – 8) Identify the four abdominopelvic quadrants and the nine abdominopelvic regions on a diagram and torso. Be able to identify both right and left sides. Quadrants: Right Upper Left Upper Abdominopelvic Regions: Right Hypochondriac Left Hypochondriac Right Lumbar Left Lumbar Epigastric Right Lower Left Lower Umbilical Right Iliac Left Iliac Hypogastric