SIGN OCT 2006 – Management of PVD
advertisement

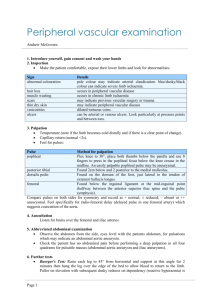
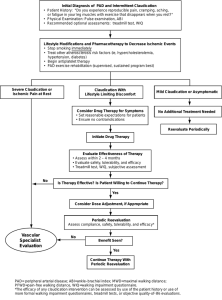
Peripheral vascular disease-2015 /16 Intermittent claudication = ischaemic pain due to decompensation of the blood supply typically occurring with physical activity. . Most common- distal superficial femoral artery (located just above the knee joint), = claudication in the calf muscles . If proximal vessels involved - symptoms in thighs and buttocks, ED. PAD affects 20% of people >60years age & usually about 60% of affected will be asymptomatic. Of those with intermittent claudication, over 5 years: - 70–80% will remain with stable claudication - 10–20% will get worsening claudication symptoms - 5–10% will develop critical limb ischaemia Of those who develop critical limb ischaemia 33% will require a major amputation within the next 12 months. But Cardiovascular disease is the biggest concern Of those with intermittent claudication: 10–15% will die from a CV event within 5yrs A further 20% will have a non-fatal CV event over those 5yrs. Of those who develop critical ischaemia, 25% will die from cardiovascular disease in the next 12months (So prognosis similar to many cancers!). The Edinburgh Artery Study has shown that even a near-normal ABPI (0.9-1.0) is associated with reduced 5 year survival. Up to 20% of symptomatic may be diabetic so important to screen for DM. Mechanisms • Atherosclerosis .Vasospasm . Inflammation/ vasculitis .Thrombosis/ Embolism The Fontaine Classification: • Stage I asymptomatic • Stage II intermittent claudication • Stage III rest pain / nocturnal pain • Stage IV necrosis / gangrene Assessment: History= likelihood ratio of positive diagnosis 4.8 Inspection - Gait, colour, hair, temperature, muscle bulk, toenails, ulcers etc. Palpation- Aortic aneurysm. Cool skin in those with positive history has LR of 5.9 BP- not because you are going to dx something but because you want to control BP as a CVD risk factor. Pulses (Abnormality has LR of 3.1) Normal pulses reduce chance of PAD but don’t exclude it. 1 Auscultation- Renal, femoral and carotid bruits, Femoral artery bruit has LR of 4.8. Also you might need to start ACEI. ABPI in all -See interpretation later on Think about medication - Certain drugs can also reduce blood flow to the extremities. These can cause Raynaud's phenomenon. e.g. Oral contraceptives, Clonidine, Ergotamine, Cyclosporin, Cocaine Bloods- FBC, HbA1C and non fasting lipid profile, Cr&Es, LFTs( need statins). But Autoantibodies, Bone profile, Coagulation screen, CRP, Myeloma screen, if other pathology suspected Surgical Rx Rest pain/gangrene – admit or discuss with on call vascular surgeon IC limiting lifestyle and patient willing to consider operation or angioplasty, then refer vascular surgery. Foot ulcer – refer foot ulcer service & consider vascular referral Others – manage in Primary Care as Endovascular and surgical Rx not recommended in majority of patients. Medical Treatment . Supervised exercise programme; 2 hours per week for 3 months . Smoking cessation . Treat with Atorvastatin 80 to target Cholesterol (40mg if on CCBs) . HTN to target (<150/<90 mmHg) If BP suboptimal opt for ACEI- According to HOPE study for reduction by CVD . Clopidogrel 75mg a day or Aspirin if not tolerated. If both Aspirin and Clopidogrel are contraindicated then Dipyridamole may be used. . Naftidrofuryl - vasodilator effects and is licensed for the medical treatment of IC, but has fair few interactions so beware. Dose -100 mg TDS initially, increasing to 200 mg TDS. Consider naftidrofuryl oxalate for treating people with IC if supervised exercise has not led to satisfactory improvement and the person prefers not to be referred for consideration of angioplasty or bypass surgery. Review progress after 3-6 months and discontinue naftidrofuryl oxalate if there has been no symptomatic benefit. • Nifedipine mentioned for Raynaud’s not proper Peripheral Vasc Disease • Oxypentifylline, oral prostaglandins not recommended. ABPI = Ankle systolic pressure/ Brachial systolic pressure.( 2pm Wednesday Allen house, leg clinic,walk in via DNs) 2 • • In the absence of significant stenosis or occlusion in these vessels the two values are usually within 10 mmHg of each other even in the presence of more proximal disease. The maximum cuff pressure at which the pulse can just be heard with the probe is recorded .BP measured in both arms and the higher of both used. Interpretation of values • Symptom free - 1 or more • Intermittent claudication - 0.95 - 0.5 • Rest pain - 0.5 - 0.3 • Gangrene and ulceration - <0.2 • The measured ankle cuff pressure may be falsely elevated in patients with calcified arteries (particularly occurs in diabetic and renal patients). An ABPI of >1.3 has been suggested as a strong indicator of calcification. • For ABPI >1 esp diabetics consider Toe-Brachial Index(TBI) done via vascular clinic if compression bandaging considered. Mainly as high incidence of vascular calcification. • In patients with chronic venous ulceration, it is currently recommended that the ABPI should be >0.8 if compression bandaging is to be applied safely in the community. Annual review Patients, as a result of remembering their annual review date or having a reminder on their prescription will ring to book their annual review. The reception team will book appointments with PN/ HCA as per flow charts for investigations. QOF QOF Description indicator Points Threshold Any changes from 2014/15 PAD001 Register of people with peripheral arterial disease PAD002 Percentage of patients with PAD in whom the last BP reading (measured in the preceding 12 months) is ≤150/90 PAD004 Percentage of patients with peripheral arterial disease with a record in the preceding 12 months that aspirin or an alternative antiplatelet is being taken 2 No 2 40-90% No 2 40-90% No References: SIGN OCT 2006 – Management of PVD NICE TA210 Dec 2010 – Clopidogrel and PVD NICE TA223 May 2012 – Naftidrofuryl and PVD NICE CG 147 August 2012 Lower limb peripheral arterial disease GP Notebook online handbook 2015 FB presentation 2012. 3