Week 2 - University College Cork
advertisement

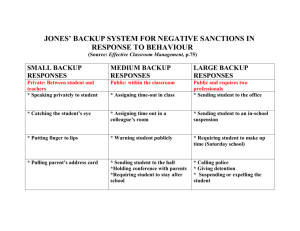
Business Information Systems COURSE OUTLINE: IS3311 - BUSINESS DATA COMMUNICATIONS COURSE OBJECTIVE: To introduce students to the concepts and practical issues involved in the management of local and wide area networks. Students study the theoretical aspects of Networking in the lectures and gain practical experience of administrating a network from the practicals. LECTURER: Karen Neville kneville@afis.ucc.ie LECTURES: Monday Tuesday 2pm – 3pm 3pm – 4pm Ext. 3668 R.2.118 (http://afis.ucc.ie/kneville) C_LL_2 C_LL_1 COURSE CONTENT: On completion of this course, students will have an in-depth understanding of networking and practical experience in administrating Windows 2000. The following checklist outlines the topics to be covered: Data Communications Concepts & Media Understanding Network Architectures Network Standards & Protocols LAN, WAN & Wireless Concepts & Architectures Internetworking Devices Network Management Network Storage Business Continuity & Security ASSESSMENT: CA 40% Final Exam 60% Continuous Assessment: Continuous assessment of the students accounts for 40% of the final grade. It is effectively split up into three methods of testing their knowledge: 1. Two MCQ exams, worth 20% of the final grade, are used to examine lecture material and additionally to determine student understanding of the topics covered in class. 2. The second type of assessment is a 15% Windows 2000 Written Exam. 3. 5% will be awarded for Lecture/Tutorial attendance and in class participation. Final Exam (60%) The final exam examines each of the learning objectives of the course (Past papers are available @ http://afis.ucc.ie/kneville). Page 1 of 5 LEARNING OBJECTIVES & OUTCOMES: Overall Objective & Description: This course introduces students to networking concepts, various technologies, and the rules that govern communication. It was designed with the objective of showing students how a network is designed, to the requirements of end-users needs, and expanded through the use of connectivity devices and wide area network (WAN) services. The theory and concepts applied, in this course, are drawn from both academic and practitioner resources to provide both fundamental concepts and up to date applications of the technologies outlined in class. Therefore students gain an overall knowledge of networking and examples of its practical application in organisations. The course covers a wide range of networking topics to provide students with a greater appreciation and understanding of data communication. During the practicals assigned to this course, students will also learn how to physically manage a network. They use a simulated Windows 2000 environment to provide them with the same ability as a network administrator and therefore learn how to create and administrate a network. Learning Objectives & Outcomes: On completion of this course, students will have an in-depth understanding of the following: Network Standards: IEEE 802.X Standards Categories, TCP/IP Model, & TCP/IP Hybrid Model. Protocols & Layering: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, TCP, IP, RIP & PPP. Basic Network Media: Signal Transmission, Coaxial), Twisted Pair & FibreOptic cables, selecting cables, the Network Interface Card. Understanding Network Architecture: Access Methods, Logical and Physical Topologies. LAN (Local Area Network) & MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) Concepts & Architectures: Network Configurations (Access Methodology, Logical Topology, Physical Topology & Media) & Implementations of the following: Fast Ethernet & FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interchange). Elements of Network Connectivity: Modem Technology, Hubs, Repeaters, Switches, Bridges, Routers, Brouters Gateways & Multiplexers. WAN Concepts & Architectures: Switching (Circuit & Packet), Analog & Digital transmission, T1, ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode), ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), SONET & SMDS Services. Wireless Networking: 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g & Bluetooth. Network Storage: Growth/value of Information, Storage Systems Architecture, SAN (Storage Area Network), NAS (Network Area Network) & Managing & Monitoring. Business Continuity: Business Continuity Planning, Backup Recovery (Recovery Point / Time Objective, Disaster Recovery). Security: Goals, Types, People, Processes & Technology. Additional Support: A website (http://afis.ucc.ie/kneville/) in addition to the lecture material is used to illustrate the theory covered in class with Video clips, demonstrations and access to online tutorials related to the technologies discussed in class. Reading Material: Handouts will be distributed to supplement Lecture Notes. A list of books and practical guides are available on the Website. Page 2 of 5 ADMINISTRATING WINDOWS 2000 TUTORIALS Week 1 – Introduction Installing Windows 2000 Professional 2.0 Windows 2000 Administration Tools Week 2 – 3.0 Users & Groups Administer Local Users & Groups Administer Domain Users & Groups Week 3 – 4.0 Hardware Devices Configure Hardware Devices Configure Display Devices Manage Drivers Week 4 – 5.0 Disk Management Manage Disks Create and Manage Volumes 6.0 Desktop Environment Configure User Settings Configure User Profiles Install Applications Week 5 – 7.0 NTFS Features Configure Compression Encrypt Folders & Files Manage Quotas Configure NTFS Permissions 8.0 Shared Folders Manage Shared Folders Configure Shared Folder Access Use Offline Files Week 6 – 9.0 Printer Access Install & Share a Printer Manage Printing Control Printer Access 10. System Security Week 7 – 11. System Performance & Reliability 12. Network Connections Configure TCP/IP Configure Network Connections Configure Dial-up Networking Configure Internet Connections 13. MS Dos Tutorials Page 3 of 5 OLLSCOIL NA hEIREANN, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLAISTE NA hOLLSCOILE, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK Spring Examination, 2007 BSc Business Information Systems Third Year IS3311 Business Data Communications and Networks Professor G. Philip Professor C.M. Murphy Ms. K. Neville Students are required to attempt FOUR questions 3 HOURS Attempt FOUR of the following questions. All questions carry equal marks 1. (a) Write a brief note on Twisted pair and Fibre Optic cabling (5 percent) (b) Compare and contrast the network architectures of FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface) and Token Ring. (20 percent) 2. (a) Write a brief note on the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model. (5 percent) (b) Describe the network configuration of Standard Ethernet and the different implementation options available to organisations when selecting an appropriate media for the technology. (20 percent) 3. (a) Explain how administrators can cut costs in the implementation of FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface) in an organisation. (5 percent) (b) Discuss the role of management in organisation security in both the internal and external operations (network design) of an organisation of your choice. Page 4 of 5 (20 percent) 4. (a) Write a brief note on Wireless 802.11. (5 percent) (b) Describe the operating characteristics and distinguish between the following devices: a repeater, bridge, router and a firewall. (20 percent) 5. Discuss the concept of ‘Packet Switching’ using X.25, Frame Relay, ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) and SONET (Synchronous Optical Network) to explain how it is implemented (25 percent) 6. (a) Write a brief note on business continuity. (5 percent) (b) Propose a backup and recovery solution to address the concerns of the company described below and justify how your solution will ensure that the company’s needs are met: A manufacturing corporation uses tape as their primary backup storage media throughout the entire organization. Currently full backups are run every Sunday. Incremental backups are run from Monday through Saturday. There are many backup servers in the environment, backing up different groups of servers. Their e-mail and database applications have to be shut down during the backup process. The main concerns facing the corporation are: 1. Due to the de-centralized backup environment, recoverability of the backup servers is compromised. 2. Key applications have to be shut down during the backup process. 3. Too many tapes need to be mounted in order to perform a full recover, in case of a complete failure. The company would like to: 1. Deploy an easy-to-manage backup environment. 2. Reduce the amount of time the email and database applications need to be shutdown. 3. Reduce the number of tapes required to fully recover a server in case of failure. (20 percent) Page 5 of 5