Review - Mrs. Lucky's Webpage
advertisement

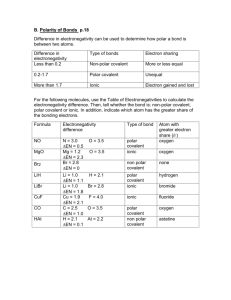
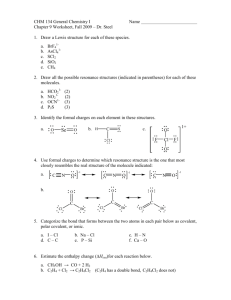
Covalent Bonding Test Review Covalent Bonds: _____________________________________________________________________________ Two types of covalent bonds: _____________________ and _____________________________. __________________ :Unequal sharing of electrons because one atom is more electronegative __________________: Equal sharing of electrons because atoms are approximately equal in electronegativies Covalent bonds can be single, double or triple bonded. ______________ are the strongest bonds. Comparing Ionic, Polar Covalent and Non-Polar Covalent Ionic Polar Covalent Non-Polar Covalent _______________________ ____________________ ____________________ High melting point ___________ melting point Low melting point ___________________ Solids and liquids Liquids and gases No dipoles ______________________ No dipoles Dissolves in ______________ Dissolves in ________________ Dissolve in _________________ Lewis Structures 1. 2. 3. 4. Determine number of ___________________________________________ for each element. Determine central atom (____________________________________________). Write central atom and valence electron dots. Fill in remaining elements with their valence electron dots. Draw Lewis Structures for the following: H20 NH3 F2 Identify the Bond Type and Solubility Electronegativity:_______________________________ _____________________________________________ Bond Type Bond Type Ionic Polar Ionic Non-Polar Polar Polar Cmpd Electro Diff Soluble / Not Soluble Bond Type A ______________ difference in electronegativity’s indicates a _____________________ of electrons and an __________________________. Polar Non-Polar Non-Polar Non-Polar Cmpd Two One BaCl H4Sn CS2 H2O NO2 KCl SiF4 HN Si4P6 H2O Electro Diff Bond Type Soluble Yes/No Naming Diatomic Elements: _________, __________, ________, __________, _____________, ___________, __________ Covalent Prefixes: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 If a compound starts with a non-metal and the compound is binary, use the prefixes and the anion must end in –ide. o o o o Ex/ HCl - Hydrochloric Acid Ex/ HNO2 - Nitrite - Nitrous Acid If the anion ends in “ate”, change the ending to “ic” followed by acid. Ex: O2 - Oxygen Ex/ HNO3 - Nitrate - Nitric Acid Practice naming these compounds: Practice writing these compounds: HF Magnesium Bromide ________________________ 10 If the compound is ternary (3 elements) and starts with hydrogen (H), it is also an _________. If the anion ends with “ite,” change the ending to “ous” followed by acid. Ex: NO- nitrogen monoxide If the compound is diatomic, use the name of the elemental symbol 9 If the compound is binary (2 elements) and starts with hydrogen (H), it is an ________. Binary acids start with “hydro” and end with “ic” followed by acid. Ex: CCl4- Carbon Tetrchloride Do not use the ____________ prefix if the first element of the compound contains only one atom. o 8 ________________________ HClO2 ________________________ Triphosphorus pentachloride ________________________ I2 Hydrobromic Acid _________________________ K3PO4 _______________________ Fluorine ________________________ NO2 Dihydrogen Dioxide ________________________ ________________________ _______________________ CaF2 ________________________ Magnesium Nitrate ________________________ HCl __________________________ Silicon Tetrafluoride _______________________ HNO3________________________ Ammonium Oxide _______________________ O2___________________________ Iron (III) Bromide _______________________ NaCl__________________________ Phosphorous Acid _______________________ Fe2S3_________________________ Magnesium Hydroxide ________________________ H2___________________________ Nitrogen Monoxide ________________________ Organic Branch of chemistry devoted to _________________________________________. CnH2n+2 Single bond = ________________________________________________________________________________. Hydrocarbons:________________________________________________________________________________. CH4 C6H14 C2H6 C7H16 C3H8 C8H18 C4H10 C9H20 C5H12 C10H22 Draw the structural formula for: Draw the condensed formula for: Pentane: Ethane: Octane: Butane: Draw the skeletal formula for: Hexane: Propane: Density M • Measurement of how packed or crowed the object is • Ratio of mass to volume • Floats in water if density is _____________________; Sinks in water if density is _______________________ 1. If a substance has a mass of 573 g and a volume of 682 mL, will it float or sink? D Density V Mass Volume 2. The level of water in a graduated cylinder is 65.7 mL. After a solid object with a mass of 35.0 g is added, the level of the water rises to 92.4 mL. What is the density of the solid object? 3. The level of water in a graduated cylinder is 142.7 mL. After a solid object with a mass of 45.0 g is added, the level of the water rises to 192.4 mL. What is the density of the solid object? 4. What is the mass of and object that has a density of 1.82 g/mL and a volume of 32.3 mL? Review Metal, non-metal, metalloid P+, n0, e—: charge, location, mass Evidence of a chemical reaction