Goal 2 Critical Thinking: Students will apply
advertisement

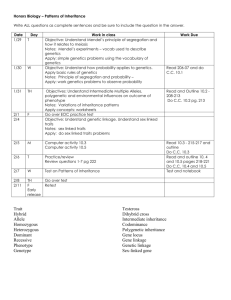
9/16/15 DATE Math/Science REQUIRED COURSE ELECTIVE COURSE X DIVISION NEW COURSE REVISION LAKE LAND COLLEGE Course Information Form COURSE NUMBER BIO160 SEM CR HRS 3 COURSE PCS # TITLE LT HRS 3 Introduction to Genetics LAB HRS 0 SOE HRS (Assigned by Administration) ECH 3 DELIVERY MODE: 1Face-to-face Fall semester, 1 On-line Spring, 1 On-line Summer PREREQUISITES: None Catalog Description (40 Word Limit): An introduction to the principles of genetics with emphasis on human heredity. Included are Mendelian genetics, hereditary disorders, gene expression, genetic engineering, and population genetics. CONTENT OUTLINE LECTURE HOURS LAB HOURS Genetics as Science 3 (6.7%) Chromosomal Basis of Heredity 6 (13.3%) Mendelian Genetics of Humans 5 (11.1%) Modes of Inheritance 5 (11.1%) Polygenic Inheritance/ Gene Expression 5 (11.1%) Chromosomal Anomalies, Genetic Mutation types, 4 (8.9%) Genetic Engineering and Technology 4 (8.9%) Genetics of Human Health and Behavior 4 (8.9%) Population/Diversity/Evolution Genetics 5 (11.1%) HOUR EXAMS 4 (8.9%) EVALUATION: Quizzes X Exams Lab Work Textbook: Title Projects X Oral Pres. X Papers Comp.Final X Human Genetics Concepts and Applications Author Publisher Ricki Lewis McGraw-Hill Volume/Edition 11th Edition Copyright Date ____ 2015 SEE REVERSE FOR CONTENT DETAIL Other X Major Course Segment _ Hours Learning Outcome (SEE ATTACHED SHEETS) Course Outcomes: At the successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Apply fundamental principles of genetics including meiosis and working genetics problems of various types. Recognize real-world examples of genetics topics and demonstrate the interaction of genetics in society. Understand and apply the concepts of population genetics and the complexity of human heredity vs. Mendelian genetics. Discover and understand the technologies that involve DNA and the applications that arise from the use of the technology. The following LLC General Education goals are met in BIO 160: Goal 1 Communication: Students will communicate professionally and effectively. In numerous class discussions regarding current events in genetics, students will be expected to professionally and effectively express their views and questions when called upon in class or when addressing the professor with questions in class or via e-mail. Goal 2 Critical Thinking: Students will apply critical thinking skills in various ways. Students will apply critical thinking to solve genetic problems. Critical thinking skills are also involved in analyzing case studies in genetics. In a case study, students must do the following: locate information, evaluate sources, analyze data and arguments, interpret results, and transfer insights to new contexts. Goal 3 Problem Solving: Students will demonstrate scientific and quantitative problemsolving skills. This goal is met through solving various genetics problems throughout the semester. Also, determining modes of inheritance requires problem solving and critical thinking skills. Goal 4 Diversity: Students will recognize the unique characteristics of others. Through the application of current events and the discussion of bioethical issues, students will realize the diversity of thoughts and cultures, along with economic, geographical, and historical perspectives regarding various issues. Goal 5 Citizenship: Students will demonstrate civic responsibility. Many of the problems in society today can be solved using biological technology. Examples of current techniques and technology used in various industries will be used to demonstrate the impact human actions have on society and the student’s role in a global society. Students will look into the controversy of new techniques used in biology and discuss the ethical problems which arose with the development of such techniques. Goal 6 Foundational Knowledge: Students will demonstrate knowledge of general education course content. Students will have a working knowledge of key components learned from a wide variety of general education courses taken. In the biological sciences, this may include a basic knowledge of: cells, DNA, energy systems, genetics and cancer. Intro to Genetics BIO 160 Course Objectives Unit 1 Overview of Genetics At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the development of genetics as a field of study. b. the historical importance of the work of Darwin and Mendel. c. the role and significance of genetics in modern society. Cells At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the structure and organization of cells in higher organisms b. chromosomes as cellular organelles that carry genetic information. c. the features that distinguish one cell from another. Meiosis and Development At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the process of meiosis and the formation of gametes. b. Mendel’s crosses involving two traits at the same time, and the accompanying principle of independent assortment. c. how Medel’s laws apply to the inheritance of traits in humans. d. the stages of mitosis. e. the significance of mitosis and the genetic control of the cell cycle. Single-Gene Inheritance At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. Mendel’s crosses involving one characteristic, the principle of segregation, the concepts of dominance and recessiveness, and the presence of factors in pairs. b. the difficulties involved in studying genetic traits in humans, by relying on indirect observations rather than direct experiments. c. the guidelines for determining whether a particular trait is genetic. d. the expectations for the appearance of autosomal recessive traits in a pedigree, and the examples of autosomal recessive traits in humans. e. the expectations for the appearance of autosomal dominant traits in a pedigree, and examples of autosomal dominant traits in humans. Unit 2 Beyond Mendel’s Laws At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the concept of multiple alleles. b. the expression of incomplete dominant traits. c. epistasis and how genes are affected. d. the difference between penetrance and expressivity e. mitochondrial DNA and it’s inheritance f. the concept of linkage Matters of Sex At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. a. the expectations for the appearance of sex-linked traits in a pedigree and examples of human sex-linked traits. b. mitochondrial inheritance, incomplete penetrance, variable expressivity, and linked genes. c. how the sex ratio is determined, and the fact that the male gamete determines the sex of the offspring. d. details of sexual differentiation and the role of the Y chromosome in this process. e. the concept of dosage compensation. f. sex-linked and sex-influenced inheritance. Multifactorial Traits At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the difference between continuous and discontinuous traits. b. the characteristics of traits that demonstrate continuous variation. c. regression to the mean. d. the measurement of twin studies and heritability. e. the relationship between genotype and environment in multifactor traits. Genetics of Behavior At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the idea that most behavior traits represent complex phenotypes with multifactor inheritance. b. the range of methods used to study human behavior genetics. c. the use of animal model systems to establish that aspects of behavior are under genetic control and to provide estimates of heritability. d. single gene defects that bring about altered behavior in humans. e. the complex nature of behavior traits such as bipolar illness and schizophrenia, and other multifactor traits. f. the need for new and innovative approaches to the study of the genetic basis of human behavior. DNA Structure and Replication At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the chemical composition and structure of DNA. b. the Watson-Crick model of DNA. c. chromosome structure from the level of DNA to the metaphase chromosome. d. the models and mechanisms of DNA replication. Gene Action: From DNA to Protein At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the central dogma for the transfer of genetic information of DNA into proteins. b. the general structure of amino acids and the RNA components of protein synthesis. c. the process of transcription and the role of messenger RNA. d. the process of translation and the role of transfer RNA. e. the polypeptide product and the functions that proteins perform in the cell. f. the organization of a typical eukaryotic gene, and the function of introns and exons. Unit 3 Gene Expression and Epigenetics At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the concept that proteins are the end product of genes. b. the study of proteomics c. the formation and use of microRNAs d. chromatin remodeling e. the procedure of alternate splicing and its importance f. the types and purposes of noncoding RNAs g. the existence of viral DNA in the human genome h. the presence and consequences of nucleotide repeats in the human genome Gene Mutation At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. how mutations are detected in humans. b. the methods used in measuring the rate of mutation in humans, and the mutation rate that is assigned as an average for human genes. c. the molecular basis of mutations, including base substitutions, deletions, and insertions. d. the existence of trinucleotide repeats and the phenotypic consequences of changing the number of such repeats. e. variations in chromosome structure such as deletions, translocations, and fragile sites. Chromosomes a. chromosome structure and its components b. the tools and processes used to visualize and study chromomomes c. methods of prenatal diagnosis including amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, and blood serum testing. d. how to read a gene locus e. the concepts of polyploidy, aneuploidy and euploidy. f. the mechanisms (nondisjunction and double fertilization) that give rise to polyploidy, and the inviability of the polyploidy condition. g. several autosomal trisomic conditions, including Down syndrome, and the risk factors that predispose to aneuploid conditions. h. sex chromosomal disorders, including Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, XYY syndrome, and XX chromosome. Unit 4 Allele Frequencies At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the role of mutation in generating genetic diversity. b. the effects of drift and selection on changing gene frequencies. c. the effects of human activities such as migration, mate selection, and diet on gene frequencies. d. genetic and nongenetic definitions of race. e. the relationship between diversity, selection and species formation. f. the current interpretation of the fossil record in human evolution. Genes and Cancer At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the multiple-hit theory of cancer. b. the application of this theory to several forms of heritable cancer. c. the concept of oncogenes as normal components of the genome that can be oncogenic when mutated or disrupted. d. the relationship between chromosome mutations and specific forms of leukemia. e. the role of oncogenes in cancers. f. methods of epidemiology. g. the role of environmental agents in causing mutations leading to cancer. Genetic Technologies At the end of this chapter, students should have an understanding of: a. the concept of cloning organisms. b. the use of restriction enzymes and vectors. c. the means of finding a specific gene in a library. d. RFLPs and their use as markers for specific chromosomes or genes. e. the uses of a cloned disease gene. f. the use of DNA fingerprints. g. prenatal and presymptomatic testing h. the goals of the Human Genome Project. i. commercial, and medicinal applications of recombinant DNA technology. j. agricultural applications of recombinant DNA technology . Topic Outline: Intro to Genetics Course Outline Getting Started FIRST ASSIGNMENT - Intro to the course quiz based up the “Getting Started” module UNIT 1 FIRST ASSIGNMENT - Intro to the course quiz based up the “Getting Started” module Chapter 2: Cells Read pages 15-41 Study Cells ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 2 Study Links (optional) Cells Note check under Assessments tab Submit the Unit 1 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Chapter 3: Meiosis and Development Read pages 42-67. Study Meiosis and Development ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 3 Study Links (optional) Meiosis Note check under Assessments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Chapter 4: Single Gene Inheritance Read pages 68-88. Study Single Gene Inheritance ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 4 Study Links (optional) Chp. 4 Note check under Assessments tab Unit 1 Mandatory Submissions Answer Unit 1 Review Quiz questions. The review quizzes are not password protected, and students can attempt the quiz unlimited times prior to the deadline. (10 pts.) Complete Unit Note Checks under assessments (points vary) Submit the Unit 1 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Unit 1 Test – (100 pts.) Password protected and only 2 attempts. Appointment must be made for exam to be proctored). UNIT 2 Chapter 5: Beyond Mendel’s Laws Read pages 89-109 Study Beyond Mendel’s Laws ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 5 Study Links (optional) Beyond Mendel’s Laws/Matters of Sex Note check under Assessments tab Chapter 6: Matters of Sex Read pages 110-129. Study Matters of Sex ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 6 Study Links (optional) Beyond Mendel’s Laws/Matters of Sex Note check under Assessments tab Chapter 7: Multifactorial Traits Read pages 130-147. Study Multifactorial Traits ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 7 Study Links (optional) Multifactorial Traits note check under Assessments tab Submit the Unit 2 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Chapter 8: Genetics of Behavior Read pages 147-162. Study Genetics of Behavior ppt. notes download (or pdf) Chp. 8 Study Links (optional) Genetics of Behavior note check under Assessments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Unit 2 Mandatory Submissions Answer Unit 2 Review Quiz questions. The review quizzes are not password protected, and students can attempt the quiz unlimited times prior to the deadline. (10 pts.) Complete Unit Note Checks under assessments (points vary) Submit the Unit 2 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Unit 2 Test – (100 pts.) Password protected and only 2 attempts. Appointment must be made for exam to be proctored). UNIT 3 Chapter 9: DNA Structure and Replication Read pages 163-179 Study Chp. 9-10 DNA Structure and Function ppt. notes download Chp. 9 Study links (optional) Chps. 9-10 DNA Structure and Function Note check under Assessments tab Chapter 10: Gene Action: From DNA to Protein Read pages 180-198. Study Chp. 9-10 DNA Structure and Function ppt. notes download Chp. 10 study links (optional) Chps. 9-10 Note check under Assessments tab Chapter 11: Gene Expression and Epigenetics Read pages 199-211. Gene Expression and Epigenetics ppt. lecture notes download Chp. 11 Study Links (optional) Gene Expression and Epigenetics Note check under Assessments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Chapter 12: Genetic Mutation Read pages 212-236, 253-258 Genetic Mutation ppt. lecture notes download Chp. 12 Study Links (optional) Genetic Mutation Note check under Assessments tab Submit the Unit 3 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Unit 3 Mandatory Submissions Answer Unit 3 Review Quiz questions. The review quizzes are not password protected, and students can attempt the quiz unlimited times prior to the deadline. (10 pts.) Complete Unit Note Checks under assessments (points vary) Submit the Unit 3 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Unit 3 Test – (100 pts.) Password protected and only 2 attempts. Appointment must be made for exam to be proctored). UNIT 4 Chapter 13: Chromosomes Read pages 237-262 Study Chromosomes ppt. notes (or pdf) Chp. 13 Study Links (optional) Chromosomes Note Check under Assessments tab Chapter 14: Constant Allele Frequencies Read pages 263-278 Chp. 14-15 Allele Frequencies ppt. notes (or pdf) Chp. 14 Study Links (optional) Allele Frequencies Note Check under Assessments tab Chapter 15: Changing Allele Frequencies Read pages 229-301 Continue with Allele Frequencies ppt. notes (or pdf) Chp. 15 Study Links (optional) Allele Frequencies Note Check under Assessments tab Chapter 18: Genetics of Cancer Read pages 351-373 Genetics of Cancer ppt. notes (or pdf) Chp. 18 Study Links (optional) Genetics of Cancer Note Check under Assessments tab Submit the Unit 4 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Chapters 19-20: Genetic Technologies Read pages 374-421 Genetic Technologies ppt. notes (or pdf) Chp. 19 Study Links (optional) Chp. 20 Study Links (optional) Genetic Technologies Note Check under Assessments tab Unit 4 Mandatory Submissions Answer Unit 4 Review Quiz questions. The review quizzes are not password protected, and students can attempt the quiz unlimited times prior to the deadline. (10 pts.) Complete Unit Note Checks under assessments (points vary) Submit the Unit 4 Bioethics Case Study (15 pts) under Assignments tab Genetic Update Article Summary (15 pts.) under Assignments tab Answer Semester exam review questions in Blackboard. The review quizzes are not password protected, and students can attempt the module quizzes unlimited times. (10 pts.) Unit 4 Test – (100 pts.) Password protected and only 2 attempts. Appointment must be made for exam to be proctored). Semester Exam- (200 pts.) Password protected and only 1 attempt. Appointment must be made for exam to be proctored. Evaluation/ Assessment Students are recommended to have a basic interest in genetic concepts before taking this class. Reading is required of all chapters. Points for the course come from the following areas: 1 “Intro” quiz based upon Welcome page & course info links 13 Note Checks 10 pts+. each 10 pts. (1.2%) 130 pts. (16.0%) 4 responses to “Case Studies” 15 pts. each 60 pts. (7.4%) 4 “Genetics Update Articles” 15 pts. each 60 pts. (7.4%) 4 Unit review question sets (10 pts. each) 40 pts. (4.9%) 4 Unit exams 100 pts. each (lowest unit score dropped) 300 pts. (37%) 1 Semester exam review question set (10 pts.) 10 pts. (1.2%) 1 comprehensive semester exam (200 pts.) 200 pts. (24.7%) 810 pts.* *Point totals are subject to change. Course Grading: A = 90 – 100% B = 80 - 89% C = 70 - 79% D = 60 – 69% F = 59% or lower Evidence of clear integration of Science & Society topics throughout the course: Unit Case Studies: 1 per unit Unit 1 The unit 1 case study is found on page 12. Read the information and answer all of the question(s) associated with "Genetic Testing and Privacy." (15 pts.) Unit 2 In your textbook, answer all of the questions associated with Chapter 7 Case Study #2, pg. 146 regarding roots of criminal behavior and case study #4 regarding athletic ability. (15 pts). Unit 3 In your textbook, answer all of the questions associated with Chapter 12 Case Studies #6 (deafness) AND #7 (Alzheimer disease), pg. 236. Unit 4 In your textbook, answer the question(s) associated with Chapter 18 Case Study #7, pg. 373 regarding breast cancer. Also answer question to Case Study #1, pg. 405 regarding osteogenesis imperfecta. Unit 2 Case Study Unit 3 Case Study Unit 4 Case Study Genetics Update Article Reviews- 1 per unit Find a relatively recent article (less than 1 year old) in the news that discusses some topic/ concept discussed in unit 1. The news article can be cited from any type of media. The article must be cited in such a way that the professor can easily access the article for further review. After reading the article, write a summary paragraph that discussing the concept and how it ties in with concepts learned in the unit at hand. Don't forget to correctly cite the article. Many correct methods of citation will be accepted. Last of all, after summarizing the article, students must add a "discussion question" regarding their article. In other words, pose a question that could stimulate some discussion or even debate. Article reviews without a discussion question listed at the end will be deducted 3 points. All submissions are graded the day after the submission deadline.