Name: Date: Subject: Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Objectives
advertisement

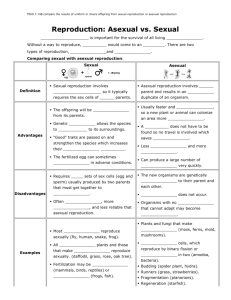
Name: Date: Subject: Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction Objectives Objective 1: ASWBAT identify the number of parents required and how the offspring compare to the parents genetically in both asexual and sexual reproduction. Objective 2: ASWBAT describe three types of asexual reproduction. Objective 3: ASWBAT describe advantages and disadvantages for both sexual and asexual reproduction. On a scale of 1 – 3 how well you can do on this objective now. (1 – Not at all 2 – I know it a little bit 3 – I know it very well) Objective: 1 Objective: 2 Objective: 3 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 Key Vocabulary Words On a scale of 1 – 3 how well you know the vocabulary words below. (1 – Not at all 2 – I know it a little bit 3– I know it very well) Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Binary Fission Fragmentation Budding Genetic Variation 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Pre-quiz Do your best to answer the following questions. 1. What are sex cells for? How many chromosomes do they have? Answer: 2. What are the male and female sex cells called? Answer: 3. What is fertilization? Answer: 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Asexual Reproduction Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. We call them clones. This doesn’t mean that they are exactly the same, it just means that they have the same DNA or genes. Asexual reproduction requires only 1 parent so asexually reproducing organisms do not require males. Unicellular organisms reproduce asexually, including prokaryotes, and unicellular eukaryotes. Many plants and fungus can reproduce asexually as well. Some animals can asexually reproduce, but it is much less common. 1. How many parents are required in asexual reproduction? Answer: 2. How do the offspring compare to the parent organism in asexual reproduction? Answer: Types of Asexual Reproduction There are three main types of asexual reproduction, binary fission, fragmentation and budding. Binary Fission Unicellular organisms use binary fission. In binary fission the parent cell is replaced by two daughter cells, when it divides in two. Prokaryotes (bacteria) and unicellular eukaryotes reproduce this way. Binary fission is when unicellular organisms split into two new cells. Binary Fission (Eukaryotes) 1 Parent Cell Binary Fission (Prokaryotes) Two Daughter Cells Video Link: Binary Fission - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DY9DNWcqxI4 Fragmentation Some organisms have the ability to regrow into a new organism from small fragments of an organism. Each fragment or piece grows into an new genetically identical organism. This type of reproduction is called fragmentation. This type of reproduction can sometimes happen when an organism is injured. Many plants and some animals can reproduce through fragmentation. Fragmentation of Planarian Worm Parent Budding Budding is a type of asexual reproduction where a new organism that grows from an outgrowth or bud of the parent organism. Just like all asexual reproduction, the new organism is a clone of the parent. This type of reproduction is very common in plants, but some animals can also reproduce this way. Budding of a Hydra Parent Clone Video Link: Hydra Budding - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a5oHMjGqjyo 1. What is binary fission? Answer: 2. What is fragmentation? Answer: 3. What is budding? Answer: Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction is the combining of the genetic information of two parent organisms to create offspring that are a genetic mix of the parent. Sexual reproduction requires the creation of sex cells, which carry half of the chromosomes from each of the two parents. The sex cells are created during a process called meiosis. 1. How many parents are required in sexual reproduction? Answer: 2. How do the offspring compare to the parents in sexual reproduction? Answer: Video: Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jk2RJm5RBEk Advantages and Disadvantages Both asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction have their advantages and disadvantages. They both have trade offs of quantity or diversity. Asexual Reproduction – (Advantages and Disadvantages) Advantages Allows an organism to reproduce more often Requires less energy because it does not require the production of sex cells or males Disadvantages Creates offspring that are genetically identical to the parents so they adapt much slower to the changing environment Sexual Reproduction – (Advantages and Disadvantages) Advantages Creates offspring that are a genetic mix of the parents so they adapt to changes in the environment faster Creates genetic variation in the species Disadvantages Requires more energy because it requires the creation of sex cells and males Takes more time for the organism to reproduce so they reproduce less often 1. What is one advantage of asexual reproduction? Answer: 2. What is one disadvantage of asexual reproduction? Answer: 3. What is one advantage of sexual reproduction? Answer: 4. What is one disadvantage of sexual reproduction? Answer: Quiz Directions: Answer the following questions to see if you met the objectives. 1. How many parents does asexual reproduction require? Answer: 2. How do the offspring compare to the parents in asexual reproduction? Answer: 3. How many parents does sexual reproduction require? Answer: 4. How do the offspring compare to the parents in sexual reproduction? Answer: 5. What is binary fission? Answer: 6. What is fragmentation? Answer 7. What is budding? Answer: 8. Name one advantage and one disadvantage to asexual reproduction. Answer: 9. Name one advantage and one disadvantage to sexual reproduction. Answer: