Quiz 2
advertisement
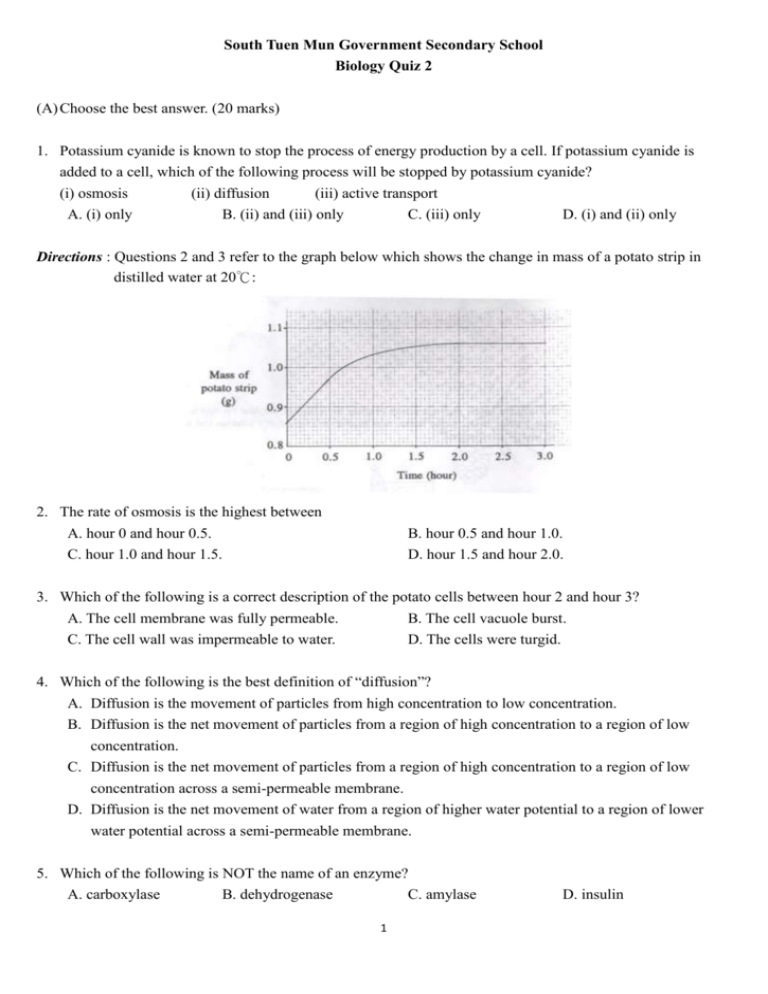
South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School Biology Quiz 2 (A) Choose the best answer. (20 marks) 1. Potassium cyanide is known to stop the process of energy production by a cell. If potassium cyanide is added to a cell, which of the following process will be stopped by potassium cyanide? (i) osmosis (ii) diffusion (iii) active transport A. (i) only B. (ii) and (iii) only C. (iii) only D. (i) and (ii) only Directions : Questions 2 and 3 refer to the graph below which shows the change in mass of a potato strip in distilled water at 20℃: 2. The rate of osmosis is the highest between A. hour 0 and hour 0.5. C. hour 1.0 and hour 1.5. B. hour 0.5 and hour 1.0. D. hour 1.5 and hour 2.0. 3. Which of the following is a correct description of the potato cells between hour 2 and hour 3? A. The cell membrane was fully permeable. B. The cell vacuole burst. C. The cell wall was impermeable to water. D. The cells were turgid. 4. Which of the following is the best definition of “diffusion”? A. Diffusion is the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration. B. Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. C. Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration across a semi-permeable membrane. D. Diffusion is the net movement of water from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential across a semi-permeable membrane. 5. Which of the following is NOT the name of an enzyme? A. carboxylase B. dehydrogenase C. amylase 1 D. insulin Directions : Questions 6 to 8 refer to the following set-up. In the set-up, the bag is made of a semi-permeable membrane. 6. In the set-up, there is a net movement of water from A. X and Y to Z. B. X to Z and Z to Y. C. Z to X and Y to Z. D. Z to both Z and Y. 7. After a period of time, the salt concentration in Z is A. the same as X and Y. C. greater than both X and Y. B. greater than X and less than Y. D. greater than Y and less than X. 8. The salt concentrations in X, Y and Z are changed because (i) there is a net movement of salt particles from a higher concentration to a lower concentration, (ii) there is a net movement of water particles from a higher water potential to a lower water potential, (iii)there is a net movement of salt across the membrane by active transport. A. (i) and (ii) only B. (ii) and (iii) only C. (i) and (iii) only D. (i), (ii) and (iii) 9. Which one of the following graphs below shows the effect of pH on the reaction velocity (= rate of reaction) of a typical enzyme? Directions : Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following diagram which shows a chemical pathway when chemical W is changed into chemical Z through the actions of different enzymes: enzyme P W enzyme Q enzyme R X Y Z 10. An addition of a chemical M will result in no change in the concentration of W, an increase in the concentration of X and the concentrations of Y, Z become nearly zero. At the same time, if Y is added, the concentration of Z will increase. What can you deduce about M from the given information? A. M is an inhibitor of enzyme P. B. M is an enzyme that catalyses the formation of X. C. M is an inhibitor of enzyme Q. D. M reacts with Y. 2 11. Which of the following statements about the chemical pathway is CORRECT? A. Enzyme P can speed up the chemical reaction of X Y. B. Enzyme R can form an enzyme-substrate complex with Y. C. Enzyme Q can speed up the chemical reactions of X Y and Y W. D. Z can inhibit the catalytic function of enzyme P. Directions : Questions 12 and 13 refer to the diagram below which shows a chemical reaction, with and without an enzyme. 12. Which of the energy difference, A, B, C or D represents the activation energy of the reaction when the enzyme is NOT added? 13. Based on the diagram, what is the function of an enzyme in a chemical reaction? A. The enzyme increases the energy difference between the reactants and products. B. The enzyme provides an active site to bind with the reactants. C. The enzyme promotes the formation of the products. D. The enzyme reduces the activation energy of a chemical reaction. 14. Which of the following statement is TRUE for ALL enzymes? A. All enzymes are denatured at temperatures above 37℃. B. All enzymes speed up the reaction of the breaking down processes. C. All enzymes are made of protein. D. All enzymes have an optimum pH of 7. 15. In the graph below, curve X represents the relationship between an enzyme and the concentration of a substrate under optimal conditions and without an inhibitor. The same experiment is repeated in the presence of a fixed, low concentration of a competitive inhibitor. Which curve, A, B, C or D best represents the expected result? 3 Directions : Questions 16 – 20 refer to the following diagram shows the fluid mosaic model that describes the structure of the cell membrane: 16. W acts as A. a carrier on the cell membrane. C. a phospholipids molecule for diffusion. B. a recognition site for white blood cell. D. an antigen on the cell membrane. 17. What are the names of W, X, Y and Z? W A. glycoprotein B. protein C. protein D. glycoprotein X protein glycoprotein protein protein Y glycoprotein phospholipid glycoprotein phospholipids Z phospholipid glycoprotein phospholipids glycoprotein 18. What are the functions of X and Y? X A. To act as an enzyme on the membrane Y To carry out active transport B. To act as an enzyme on the membrane C. To act as a channel protein for transport D. To act as a channel protein for transport To act as a receptor for binding with hormones To act as a receptor for binding with hormones To carry out active transport 19. Why is the cell membrane considered as “semi-permeable”? (i) the bilayer made by Z allows the passage of fat-soluble substances but not most water-soluble substances, (ii) the carrier allows the passage of specific substances, but not all substances, (iii) the transmembrane protein allows the passage of certain ions and water soluble substances. A. (i) and (ii) only B. (i) and (iii) only C. (ii) and (iii) only D. (i), (ii) and (iii) 20. Why is the structure of the cell membrane called fluid mosaic model? It is because (i) molecules Z forms the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane, (ii) molecules W and X embed and float on the phospholipid bilayer, (iii) molecules W, X, Y and Z can move laterally with each other. A. (i) and (ii) only B. (i) and (iii) only C. (ii) and (iii) only 4 D. (i), (ii) and (iii) (B) Answer the following questions. (35 marks) 1. The following diagram shows 5 chemical molecules, A, B, C, D and E in a breaking down reaction. (a) Using letter(s) in the diagram, state which chemical molecule(s) is / are (i) the substrate(s), (ii) the product(s), (iii)the enzyme (s) of the reaction. (3 marks) (b) Using letter(s) in the diagram, write the breaking down reaction. (1 mark) (c) It is known that enzyme is specific in action. Explain, with reference to the structure of the enzyme, how does the specific action arise? (2 marks) (d) If the reaction mixture has been put in pH = 7 and temperature 40℃ where the pH and temperature are the optimum conditions of the enzyme, suggest TWO more ways by which the rate of enzymatic reaction can be further increased. (2 marks) (e) Draw a chemical molecule, F, that can be a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme in the reaction. Explain how the competitive inhibitor reduces the rate of an enzymatic reaction. (4 marks) 2. The diagram below shows two funnels, A and B which are put in a trough of distilled water. (a) In A, the liquid level rises and then it stops rising, maintains at the same height. Explain the observation. (4 marks) (b) If concentrated sucrose solution is also put inside the funnel in B, describe and explain what you can see in B. (3 marks) 5 3. Ordinary washing powder does not remove egg stains from clothes easily. These stains, however, can be removed by biological washing powder. Below is some information given on a packet of biological washing powder: Ingredients: Protease 0.2% Detergent 15% Directions: Soak clothes in a solution of washing powder for several hours before washing. Use warm water for best results. Do not use water at temperatures above 60℃. Cautions: Do not use with silk and wool. Rinse your hands well after contact with this product. (a) Explain why the biological washing powder can remove egg stains from clothes more easily. (3 marks) (b) Why is it necessary to soak the clothes in a solution of this washing powder for several hours before washing? (1 mark) (c) Suggest ONE way to shorten the soaking time. Explain your answer. (2 marks) (d) Why is it not advisable to use this washing powder with water at temperature above 60℃? (1 mark) (e) Suggest why this washing powder should not be used with silk and wool. (1 mark) 4. Potato cylinders were cut from fresh potatoes into equal lengths. Several cylinders were weighed and then put into a series of sucrose solutions at different concentrations for 24 hours and then the cylinders were re-weighed again. The results are tabulated as follows: Concentration of sucrose solution (mol dm-3) 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 Average change in weight of potato cylinders (%) +6.50 +1.60 -1.20 -5.80 -11.30 (a) By means of a graph, determine the initial water potential of the potato cylinders. (5 marks) (b) Describe and explain the changes in the weight of the potato cylinders after putting the potato cylinders in 0.10 mol dm-3 (3 marks) 6 South Tuen Mun Government Secondary School Biology Quiz 2 Marking Scheme (A) Choose the best answer. (20 marks) 1. C 2. A 3. D 4. B 6. B 7. A 8. A 9. B 11.B 12. D 13. D 14. C 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. D 5. D 10. C 15. A 20. C (B) Answer the following questions. (35 marks) * spelling must be correct 1. (a) (i) D (1) (ii) A, E (1) (b) D A + E (1) (iii) C (1) (c) The enzyme / C has an active site that has a complementary shape with the substrate / D (1). Only the substrate(s) that can fit into the active site, can carry out the enzymatic reaction (1). (d) Increase the concentration of A / E / A + E / substrate(s) (1); increase the concentration of the enzyme / C (1) (e) Any molecule with the same shape as D (1) [deduct ½ mark if title is not given] Diagram of competitive inhibitor F The competitive inhibitor has a similar shape as the substrate (or F has a similar shape as D) (1), thus it competes with the substrate / D for the active site (1), when it binds at the active site, the substrate(s) cannot bind with it (1), thus the rate of reaction is reduced. 2. (a) Distilled water has a higher water potential than the concentrated sucrose solution (1), there is a net movement of water into A / the funnel by osmosis (1). Thus the liquid level rises. When the liquid level is high, it produces a hydrostatic pressure (1) to prevent the further entry of water (1) [accept : to make the water inside and outside equal]. Thus the liquid level cannot rise further. (b) The liquid level drops (1) because the boiled swim bladder is freely permeable (1), the solution moves out due to the hydrostatic pressure (1). 3. (a) The washing powder contains protease (1) that catalyses the breakdown of egg stains (1) into soluble substances that can be washed away by water easily (1) [accept : breakdown of protein (1) into amino acids that is soluble in water (1)] (b) It is because the action of enzyme / protease takes time (1) (c) To increase the amount of washing powder / increase the concentration of protease OR to soak clothes at the optimum temperature / optimum pH (1), with a higher concentration of protease / optimum temperature / optimum pH, the rate of enzymatic / protease reaction is faster (1). (d) At above 60℃, most enzymes / protease is denatured (1). (e) silk and wool are made of protein that can be broken down by protease (1). 7 4. (a) Title : The effect of [accept : The relationship between] concentration of sucrose solution on the average change in weight of potato cylinders (1) Correct choice of axis (½) Label of axis : X axis – concentration of sucrose solution (mol dm-3) (1) Y axis – average change in weight of potato cylinders (%) (1) Correct plotting of points and joining of points (½) The effect of concentration of sucrose solution on the average change in weight of potato cylinders 8 Av er ag e ch an g e in weig h t o f p o tato cy lin d er s ( %) 6 4 2 0 -2 0 .1 0 .1 5 0 .2 0 .2 5 0 .3 -4 -6 -8 -10 -12 -14 C o n cen tr atio n o f su cr o se so lu tio n ( mo l d m - 3 ) The initial water potential of the potato cylinder = water potential of sucrose solution of 0.175 (+/- 0.005) mol dm-3 (1) (b) At 0.10 mol dm-3, the weight of the potato cylinder increases (1) because the sucrose solution has a higher water potential than the potato cells (1), there is a net movement of water into the potato cylinder by osmosis (1). 8