PELTON TURBINE
advertisement

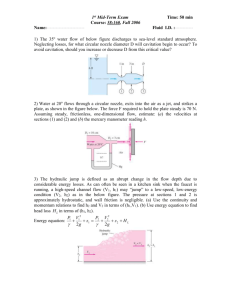
VIGNAN UNIVERSITY::VADLAMUDI Expt No: Date: PELTON TURBINE AIM: To determine the characteristic curve of pelton wheel under a constant head and constant speed. DESCRIPTION: Pelton Turbine is an impulse turbine, which is used to utilize high heads for generation of electricity. All the available head is converted into velocity energy by-means of spear and nozzle arrangement. The water leaves the nozzle in jet formation. The jet of water then strikes the buckets of the pelton wheel runner. The buckets are in the shape of double semi ellipsoidal cups, joined at the middle portion. The jet strikes the knife-edge of the buckets with least resistance and shock. Then the jet glides along the path of the cup, and the jet is deflected through more than 1600 to 1700. While passing along the buckets, the velocity of the water is reduced and hence an impulsive force is supplied to the cups which in turn are moved and hence the shaft is rotated. The specific speed of the pelton wheel changes from 10 to 100. The pelton wheel is supplied with water under high pressure by a centrifugal pump. The water is conveyed through venturimeter to the pelton wheel. The venturimeter with manometer connection is used to determine the discharge of water in the pipe. The nozzle opening can be decreased by operating the spear wheel at the entrance side of turbine. The spear can be positioned in 5 places i.e. 1/5, 2/5, 3/5, 4/5, 5/5 of nozzle opening. The turbine can be loaded by applying loads on the break drum. The load at the entrance can be read by the pressure gauge. The speed of the turbine can be measured with tachometer. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS: 1. TURBINE 1. Rated supply head 2. Discharge 3. Unit Speed 4. Specific speed 5. Runner outside Dia. 6. No. of pelton cups 7. Break drum diameter -50 m -660 1pm -1500 rpm -10 to 35 -300 mm -20 Nos -300 mm 16 VIGNAN UNIVERSITY::VADLAMUDI II. SUPPLY PUMP 1. Rated head - 2. Discharge -750 1pm 3. Normal Speed -2880 rpm 4. Power required -15 Hp 5. Size -3” x 21/2” 6. Type III. - High speed monoblock Centrifugal. FLOW MEASURING UNIT 1. Size of venturimeter -65 mm 2. Area ratio -0.6 3. Throat diameter -3.9 mm 4. Pressure gauge -7kg / cm2 PROCEDURE: (for constant head) 1. Prime the pump with water and start the pump. 2. Gradually open the delivery valve of the pump 3. Adjust the nozzle at 1/5 of the opening by operating the needle valve (spear) by the hand wheel. 4. The head should be made constant by operating the delivery valve and the head should be maintained at a constant value. 5. Observe the speed of the wheel using the tachometer. 6. Observe the reading h1 and h2 corresponding to the fluid level in the two manometer limbs, which is connected to the venturimeter. 7. Adjust the load on the brake drum to vary the speed of the drum and record the readings from the tachometer, weight added and spring balance. 8. Repeat step 7 for getting at least six sets of reading 9. Repeat the experiment for 2 3 4 , , and full opening of the nozzle. 5 5 5 17 VIGNAN UNIVERSITY::VADLAMUDI Experimental procedure (constant speed method) 1. Close the delivery valve of the pump. 2. Prime the pump with water and start the motor 3. Gradually open the delivery valve of the pump and adjust the nozzle at 1 of the 5 opening. 4. Read the pressure gauge and note down the value 5. Apply the load on the brake drum so that the speed shown by the tachometer comes to the rated speed and note this rated speed. Note down the tension T1 and T2 indicated by the spring balances attached to the brake drum. 6. Observe and note the readings of the manometer limbs 7. Manipulate the discharge through pressure valve and control the speed at the rated value through hanger weights and note the reading of the spring balance. 8. Observe and note down the manometer reading h1 & h2. 2 3 4 , , and full opening of the nozzle. 5 5 5 9. Repeat the experiment for CALCULATIONS: s Head of water h = hm m 1 = 12.6 hm =____________________ s In manometer across venturimeter Discharge of water = Q = K h m3 / sec. Where K = Constant of venturimeter = a1 a 2 a12 a 22 2 g = _____________________ Where a1 = Area of cross section at the point of entry a2 = Area of cross section at the constriction and in this case d2 /d1 = 0.6 and d1 = 0.065 m hm = Pressure head in meters = (h1 – h2) meters= _____________ Sm = Specific gravity of mercury=__________ 18 VIGNAN UNIVERSITY::VADLAMUDI S BP = = Specific gravity of fluid flowing (ie) water=__________________ 2NT 60,000 KW T = (W1 – W2)R=_______________________ R = radius of Brake drum =_________________ Where R N W1 W2 IP = = = = = gQH 1000 m rpm Kg kg KW = Where H = total water head in m of Ginkgf / cm 2 10 4 water = =______________ water Where G is pressure gauge reading. Ns = specific speed = Nu = unit speed Pu = unit power = N P =_________________ H 5/ 4 N Qu = unit discharge =Qu = Efficiency, =____________________ H p = =__________________ H 3/ 2 Q H =_________________ = BP / IP X100 = ______________ % GRAPHS : 1. Speed Vs efficiency 2. Speed Vs BHP 3.Speed Vs Discharge 19