Homework 1
advertisement

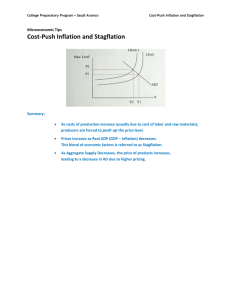
Midterm Exam 1 Economics 503 Foundations of Economic Analysis Session 5 Multiple Choice ( ½ point each) 1. Which of the following phrases means everything else held constant? A) Caveat emptor B) Post hoc, proctor hoc C) Ceteris paribus D) Carpe diem ________C__________ 2. If a excess demand suddenly appears at the current market price, which of the following could NOT be a possible cause? A) Supply has decreased suddenly and the market has not yet reached a new equilibrium. B) Demand has increased suddenly and the market has not yet reached a new equilibrium. C) Supply has increased suddenly and the market has not yet reached a new equilibrium. D) All could be possible causes ________C__________ 3. If a German firm produces cars in the United States, that production should count towards A) U.S. GDP. B) German GDP. C) U.S. GNP. D) It will not affect either U.S. GNP or U.S. GDP. ________A__________ 4. The largest component of spending in GDP is A) investment spending. B) net export spending. C) government spending. D) consumption spending. ________D__________ 5. Stagflation occurs when A) inflation falls and GDP falls. B) inflation rises and GDP falls. C) inflation falls and GDP rises. D) inflation rises and GDP rises. _______B___________ Calculation 6. (1 point) The elasticity of demand is 1 and the elasticity of supply is 1. The demand curve shifts out by 1%. What is the % change in prices? 1 1 a .01 .005 , .5% bd 11 7. (3 points) Your university is concerned about inflation in textbooks. Taking a survey in 2009, you find the average student purchases 2 accounting texts and 3 finance texts. The following table describes average prices for the two books. 2008 2009 Accounting Textbook 90 100 Finance Textbook 100 140 Market Basket CPI Inflation a. 77.42 470 77.42 620 100.00 29.17% Using 2009 as a base year, calculate the CPI of textbooks for 2008 through 2009. 100.00 b. Calculate the inflation rate for 2009. 29.17% 8. (2 points) Logs cut from forests in the Canadian province of British Columbia can only be sold to lumber mills in British Columbia. There are three charts which describe 1) the supply of tons of raw B.C. timber at different per ton price levels; 2) the demand for B.C. timber from lumber mills in B.C.; 3) the demand for B.C. timber from lumber mills in Japan. Price 25 20 15 10 5 Supply of B.C. Lumber 800 700 600 500 400 Demand for B.C. Timber in B.C. 200 400 600 800 1000 Demand for B.C. Timber in Japan 100 300 500 700 900 a. Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity if logs can only be sold in B.C. P = 15, Q = 600 b. Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity if logs can also be exported to Japan. P = 20 Q = 700 9. (3 points) The GDP per worker in the economy is fixed at 1000. There are two million people in the economy half of whom would like to be employed. You believe that when the labor markets in the economy are in good working order, the unemployment rate will be 5%. Current labor market surveys show that there are 70,000 people who are unemployed. a. Calculate the GDP in the economy. GDP = 930,000*1000 = 930 million b. Calculate the potential output in the economy defined as the amount of output that we would have if the labor markets were in good working order. If unemployment rate were 5%, 950,000 people would work and GDP = 950,000,000 c. Calculate the output gap. (930-950)/950 = -2/95 = -.021 10. (3 points) The Japanese economy is hit by an earthquake which destroys substantial amount of the energy infrastructure of Japan. This means that the energy companies cannot provide as much electricity and will need to replace substantial quantities of capital equipment. Using the AS-AD model, demonstrate the effect that this would have in the short-run assuming the economy started at the level of potential output. AS’ P AS 2 1 AD AD’ Y