Northouse Chart Final - Urban Leadership Program, 2009 Cohort
advertisement
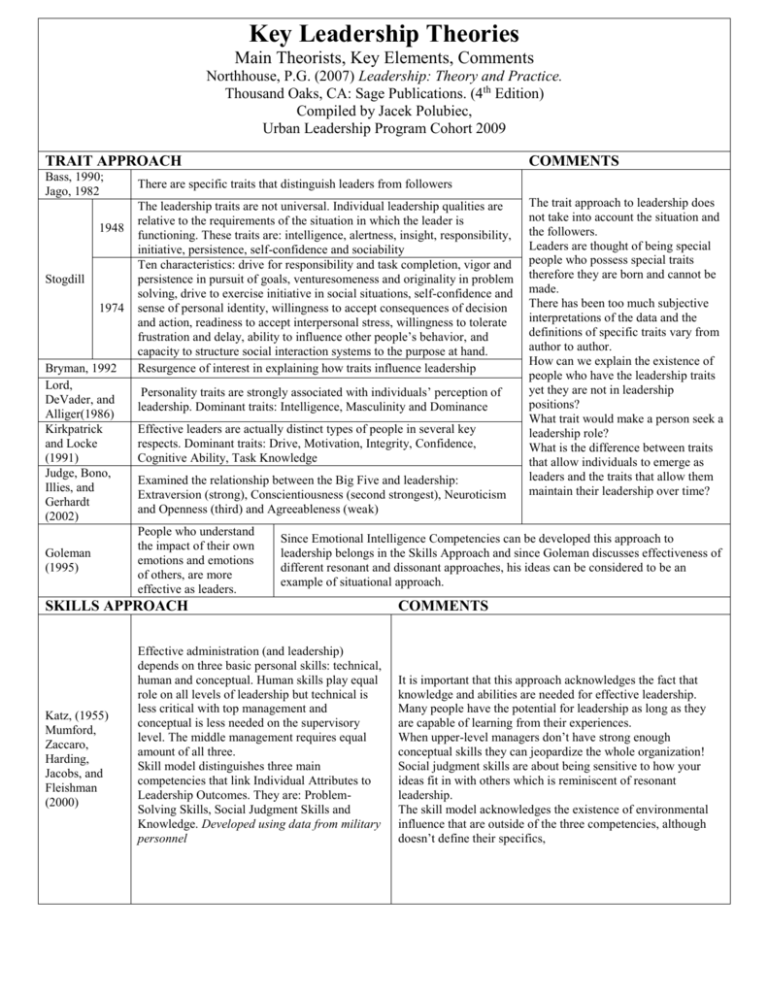
Key Leadership Theories Main Theorists, Key Elements, Comments Northhouse, P.G. (2007) Leadership: Theory and Practice. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. (4th Edition) Compiled by Jacek Polubiec, Urban Leadership Program Cohort 2009 TRAIT APPROACH Bass, 1990; Jago, 1982 1948 Stogdill 1974 Bryman, 1992 Lord, DeVader, and Alliger(1986) Kirkpatrick and Locke (1991) Judge, Bono, Illies, and Gerhardt (2002) Goleman (1995) COMMENTS There are specific traits that distinguish leaders from followers The leadership traits are not universal. Individual leadership qualities are relative to the requirements of the situation in which the leader is functioning. These traits are: intelligence, alertness, insight, responsibility, initiative, persistence, self-confidence and sociability Ten characteristics: drive for responsibility and task completion, vigor and persistence in pursuit of goals, venturesomeness and originality in problem solving, drive to exercise initiative in social situations, self-confidence and sense of personal identity, willingness to accept consequences of decision and action, readiness to accept interpersonal stress, willingness to tolerate frustration and delay, ability to influence other people’s behavior, and capacity to structure social interaction systems to the purpose at hand. Resurgence of interest in explaining how traits influence leadership Personality traits are strongly associated with individuals’ perception of leadership. Dominant traits: Intelligence, Masculinity and Dominance Effective leaders are actually distinct types of people in several key respects. Dominant traits: Drive, Motivation, Integrity, Confidence, Cognitive Ability, Task Knowledge Examined the relationship between the Big Five and leadership: Extraversion (strong), Conscientiousness (second strongest), Neuroticism and Openness (third) and Agreeableness (weak) People who understand the impact of their own emotions and emotions of others, are more effective as leaders. Since Emotional Intelligence Competencies can be developed this approach to leadership belongs in the Skills Approach and since Goleman discusses effectiveness of different resonant and dissonant approaches, his ideas can be considered to be an example of situational approach. SKILLS APPROACH Katz, (1955) Mumford, Zaccaro, Harding, Jacobs, and Fleishman (2000) The trait approach to leadership does not take into account the situation and the followers. Leaders are thought of being special people who possess special traits therefore they are born and cannot be made. There has been too much subjective interpretations of the data and the definitions of specific traits vary from author to author. How can we explain the existence of people who have the leadership traits yet they are not in leadership positions? What trait would make a person seek a leadership role? What is the difference between traits that allow individuals to emerge as leaders and the traits that allow them maintain their leadership over time? Effective administration (and leadership) depends on three basic personal skills: technical, human and conceptual. Human skills play equal role on all levels of leadership but technical is less critical with top management and conceptual is less needed on the supervisory level. The middle management requires equal amount of all three. Skill model distinguishes three main competencies that link Individual Attributes to Leadership Outcomes. They are: ProblemSolving Skills, Social Judgment Skills and Knowledge. Developed using data from military personnel COMMENTS It is important that this approach acknowledges the fact that knowledge and abilities are needed for effective leadership. Many people have the potential for leadership as long as they are capable of learning from their experiences. When upper-level managers don’t have strong enough conceptual skills they can jeopardize the whole organization! Social judgment skills are about being sensitive to how your ideas fit in with others which is reminiscent of resonant leadership. The skill model acknowledges the existence of environmental influence that are outside of the three competencies, although doesn’t define their specifics, STYLE APPROACH Ohio State Studies Based on Stogdill (1948) University of Michigan Studies Carthright & Zander 1960; Katz & Kahn, 1951; Likert, 1961, 1964 Blake and Mouton (1964, 1978, and 1985) COMMENTS Emphasis on two types of leader behavior: task behavior and relationship behavior and how combination of these two kinds of behaviors influences subordinates in their efforts to reach a goal. Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire LBDQ-XII The core findings: Leaders provide structure for subordinates and they nurture them Two types of leadership behaviors: employee orientation (personal needs) and production orientation (technical aspect) and they are not on the opposite sides of the spectrum. Leadership Grid: leaders help organizations meet their goals through concern for production and concern for people. Five major leadership styles: AuthorityCompliance (task 9, people 1), Country Club Management (1,9) , Impoverished (1,1), Middle-of-the-Road Management (5,5) Team Management (9,9) ! Benevolent Dictator (1,9 or 9,1 but does not integrate the two) Opportunismusing combination of all styles for personal advancement. SITUATIONAL APPROACH Hersey and Blanchard (1969) based on Reddin’s (1967) 3-D Management Style Theory COMMENTS Different situations demand different kinds of leadership. Leadership has two dimensions: directive and supportive. Leader needs to match his style to the competence and commitment of the subordinates. Leadership styles are: directive style (high directive-low supportive), coaching style (high directive-high supportive), supporting style (high supportive-low directive), delegating style (low supportive-low directive). First leader needs to address the nature of the situation and adopt one of the styles. How can leader supervising several employees and several different situations decide what style to apply? How does the dynamic a group of subordinates impact the leader’s decision? CONTINGENCY THEORY Fiedler (1964, 1967) Fiedler & Garcia (1987) Fiedler & Chemers (1974) COMMENTS Matching leaders to appropriate situations. Leaders effectiveness depends on how well leader’s style fits the context. Leadership styles are either task motivated or relationship motivated. Situation can be categorized using three factors: leadermember relations (confidence, loyalty or attraction towards leader), task structure (how clearly are requirements of the task spelled out) and position power (the amount of authority to reward and punish does the leader have). Leader whose style does not match particular situation experiences stress and anxiety which results in reverting to less mature ways of dealing with situation which leads to poor decision making and negative work outcomes Requires objectivity in assessing the situation in order to assure that there is a match between the leader and situation. If there is no match, serious consequences can follow. PATH-GOAL THEORY Evans (1970), House (1971), Michell (1974) Graen, (1976) Graen & UhlBin, 1995) COMMENTS Subordinates will be motivated if they think they are capable of performing their work. Leadership style must meet subordinates’ motivational needs by choosing behaviors that complement of supplement what is missing in the work setting. Leaders define goals, clarify paths, remove obstacles and provides support. Characteristics of the subordinates’ needs determine to what degree behavior of a leader causes satisfaction. These characteristics are: need for affiliation, preference for structure, desires for control, and self-perceived level of task ability. Leaders need to choose a leadership style that fits the needs of subordinates and the work they are doing LEADER-MEMBER EXCHANGE THEORY-LMX Theory Leadership is a process which is centered on the interaction between leaders and followers. Subordinates and part of ingroup and out-group. Subordinates must be interested in taking on new and different job responsibilities to be in the in-group. Leadership making develops in three phases: stranger, acquaintance and mature partnership. A person has a dominant style and a back-up style he/she reverts to under pressure when usual ways don’t work or don’t seem to work. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation is an important topic to study in depth. COMMENTS Research indicates that high-quality leader-member exchanges produces great result but are those different for the in-group and out-group? It is only fair if everyone can be considered for being in the in-group. What about the bias? TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP Burns’ Leadership (1978) Bryman, (1992) Bass and Riggio, (2006) Lowe and Gardner (2001) Bass (1985) COMMENTS Transformational Leadership is a process that transforms people and it is concerned with emotions, values, ethics, standards, long-term goals and includes assessing followers’ motives, satisfies their needs and treating them as human beings. It moves followers to accomplish more than what is usually expected. Transformational Leaders seeks to change company’s values by promoting justice and fairness. It often incorporates charismatic and visionary leadership. Leaders and followers are inextricably bound together. Transformational Leadership Factors: Idealized Influence (followers identify with and emulate the leader) Inspirational Motivation, Intellectual Stimulation (stimulating creativity and challenging their values, supports followers as they try to think things out and engage in problem solving), Individualized Consideration (supply supportive environment and listen to the needs of individuals). One of the first theories that specified these varieties of leadership: directive, supportive, participative and achievement oriented. TEAM LEADERSHIP Porter and Beyerlin McGrath COMMENTS Groups are composed of members who are interdependent, share common goals and must coordinate their activities. Effective leadership processes are the most critical factor in success of organizational teams. Shared and distributed leadership is a team leadership capacity. Leadership decisions that must be made: Should I monitor or take action? Should I intervene to meet the task or relational needs? Should I intervene internally or externally? PSYCHODYNAMIC APPROACH Berens (2001) Maccoby (1981) Zaleznik (1977) Based of Freud and Jung Probably the most effective type of leadership best suited for contemporary progressive organizations. Can’t other types of leadership be used to assure success of organizational teams? COMMENTS Several different ways of looking at leadership with the underlining concept of personality: consistent pattern of thinking, feeling and acting with regard to people and environment. Several questionnaires can be used to characterize the personality of a person. Certain personality types are better suited for particular leadership situations but there is no need to match it to the personality types of subordinates. Personality characteristics are ingrained and difficult to change so the key is to accept them and accept the fact that subordinates have them too. To what degree does this approach encourage leaders and followers to reflect on their personalities and where they are coming from when dealing with people and situations? GENDER AND LEADERSHIP COMMENTS Dobbins & Platz (1986) Engen, Leeden & Willemsen (2001) Powell (1990) Building relationships is often considered as one of the most important aspects of leading a school so wouldn’t “typical” (democratic and transformational) leader women be better leaders? Gender has little or no relationship to leadership style and effectiveness although women’s styles tend to be more democratic and more transformational. Women are devalued when they lead in masculine manner (autocratic or directive). Women face the glass ceiling but the disparity is slowly eroding. CULTURE AND LEADERSHIP House and Javidan (2004) Hofstede (2001) Globalization has created interdependence between nations and created a need to understand how cultural differences affect leadership performance. Related concepts: ethnocentrism (can prevent respecting others), prejudice which we all have to certain degree. Leader needs to negotiate with followers from different cultural backgrounds. There are 9 cultural dimensions and each has high and lowscore clusters. Each cluster has a leadership profile which is most effective with this cluster. There are universally positive and negative leader attributes. COMMENTS Choosing school leaders is often driven by ethnocentrism but it should be driven by leadership profile. LEADERSHIP ETHICS Plato, Aristotle, W.K. Kellogg Foundation, Dr. Lee 9/12/09 5 Principles: respect, service, justice, honesty and community. Theories fall within two broad domains: conduct (what are their actions) and character (who they are as people). Conduct of a leader: consequences of actions and duty (rules) governing his/her actions. Teleological theories (focus on consequesnces): Ethical egoism, utilitarianism (greatest good for the greatest number) and altruism. Deontological theory (moral obligation to do the right thing). Three perspectives tied by the theme that leader-follower relationship is central to ethical leadership. Heifetz’s perspective-leaders use authority to help followers deal with conflicting values, Burnstransformational leaders should be involved in moving followers to higher standard of moral responsibility, Greenleaf-servant leadership where leaders attends to and empathizes with the concerns of followers. Principles of Ethical Leadership: Respects Others, Serves Others, Shows Justice, Manifests Honesty, Builds Community. COMMENTS Ethics must be taken into account any time people with different levels of power or influence are working together. It is important to have a common language for talking about leadership and educational leadership. Most leadership studies originated outside of the education. Qualifying paper: Late May this chart will be very useful for writing it. Meaningful long-term leadership is a process that takes place over time and not an act. One of the issues of being charismatic leader is that once you are gone there is nothing left. BLOG IDEA: Do leaders ever throw in a towel? Dissertation needs to be relevant, compelling.