Linear Motion Laboratory
advertisement

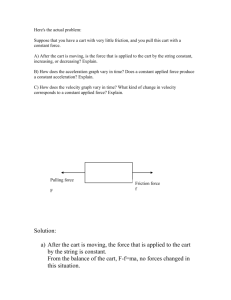
Graphical Analysis of Linear Motion State Standard: Motion and Forces 1. Newton’s laws predict the motion of most objects. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. how to solve problems involving constant speed and average speed. b. when forces are balanced no acceleration occurs, and thus an object continues to move at a constant speed or stays at rest and when there is an unbalanced force on an object it will accelerate (Newton's First Law). State Standard: Investigation and Experimentation 1. Scientific progress is made by asking meaningful questions and conducting careful investigations. As a basis for understanding this concept, and to address the content the other four strands, students should develop their own questions and perform investigations. Students will: a. select and use appropriate tools and technology (such as computer-linked probes, spread sheets, and graphing calculators) to perform tests, collect data, analyze relationships, and display data. b. identify and communicate sources of unavoidable experimental error. c. identify possible reasons for inconsistent results, such as sources of error or uncontrolled conditions. d. formulate explanations using logic and evidence. Knowledge Targets Acquire vocabulary and learn relationships of variables expressed in the equations for linear motion. Know how to present data using significant figures and tolerances. Reasoning Targets Use knowledge of linear motion to solve word problems. Understand the relationships of time, displacement, velocity and acceleration through graphs. Justify how an object is moving through the interpretation of experimental data. Skill Targets Collect experimental data within the tolerance of the measuring instruments. Graph and tabulate experimental data. Product Targets Make graphs of experimental data graphing the dependent variable on the y axis and the independent variable on the x axis. Use knowledge, reasoning, and skills to create a formal laboratory report that includes the following sections: Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Experimental, Results and Conclusion. Task: Through out life you observe objects in motion relative to you. Motion is seldom constant. Objects speed up and slow down which is a change in velocity. Velocity has two components, one for direction and one for its size or magnitude. A change in either its direction or magnitude would represent acceleration. It requires a force to accelerate an object. When an object is pushed or pulled the velocity it has will change. You will analyze the motion of a laboratory cart through graphical analysis. The data will be graphed in two ways. The first will be distance traveled versus time and the other will be velocity versus time. These graphs represent two different views of the same data and motion. These graph will allow you to see what the cart is doing as it rolls across the counter. Background Information: The recording timer is used to measure small intervals of time. The motion of a dynamics cart accelerating across a laboratory table can be analyzed using the recording tape from a timer. A timer uses a regularly vibrating clapper and carbon disk to make dots on a recording tape. The dots are made at regular intervals so the distance between the dots can be used to determine the distance traveled and the velocity of the cart at any time during the motion. It is essential to determine the time for one interval of the timer for the velocity to be calculated. The timer can be calibrated using a digital strobe. A flashing strobe can be adjusted to coincide with the vibration of the timer and thus the recording timer will appear to remain still. The reading on the strobe can then be used to determine the time period for one vibration or the time it takes the timer to move through one cycle. A cycle records a dot on the timer tape or the time it take for the timer to move up from the previous dot and then move back down to place a second dot on the recording tape. Once the timer is calibrated or the time for one cycle has been determined it can be used to measure time intervals for the travel of a dynamics cart. The record of the distance and time taken to move that distance can be recorded using the timer and a tape which is pulled through the timer by the dynamics cart. This permanent record of dots shows how far the cart travels and the calibration of time per cycle shows the time it takes to move the distance between the dots. The average speed of a cart can be determined at a mid point of many periods. The set of data for time, total distance traveled, and average speed or velocity at each successive distance can be graphed to analyze the motion of the cart. In the distance versus time graph the instantaneous velocity of the cart can be determined using the slope or tangent of the curve at a point. tangent distance time On the speed or velocity versus time graph the velocity can be determined at any point directly off the graph and the acceleration can be found from the slope or tangent to the curve. a tangent to the curve is acceleration velocity or speed time A method to determining the tangent and thus the slope of the curve is by using a flat mirror. The mirror is placed along side the curve so there is continuity between the curve and the mirror. This continuity must be smooth and then a line along the base of the mirror represents the tangent to the curve at that point. Apparatus: recording timer, timing tape, digital strobe, cart, ruler, 200 gram mass, pulley, mirror. Data Collection: The recording timer can be calibrated using the strobe. Turn on the timer and then adjust the strobe in a darken room until the timer appears to stop. Once the two are synchronized the value on the strobe can be noted. The timer will appear to stop when the strobe flashes every third time it vibrates, every second, every time or other multiples. It is important to find a one to one correspondence between the number of flashes and the number of cycles or vibrations. To do this continue to raise the rate at which the strobe flashes until the timer appears to stop again. Record the higher value from the strobe. Continue this process until the timer no longer stops. The final or largest number of flashes per minute recorded is the value you should use for calibration since there should be a one to one correspondence for this value. The other values should be half, a third, a fourth or other fractions of the highest value. Repeat this procedure six time and then take the average for a more precise value of time. Record the top six values. These are flashes per minute and must be divided by 60 seconds in a minute to determine the number of flashes per second and finally the reciprocal of that value must be found to determine the seconds per period on the timer. After the timer is calibrated it may be used to measure distance and time for the motion of the dynamics cart. Attach a 200 gram mass to the cart using a string and arrange the mass over the side of the table placing the string into the pulley at the end of the table to reduce friction. Hold the cart in place with a book so that it does not accelerate while the rest of the apparatus is set up. Attach a timer tape to the bottom of the cart with tape. Thread the tape through the timer over the top of a carbon disk so that dots are tapped onto the tape as it is pulled through the timer. Make sure there is plenty of room between the pulley and the cart so that the mass will hit the floor before the cart hits to pulley. Start the timer and then release the cart. Catch the cart prior to it hitting the pulley. On the underside of the tape will be the dots corresponding to the motion of the cart. Tape 0 1 d1 2 Circle the first dot and number it zero. Count over successive ten dots and circle each. Number each successive circled dot with the next higher integer. Now count back three spaces and forward three spaces from the circle dots to measure the distance, d1, over six intervals surrounding the numbered dots. Record the distance for the first dot as zero as the dot represents that the cart was at rest. Next, record the distance for the six intervals surrounding each numbered dot in the table. Determine the time for six intervals by multiplying the time per period, determined with the strobe, by six. Divide each of the distances by the time for the six periods to determine the average velocity over that distance. This is the instantaneous velocity or speed at each numbered point. Record that speed or velocity in the table next to the distance interval. Make note that this distance is used to determine the average speed or velocity and will not be used in the graph. Now the total distance or d2 traveled will be determined for each successive numbered dot. The distance from zero to each dot must be measured and recorded since this is the total distance traveled to reach each of the velocities at the numbered points. The distance d2 is used in the graph of distance versus time. To determine the total time interval to reach each successive numbered dot it is necessary to multiple the time per period by the total number of periods recorded from zero to that dot. For dot number 1 the total time to reach that point is 10 periods times the time per period. For dot number 2 the total time is 20 times the time per period and for 3 it is 30 times the time per period. Record the time values in the table next to the corresponding distance to the dot. Data Analysis: Create two graphs: one with the distance traveled to the numbered points versus the total time required to reach each successive numbered point and the other velocity at each point versus the time required to reach that point. The slope of the first graph is the velocity and the slope of the second graph is the acceleration. Describe the motion of the cart by analyzing the graphs. Determine the slope of the distance versus time graph for three points using the mirror and drawing a tangent at a point. Remember the slope of a line or the tangent is the change in y over the change in x. Record the x and y values for two points on each tangent line and determine the slope or velocity for three points. Record those values in a second table. On the velocity versus time graph find the velocity values you determined from the first graph and determine the acceleration of the cart at that time. To determine the acceleration of the cart look at the y axis of velocity and find the values corresponding to the points. Next move over to the graph at that point and draw the tangent at that point. Find the slope of the line at that point. This will be the acceleration. Record that value in the table next to the velocity. Questions: 1. What are the numbers of significant figures in the speed values? 2. What is the limiting factor for this number of significant figures? 3. Speed was determined using a six period interval. What determines the size of the interval used to find the speed?