PRODUCTS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONS
advertisement
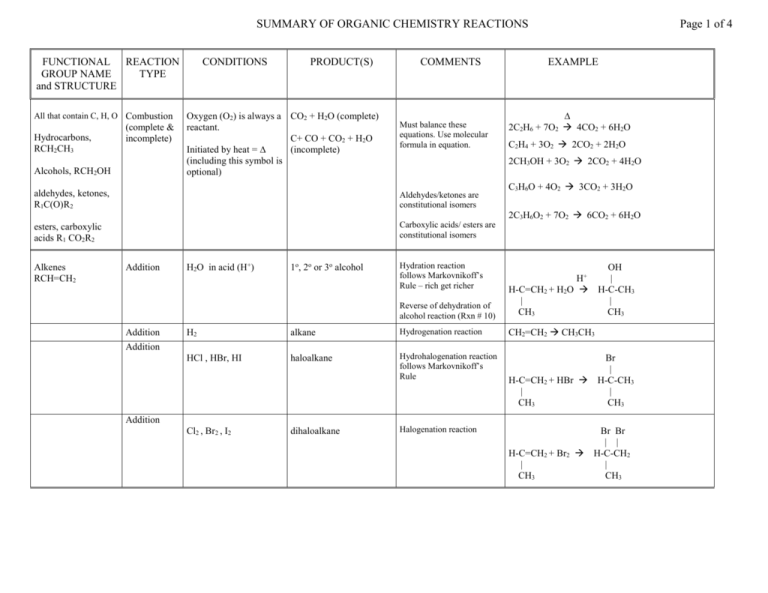
SUMMARY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONS FUNCTIONAL REACTION GROUP NAME TYPE and STRUCTURE All that contain C, H, O Combustion Hydrocarbons, RCH2CH3 (complete & incomplete) Alcohols, RCH2OH CONDITIONS PRODUCT(S) Oxygen (O2) is always a CO2 + H2O (complete) reactant. C+ CO + CO2 + H2O Initiated by heat = ∆ (incomplete) (including this symbol is optional) COMMENTS Must balance these equations. Use molecular formula in equation. Aldehydes/ketones are constitutional isomers esters, carboxylic acids R1 CO2R2 Carboxylic acids/ esters are constitutional isomers Addition Addition H2O in acid (H+) 1o, 2o or 3o alcohol EXAMPLE ∆ 2C2H6 + 7O2 4CO2 + 6H2O C2H4 + 3O2 2CO2 + 2H2O 2CH3OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 4H2O aldehydes, ketones, R1C(O)R2 Alkenes RCH=CH2 Page 1 of 4 Hydration reaction follows Markovnikoff’s Rule – rich get richer C3H6O + 4O2 3CO2 + 3H2O 2C3H6O2 + 7O2 6CO2 + 6H2O OH | H-C-CH3 | CH3 Reverse of dehydration of alcohol reaction (Rxn # 10) H+ H-C=CH2 + H2O | CH3 CH2=CH2 CH3CH3 H2 alkane Hydrogenation reaction HCl , HBr, HI haloalkane Hydrohalogenation reaction follows Markovnikoff’s Rule Addition H-C=CH2 + HBr | CH3 Br | H-C-CH3 | CH3 Addition Cl2 , Br2 , I2 dihaloalkane Halogenation reaction H-C=CH2 + Br2 | CH3 Br Br | | H-C-CH2 | CH3 SUMMARY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONS (continued) FUNCTIONAL GROUP NAME and STRUCTURE Alcohols – 1o RCH2OH REACTION TYPE Elimination , dehydration – CONDITIONS PRODUCT(S) COMMENTS Page 2 of 4 EXAMPLE Acid catalyzed (H+) with Most substituted alkene heat. Saytseff’s rule – poor get poorer (this C atom is bonded to only 2Hs – the others are bonded to 3) OH | H+ CH3-CH2-C-CH3 CH3-CH=C-CH3 + H2O | | CH3 CH3 Base catalyzed (OH-) with heat if asymmetric can form several products (cis and trans as well) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2(Br) loss of H2O 2o RCHOHCH3 3o RC(CH3)2OH Haloalkanes Elimination alkene and alcohol alcohol Substitution reacting with binary acid haloalkane and water (e.g. HCl, HI, HF) base that releases OHalcohol UV catalyzed a number of isomers haloalkane alkane substitution substitution benzene substitution different catalysts possible Oxidation [O] conditions. Some oxidizing agents = 1o give aldehydes first, CrO3 , H2CrO4 , K2Cr2O7 then carboxylic acids a halobenzene ethene and others ethanol + HF fluoroethane + H2O number of products depends on amount of halogen present same as above 1-chloropropane + OH propan-1-ol see textbook, page 103 for example see textbook, page 103 for an example alcohol OH O O | [O] || [O] || CH3-CH2 CH3-CH CH3-COH Reverse of reduction of aldehyde or ketone reaction 2o give ketones OH | [O] CH3-C-CH3 NR | CH3 3o No Reaction aldehyde or ketone reduction alkene reduction [H] reducing conditions eg. LiAlH4 or H2 OH O | [O] || CH3-CH2-CH-CH3 CH3-CH2-C-CH3 alcohol reverse of oxidation pentanal + [H] pentan-1-ol alkane also know as hydrogenation or saturation ethane + [H] ethane SUMMARY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONS (continued) FUNCTIONAL GROUP NAME and STRUCTURE REACTION TYPE CONDITIONS PRODUCT(S) Condensation Reaction of any ester (esterification) carboxylic acid with any alcohol , catalyzed by acid and heated Condensation- Acid + amine + heat. amide product Reaction with 1o gives a 2o amide. Reaction with 2o amine gives 3o amide COMMENTS Catalyzed by acid. Anhydride + alcohol gives ester product without acid catalysis Same reaction as amide formation reaction already described in amines Reaction with 3o amine does not give amide, only neutralization product. Ester R1-C=O | OR2 Hydrolysis Ester + acid or base + heat Reverse of esterification reaction Acid catalysiscarboxylic acid + alcohol Base catalysis carboxylate ion + alcohol Reverse of ester forming reaction Page 3 of 4 EXAMPLE O O || H+ || CH3OH + CH3-COH CH3-COCH3 + H2O O O O O || || || || H-C-O-C-H + CH3-OH H-COH + CH3-O-C-H ester O O || ∆ || CH3NH2 + CH3-COH CH3-CNHCH3 + H2O O O || ∆ || (CH3)3N + CH3-COH CH3-CO- + (CH3)3NH+ not an amide+ O O || H+ || CH3-COCH3 + H2O CH3OH + CH3-COH O O || OH|| CH3-COCH3 CH3OH + CH3-CO- SUMMARY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONS (continued) FUNCTIONAL GROUP NAME and STRUCTURE REACTION TYPE Condensation – amide formation CONDITIONS PRODUCT(S) COMMENTS O O || ∆ || CH3NH2 + CH3-COH CH3-CNHCH3 + H2O Reaction with 2o amine gives 3o amide (rxn not shown) O O || ∆ || (CH3)3N + CH3-COH CH3-CO- + (CH3)3NH+ not an amide+ Reaction with 3o amine does not give amide, only neutralization products. Hydrolysis Acid or base catalzyed Acid catalysis carboxylic acid + ammonium ion Base catalysis carboxylate ion + amine EXAMPLE O O || ∆ || NH3 + CH3-COH CH3-CNH2 + H2O Reaction with carboxylic Ammonia + carboxylic acid acid Requires heat. gives primary amide Otherwise only neutralization occurs Reaction with 1o amine gives a 2o amide. Amides R-C=O | NH2 Page 4 of 4 Reverse of amide forming reaction (Rxn # 18 and 2124 above) O || CH3-CNHCH3 H+ O || CH3-COH + CH3NH4+ O || CH3-CNHCH3 O OH|| CH3-CO- + CH3NH2