Human Anatomy & Physiology - The Muscular System Quiz PLEASE
advertisement

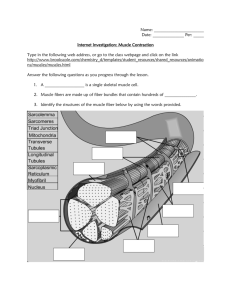
Human Anatomy & Physiology - The Muscular System Quiz PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ SHEET Matching: Match the terms below with the statements that follow. A) Cardiac B) Skeletal C) smooth D) Cardiac & Smooth E) Cardiac & Skeletal 1. Muscle tissue that is involuntary. 2. Located in the walls of the digestive tract. 3. Attached to bones. 4. Found in the walls of the heart. 5. Muscle tissue that is voluntary. 6. Branching chains of cells, uninucleate; striations; intercalated discs. 7. Single cells, spindle-shaped, uninucleate, no striations. 8. Single cells, very long, cylindrical, multinucleated, very obvious striations. 9. Muscle contraction would be slow and sustained. 10. Muscle contraction would be at a fairly steady rate. 11. Muscle contraction can be rapid and with great force, but tires easily and must rest after short periods of activity. 12. 13. 14. Multiple Guess: Choose the best answer; fill in the corresponding letter on the answer sheet. 15. Skeletal muscle cells contain many A) nuclei B) mitochondria C) A & B are correct D) neither A or B are correct 16. Which of the following is NOT a function of the muscular system: A) hematopoiesis B) producing movement C) generating heat D) maintaining posture E) stabilizing joints 17. A fibrous, flattened, sheet-like tendon is known as: A) fascia B) aponeurosis C) a tendon sheath D) a broad ligament 18. The connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle fibers is: A) perimysium B) epimysium C) endomysium D) elastin 19. The dark bands in skeletal muscle fibers that contribute to its striated appearance are known as: A) I bands B) Z bands C) H bands D) A bands 20. The sarcomere, the basic unit of skeletal muscle extends from: A) A band to A band B) M line to M line C) H band to H band D) Z line to Z line 21. The segment of a muscle fiber that contains actin and myosin is the: A) A band B) Z lines C) H zone D) sarcomere 22. An entire skeletal muscle is covered by a course sheath called: A) perimysium B) epimysium C) endomysium D) aponeurosis 23. The plasma membrane of a muscle cell is termed a: A) sarcoplasmic reticulum B) sarcomere C) intercalated disc D) sarcoplasm E) sarcolemma 24. Myofibrils are composed mostly of: A) tropomyosin B) actin and myosin C) myotomes D) ADP and ATP E) troponin 25. An elaborate network of membranes in skeletal muscle cells that function in calcium storage is the : A) sarcoplasmic reticulum B) myofibrillar network C) sarcolemma D) mitochondria E) intermediate filament network 26. Which of the following are composed of myosin: A) light bands B) thick filaments C) all myofilaments D) thin filaments E) Z lines 27. The correct order of arrangement of skeletal muscle cells, from largest to smallest, is: A) fiber, myofibril, myofilament B) myofibril, myofilament, fiber C) myofilament, myofibril, fiber D) fiber, myofilament, myofibril 28. When the cross bridge of the myosin molecule forms linkages with actin filaments, the result is: A) shortening of the muscle fiber B) creation of a high energy bond C) membrane polarization D) release of acetylcholine 29. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction says: A) Actin filaments become shorter when they combine with myosin. B) Myosin rotates and has actin wrap around it. C) Friction is reduced between thin and thick filaments causing thick to move, inside the thin. D) Myosin filaments slide between the actin, making the muscle shorter. E) A neurotransmitter alters the arrangement of collagen fibers in the endostium, causing it to shrink. 30. When a nerve impulse reaches the end of a motor neuron, A) the number of synaptic vesicles increase B) muscle fibers stretch C) calcium ions move out of the cytoplasm of the neuron D) acetylcholine is released 31. In order for a muscle contraction to occur: A) lactic acid must be present B) lysozyme must be present C) iron ions must be available D) a nerve impulse must stimulate the muscle fiber 32. Muscle fibers undergoing sustained, strenuous exercise depend upon: A) aerobic respiration B) increased metabolism of glucose C) anaerobic respiration D) increased blood supply 33. The energy source that is directly responsible for muscle fiber contraction is: A) lactic acid B) glycogen C) glucose D) ADP E) ATP 34. Oxygen debt secondary to strenuous exercise is due to: A) insufficient oxygen to promote conversion of lactic acid to pyruvic acid B) lack of available oxygen to convert ADP to ATP C) both A & B D) neither A or B 35. What is the specific neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle? A) dopamine B) epinephrine C) endomysium D) acetylcholine (Ach) Use the back of the Answer Sheet for questions 51- 64. Match the terms with the statements, darken the corresponding number on the answer sheet. 51. The distance between two Z lines 1. Z discs 52. Otherwise known as thick filaments 2. H zone 53. Contains only the actin filaments 3. sarcomere 54. Both actin and myosin are found in this band 4. actin filaments 55. The type of filament that is studded with myosin heads 5. I band 56. Tiny contractile unit that shortens during muscle contraction 6. myosin filament 57. Actin filaments are anchored to these disc like membranes 7. A band 58. Lighter central portion of the A band Match the terms below with the statements that follow; darken the corresponding number on the answer sheet. 8. acetylcholine 10. aerobic respiration 12. calcium ions 14. potassium ions 9. enzymes 11. sodium ions 13. anaerobic respiration 15. creatine phosphate 59. Serves as the actual “go” signal for muscle contraction 60. Neurotransmitter substance released at motor end plates by the motor neuron 61. Normally stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum 62. A metabolic pathway that produces water, carbon dioxide, and ATP, and provides for a large amount of ATP per glucose because oxygen is used 63. A reserve, high energy compound used to convert ADP to ATP by the transfer of a high-energy phosphate group 64. Destroys acetylcholine Place the following events in their proper sequence: Place the number on the line on the answer sheet. 66. The muscle cell contracts. 67. Action potential propagates along the sarcolemma and down the T Tubules. 68. Acetylcholine binds to receptor sites on the motor end plate. 69. Motor end plate becomes depolarized. 70. Action potential is initiated on the sarcolemma. 71. Calcium ions enter the axon terminal. 72. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft. 73. Synaptic vesicles fuse to membrane of axon terminal. 74. Calcium ions are released from the terminal cisternae. 75. Action potential arrives at the axon terminal. Name _____________________________________________ #__________ Period _________ Human Anatomy & Physiology Quiz – The Muscular System (Ch. 6) Use the diagrams to indentify the structures, place the terms on the lines provided. Slide 1 - Connective Tissue Wrappings of Skeletal Muscle 1._________________________________ 5._________________________________ 2._________________________________ 6._________________________________ 3._________________________________ 7._________________________________ 4._________________________________ 8._________________________________ Slide 2 - Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle 1._________________________________ 4._________________________________ 2._________________________________ 5._________________________________ 3._________________________________ Slide 3 - Myofibril or fibril 1._________________________________ 6._________________________________ 2._________________________________ 7._________________________________ 3._________________________________ 8._________________________________ 4._________________________________ 9._________________________________ 5._________________________________ 10.________________________________ Slide 4 - Sarcomere 1._________________________________ 4._________________________________ 2._________________________________ 5._________________________________ 3._________________________________ Slide 5 - Myofilament structure. 1._________________________________ 3._________________________________ 2._________________________________ Slide 6 - Neuromuscular Junction 1._________________________________ 6._________________________________ 2._________________________________ 7._________________________________ 3._________________________________ 8._________________________________ 4._________________________________ 9._________________________________ 5._________________________________