Chapter 8 Summary
advertisement

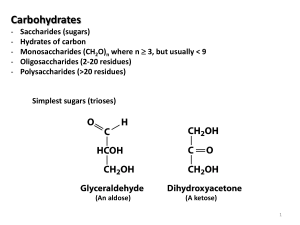
Chapter 8 1) Know functional roles of carbohydrates 2) Know carbohydrate classifications. 3) Know the differences between aldoses and ketoses. 4) Be able to identify chiral carbons in monsaccharides. 5) Be able to calculate the number of possible stereoisomers for a given monosaccharide. 6) Define enantiomer, epimer, diastereomer. 7) Understand how hemiacetal and hemiketal formation occurs and how this relates to sugar cyclization. 8) Be able to draw Fischer and Haworth projections of D-glucose, D-galactose, Dfructose, D-ribose and D-ribulose. Be able to identify the anomeric carbon. Be able to write and recognize the differences between alpha- and beta- forms. Know the difference between furanoses and pyranoses. 9) Be familiar with chair and boat conformations of pyranose sugars. 10) Know what makes a reducing sugar a reducing sugar. 11) Be able to recognize derivatives of monosaccharides. 12) Know how glycosidic linkages form. 13) Be able to identify anomeric carbon in oligo/polysaccharides. 14) Know how to distinguish reducing oligosaccharide from none reducing oligosaccharide. 15) Know the basic properties (monomers involved, linkage description, branching linkages, functions, structural geometry, biological role) of starch (amylose and amylopectin), glycogen, chitin. 16) Glycoproteins. N-linked and O-linked. Know the amino acid residues involved in these types of glycosylations. Know the biological role of N-linked and O-linked glycoproteins.