Practice Exam for Chapter 14 on Firms in Competitive Markets
advertisement

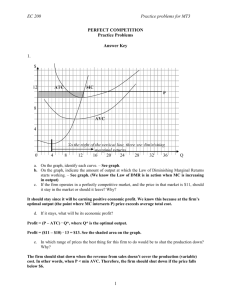
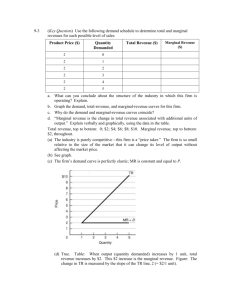
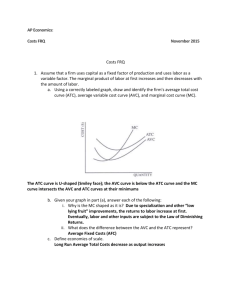
Practice Exam for Chapter 14 on Firms in Competitive Markets MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive 1) _______ market? A) Each firm is a price taker. B) The products sold by the firms in the market are homogeneous. C) There are many buyers and sellers in the market. D) It is difficult for a firm to enter or leave the market. 2) Perfect competition is characterized by A) high barriers to entry. B) differentiated products of firms in the industry. C) a small number of firms. D) many buyers and sellers. 2) _______ 3) Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive industry? A) There is free entry and exit in the long run. B) Economic profits must be positive in the short run. C) Each firm produces the same homogeneous product. D) The industry demand curve is downward sloping. 3) _______ 4) Being a price taker essentially means A) a firm cannot influence the market price. B) the firm cannot legally set its price above the market price. C) a firm can influence the market price. D) the firm cannot legally set its price below the market price. 4) _______ 5) All firms in a perfect competition industry A) produce identical products. B) lose money. C) produce differentiated products. D) are price makers. 5) _______ 6) If a firm is perfectly competitive, then A) it can independently set the price of the product it sells without regard to what other firms in the market are doing. B) it is impossible for the firm to earn short-run economic profits. C) its marginal cost will exceed marginal revenue at the optimal level of output. D) its demand curve is perfectly elastic. 6) _______ 7) For a firm in perfect competition, its demand curve will be A) horizontal. B) downward sloping. C) upward sloping. D) vertical. 7) _______ 8) For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, average revenue equals A) average cost. B) the change in total revenue. C) price divided by quantity. D) the market price. 8) _______ 9) For a firm in perfect competition, which of the following is TRUE? A) AFC = ATC B) MR < P C) AVC = ATC D) MR = P 9) _______ 10) Economists generally assume that firms attempt to maximize A) marginal revenue. B) sales. C) total revenue. D) total economic profits. 10) ______ 11) Which is always true at a firm's profit-maximizing rate of production? A) Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost B) Marginal Revenue > Marginal Cost C) Total Revenue = Total Costs D) The total revenue curve lies below the total cost curve. 11) ______ 12) Refer to the above table. This firm operates in a perfectly competitive market in which the market price is $10 per unit. What is its profitmaximizing rate of production? A) 108 units B) 104 units C) 110 units D) 106 units 12) ______ 13) Refer to the above table. This firm operates in a perfectly competitive market in which the market price is $10/unit. What is true when the firm produces 103 units? A) Total costs exceed total revenue by $403. B) Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost. C) Total revenue equals $5,060. D) Its total profit is $524. 13) ______ 14) If price is $5, marginal cost is $5, average total cost is $3, and the quantity produced is 150 units, then the firm is A) not maximizing economic profit. B) earning $300 and maximizing economic profit. C) earning $150 and not maximizing economic profit. D) earning $2 and maximizing economic profit. 14) ______ 15) When a firm is earning zero economic profits, A) accounting profit is zero. B) P is greater than ATC. C) P = ATC. D) total revenue is greater than total cost. 15) ______ 16) According to the above figure, if the firm is earning zero economic profits, what quantity is the firm selling and at what price? A) Q = 1,000; P = $5 B) Q = 1,200; P = $7.00 C) Q = 200; P = $4 D) Q = 800; P = $4 16) ______ 17) Suppose a perfectly competitive firm faces the following short-run cost and revenue conditions: ATC = $6.00; AVC = $4.00; MC = $3.50; MR = $3.50. The firm should A) remain at the same position. B) increase price. C) shut down. D) increase output. 17) ______ 18) A firm should never produce any output if A) AR < ATC. B) P < ATC. C) P < AVC. D) MR < MC. 18) ______ 19) Suppose that at the current level of output, price = $10, MC = $4, AVC = 7, and ATC = $11. Which of the following is true? A) The firm should maintain the current level of output. B) The firm should decrease output. C) The firm should increase output. D) The firm should shut down. 19) ______ 20) In the above figure, assume d1 is the relevant demand curve for this 20) ______ firm. Which is true? A) This firm is earning an economic profit. B) This firm is experiencing an economic loss. C) This firm's total costs equal EJA0. D) This firm is breaking even. 21) In the above figure, assume this firm is operating on d3. Which is true? A) B) C) D) This firm is breaking even. This firm is experiencing an economic loss. This firm's total revenues equal HRD0. This firm is earning an economic profit. 22) In the above figure, what happens to the firm's optimal level of output if the price it receives for its product increases from P2 to P3? A) B) C) D) 21) ______ Output decreases. Output stays the same. Output increases. There is not enough information provided to know what happens to output. 22) ______ 23) In the above figure, if the firm is facing demand curve d 2, then to maximize profits it will produce at output level A) B. B) A. C) C. 23) ______ D) D. 24) For a perfectly competitive firm, when MC is less than MR, A) the producer has an incentive to decrease output. B) the producer has an incentive to expand output. C) economic profits must be positive. D) the producer has no incentive to change production. 24) ______ 25) Suppose a perfectly competitive firm faces the following short-run cost and revenue conditions: ATC = $12.00; AVC = $8.00; MC = $12.00; MR = $10.00. The firm should A) change nothing. B) increase price. C) decrease output. D) increase output. 25) ______ 26) Which of the following could generate economic profits for perfectly competitive firms in the short run, if they initially earn zero economic profits? A) A unit tax on output B) A decrease in input prices C) A fall in demand D) An increase in total fixed costs 26) ______ 27) The perfectly competitive seller's short-run supply curve is A) its entire marginal cost curve. B) the part of its marginal cost curve above the average variable cost curve. C) its marginal revenue curve. D) its average fixed cost curve. 27) ______ 28) In the above figure, assuming Firm 1 and Firm 2 are the sole producers in the industry, the industry quantity supplied at price P1 is equal to A) Q4 - Q2. B) Q1 + Q3. C) Q1 + Q2. 28) ______ D) Q2 + Q4. 29) A perfectly competitive industry's short-run supply curve is best described as A) horizontal. B) the horizontal summation of the individual firms' supply curves. C) perfectly inelastic. D) the upward-sloping portion of the industry's marginal cost curve. 29) ______ 30) A perfectly competitive industry's market or "going" price is established by A) the largest firm in the industry. B) the forces of supply and demand. C) each individual producing firm and reflects that firm's costs. D) the largest purchaser of this industry's output. 30) ______ 31) In a perfectly competitive market, positive economic profits act to A) signal resource owners elsewhere not to invest their capital in this industry. B) attract new entrants into the industry. C) drive potential competitors away from the industry. D) prevent reinvestment on the part of firms within the industry. 31) ______ 32) Which of the following is true in perfect competition at long-run equilibrium? A) economic profit is $0 B) ATC is minimized C) P = ATC = MC = MR D) all of the above 32) ______ 33) For a firm in a perfectly competitive industry, A) both short-run and long-run economic profits may be negative. B) short-run economic profits must be zero. C) short-run economic profits may be positive, but long-run economic profits must be zero. D) short-run and long-run economic profits must be zero. 33) ______ 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) 21) 22) 23) 24) 25) 26) 27) 28) 29) 30) 31) 32) 33) D D B A A D A D D D A D D B C A C C C B A C A B C B B D B B B D C