geometry pacing guide updated _2009
advertisement

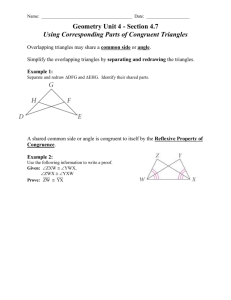
Year-at-a-Glance MUHSD Geometry Pacing Guide Dates st 1 Quarter 10 days 15 days 15 days 5 days McDougal Littell Units Unit 1: Essentials of Geometry Unit 2: Reasoning & Proof Unit 3: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines Unit 4: Congruent Triangles Standards 1, 8, 10, 12 1, 2, 3 7 4, 5, 12, 13, 16 Quarter 1 Benchmark 2nd Quarter 5 days 10 days 10 days 10 days Unit 4: Congruent Triangles (Continued) Unit 5: Relationships within Triangles Unit 6: Similarity Unit 7: Right Triangles & Trigonometry 4, 5, 12, 13, 16 2, 6, 12, 15, 17 4, 5, 7, 8, 11, 12 4, 12, 14, 15, 18, 19, 20 Semester 1 Final 3rd Quarter 10 days 15 days 10 days Unit 8: Quadrilaterals Unit 10: Properties of Circles Unit 11: Measuring Length & Area 7, 12 7, 17, 21 8, 10, 11 Quarter 3 Benchmark 4th Quarter 15 days 5 days 5 days Unit 12: Surface Area & Volume of Solids Unit 9: Properties of Transformations Unit 13: Constructions 8, 9, 11 5, 22 16 Semester 2 Final * Preparation for Geometry Standard 1 of 6 Updated 7/29/2008 MUHSD Geometry Pacing Guide: 2008-2009 / 1st Quarter Dates Essential Standard Cluster McDougal Littell Sections 1.0 – Students demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning. 10 days 8.0 – Students know, derive, and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume, lateral area, and surface area of common geometric shapes. Standard Resources Unit 1: ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY 1.1 - Identify points, lines and planes. 1.2 – Use segments and congruence 1.3* – Use midpoint and distance formulas 1.4 – Measure and classify angles 1.5 – Describe angle pair relationships 1.6* – Classify polygons 1.7 – Find perimeter, circumference, and area 1.0 1.0 Prepare for 17.0 1.0 12.0 Prepare for 13.0 8.0, 10.0 Unit 2: REASONING AND PROOF 2.1 – Use inductive reasoning 2.2 - Analyze conditional statements 2.3 - Apply deductive reasoning 2.4 – Use postulates and diagrams 2.5* – Reason using properties of algebra 2.6 – Prove statements about segments and Angles 2.7 – Prove angle pair relationships 1.0, 3.0 3.0 1.0, 3.0 1.0 1.0, 3.0 1.0, 2.0 1.0, 2.0, Prepare for 13.0 Unit 3: PARALLEL & PERPENDICULAR LINES 3.1 – Identify pairs of lines and angles 3.2 – Use parallel lines and transversals 3.3 – Prove lines are parallel 3.4 *– Find and use slopes of lines 3.5 *– Write and graph equations of lines 3.6 - Prove theorems about perpendicular lines 16.0, Prepare for 7.0 7.0 2.0, 7.0 Prepare for 17.0 Prepare for 17.0 7.0 10.0 – Students compute areas of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, equilateral triangles, rhombi, parallelograms, and trapezoids. 12.0 – Students find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems. 1.0 – Students demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning. 15 days 2.0 – Students write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 3.0 – Students construct and judge the validity of a logical argument and give counterexamples to disprove a statement. 2.0 – Students write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 15 days 7.0 – Students prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal, the properties of quadrilaterals, and the properties of circles. QUARTER 1 BENCHMARK * Preparation for Geometry Standard 2 of 6 Updated 7/29/2008 MUHSD Geometry Pacing Guide: 2008-2009 / 2nd Quarter Dates Essential Standard Cluster 4.0 – Students prove basic theorems involving congruence and similarity. 5.0 – Students prove that triangles are congruent or similar, and they are able to use the concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles. 12.0 – Students find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems. 2.0 – Students write geometric proofs, including proofs by contradiction. 6.0 – Students know and are able to use the triangle inequality theorem. 12.0 – Students find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures and solve problems. McDougal Littell Sections Standard Resources Unit 4: CONGRUENT TRIANGLES 4.1 – Apply triangle sum properties 4.2 – Apply congruence and triangles 4.3 – Prove triangles congruent by SSS 4.4 – Prove triangles congruent by SAS & HL 4.5 – Prove triangles congruent by ASA & AAS 4.6 – Use congruent triangles 4.7 – Use isosceles and equilateral triangles 4.8 – Perform congruence transformations (Moved to Ch. 9) 12.0, 13.0 5.0 5.0, 16.0 4.0, 5.0 4.0, 5.0 5.0, 16.0 5.0, 12.0 22.0 Unit 5: RELATIONSHIPS WITHIN TRIANGLES 5.1 – Midsegment theorem and coordinate proof 5.2 – Use perpendicular bisectors 5.3 – Use angle bisectors of triangles 5.4 – Use medians and altitudes 5.5 – Use inequalities in a triangle 5.6 – Inequalities in 2 triangles & indirect proofs 17.0 12.0 12.0, 15.0 17.0, Prepare for 12.0 6.0, 12.0 2.0 17.0 – Students prove theorems by using coordinate geometry, including the midpoint of a line segment, the distance formula, and various forms of equations of lines and circles. * Preparation for Geometry Standard 3 of 6 Updated 7/29/2008 4.0 – Students prove basic theorems involving congruence & similarity. 5.0 – Students prove that triangles are congruent or similar, and they are able to use the concept of corresponding parts of congruent triangles. 12.0 – Students find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures 4.0 – Students prove basic theorems involving congruence & similarity. 14.0 – Students prove the Pythagorean Theorem. 15.0 – Students use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine distance and find missing lengths of sides of right triangles. 18.0 – Students know the definitions of the basic trigonometric functions defined by the angles of a right triangle. They also know and are able to use elementary relationships between them. Unit 6: SIMILARITY 6.1 – Ratios, proportions, and the geometric mean 6.2 – Use proportions to solve geometry problems 6.3 – Use similar polygons 6.4 – Prove triangles similar by AA 6.5 – Prove triangles similar by SSS and SAS 6.6 – Use proportionality theorems 6.7 – Perform similarity transformations (Moved to Ch. 9) Unit 7: RIGHT TRIANGLES & TRIGONOMETRY Prepare for 8.0 12.0 5.0, 8.0, 11.0 5.0, 12.0 4.0, 5.0 4.0, 7.0 5.0, 11.0 7.1 – Applying the Pythagorean theorem 7.2 – Use the converse of the Pythagorean theorem 7.3 – Use similar right triangles 7.4 – Special right triangles 7.5 – Apply the tangent ratio 7.6 – Apply the sine & cosine ratios 7.7 – Solve right triangles 14.0, 15.0 12.0 4.0, 12.0 20.0 18.0, 19.0, 20.0 18.0, 19.0, 20.0 12.0, 19.0 19.0 – Students use trigonometric functions to solve for an unknown length of a side of a right triangle, given an angle and a length of a side. 20.0 – Students know and are able to use angle and side relationships in problems with special right triangles, such as 30-60-90 and 45-45-90 triangles. 16.0 – Students perform basic constructions with a straight edge and compass, such as angle bisectors, perpendicular bisectors, and the line parallel to a given line through a point off the line. FINAL REVIEW * Preparation for Geometry Standard CONSTRUCTIONS 1st Semester FINAL EXAM 4 of 6 Updated 7/29/2008 MUHSD Geometry Pacing Guide: 2008-2009 / 3rd Quarter Dates Essential Standard Cluster McDougal Littell Sections 7.0 – Students prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal, the properties of quadrilaterals, and the properties of circles. 12.0 – Students find and use measures of sides and of interior and exterior angles of triangles and polygons to classify figures 7.0 - Students prove and use theorems involving the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal, the properties of quadrilaterals, and the properties of circles. 17.0 – Students prove theorems by using coordinate geometry, including the midpoint of a line segment, the distance formula, and various forms of equations of lines and circles. 21.0 – Students prove and solve problems regarding relationships among chords, secants, tangents, inscribed angles, and inscribed and circumscribed polygons of circles. 8.0 – Students know, derive and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume, lateral area, and surface area of common geometric figures. 10.0 – Students compute areas of polygons, including rectangles, scalene triangles, equilateral triangles, rhombi, parallelograms, and trapezoids. 11.0 – Students determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric figures and solids. Standard Resources Unit 8: QUADRILATERALS 8.1 – Find angle measures in polygons 8.2 – Use properties of parallelograms 8.3 – Show that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram 8.4 – Properties of rhombus, rectangle, square 8.5 – Use properties of trapezoids & kites 8.6 – Identify special quadrilaterals Unit 10: PROPERTIES OF CIRCLES 12.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 12.0 10.1 – Use properties of tangents 10.2 – Find arc measures 10.3 – Apply properties of circles 10.4 – Use inscribed angles of polygons 10.5 – Apply other angle relationships in circles 10.6 – Find segment lengths in circles 10.7 – Write and graph equations of circles 7.0, 21.0 7.0 7.0, 21.0 7.0, 21.0 7.0, 21.0 21.0 17.0 Unit 11: MEASURING LENGTH & AREA 11.1 - Areas of triangles and parallelograms 11.2 - Areas of trapezoids, rhombi, and kites 11.3 – Perimeter and area of similar figures 11.4 – Circumference and arc length 11.5 – Areas of circles and sectors 11.6 – Areas of regular polygons 11.7 – Use geometric probability 8.0, 10.0 8.0, 10.0 8.0, 11.0 8.0 8.0 8.0, 10.0 8.0 QUARTER 3 BENCHMARK * Preparation for Geometry Standard 5 of 6 Updated 7/29/2008 MUHSD Geometry Pacing Guide: 2008-2009 / 4th Quarter Dates Essential Standard Cluster McDougal Littell Sections Standard Resources Unit 12: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME 8.0 - Students know, derive and solve problems involving the perimeter, circumference, area, volume, lateral area, and surface area of common geometric figures. 9.0 – Students compute the volumes and surface areas of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres; and students commit to memory the formulas for prisms, pyramids, and cylinders. 12.1 – Explore solids 12.2 – Surface area of prisms & cylinders 12.3 – Surface area of pyramids & cones 12.4 – Volume of prisms & cylinders 12.5 – Volume of pyramids & cones 12.6 – Surface Area & Volume of spheres 12.7 – Explore similar solids 9.0 8.0, 9.0 8.0, 9.0 8.0, 9.0 8.0, 9.0 8.0, 9.0 8.0, 11.0 11.0 – Students determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric figures and solids. 22.0 – Students know the effects of rigid motions on figures in the coordinate plane and space, including rotations, translations, and reflections. 16.0 – Students perform basic constructions with a straight edge and compass, such as angle bisectors, perpendicular bisectors, and the line parallel to a given line through a point off the line. FINAL REVIEW * Preparation for Geometry Standard Unit 9: PROPERTIES OF TRANSFORMATIONS 9.1 – Translate figures and use vectors 9.2* – Use properties of matrices 9.3 – Perform reflections 9.4 – Perform rotations 9.5 – Apply compositions of transformations 9.6 – Identify symmetry 9.7 – Identify and perform dilations 4.8 – Perform congruence transformations 6.7 – Perform similarity transformations CONSTRUCTIONS 22.0 Prepare for 22.0 22.0 22.0 22.0 22.0 22.0 22.0 5.0, 22.0 16.0 2nd Semester FINAL EXAM 6 of 6 Updated 7/29/2008