Summary of Accounting Basics
advertisement

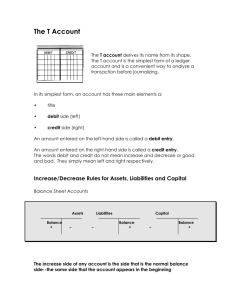
SUMMARY OF ACCOUNTING BASICS Classification of Accounts Account Title Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Accumulated Depreciation Accumulated Depletion Advertising Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Amortization Expense Appropriation for __________ Account Classification Current liability Current asset Plant asset Plant asset Operating expense Current asset Operating expense Stockholders’ equity Normal Balance Credit Debit Credit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Bonds Payable Building Capital Stock Cash Cash Dividends Cash Dividends payable Common Stock Cost of Merchandise (Goods) Sold Deferred Income Tax Long-term liability Plant asset Stockholders’ equity Current asset Stockholders’ equity Current liability Stockholders’ equity Cost of merchandise (goods sold) Current liability/Longterm liability Operating expense Long-term liability Other expense Other income Stockholders’ equity Stockholders’ equity Current liability Credit Debit Credit Debit Debit Credit Credit Debit Financial Statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Income statement Balance sheet Income statement Retained earnings statement/ Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Retained earnings statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Income statement Credit Balance sheet Debit Debit Debit Credit Debit Credit Credit Income statement Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Retained earnings statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Plant asset Other income Other expense Deferred credit Deferred debit Current liability Current liability Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit Credit Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Balance sheet (interim) Balance sheet (interim Balance sheet Balance sheet Current liability Current asset Other income Extraordinary item Other income Intangible asset Income tax Current liability Operating expense Other expense Other income Current asset Investment Investment Investment Plant asset Other expense Extraordinary item Other expense Current asset Credit Debit Credit Credit Credit Debit Debit Credit Debit Debit Credit Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Debit Balance sheet Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Income statement Balance sheet Income statement Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Income statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Income statement Balance sheet Depletion Expense Discount on Bonds Payable Discounts Lost Dividend Income Dividends Donated Capital Employees Federal Income Tax Payable Equipment Exchange Gain Exchange Loss Factory Overhead (Overapplied) Factory Overhead (Underapplied) Federal Income Tax Payable Federal Unemployment Tax Payable FICA Tax Payable Finished Goods Gain on Disposal of Plant Assets Gain on Redemption of Bonds Gain on Sale of Investments Goodwill Income Tax Income Tax Payable Insurance Expense Interest Expense Interest Income Interest Receivable Investment in Bonds Investment in Stocks Investment in Subsidiary Land Loss on Disposal of Plant Assets Loss on Redemption Bonds Loss on Sale of Investments Marketable Securities Account Title Materials Merchandise Inventory Notes Payable Notes Receivable Organization Costs Patents Paid-in Capital from Sale of Treasury Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par (Stated Value) Payroll Tax Expense Pension Expense Petty cash Premium on Bonds Payable Prepaid Insurance Prepaid Rent Preferred Stock Purchases Purchases Discounts Purchases Returns and Allowances Rent Expense Rent Income Retained Earnings Salaries Expense Salaries Payable Sales Sales Discounts Sales Returns and Allowances Sales Tax Payable Sinking Fund Cash Sinking Fund Investments State Unemployment Tax Payable Stock Dividends Stock Dividends Distributable Supplies Supplies Expense Transportation In Treasury Stock Uncollectible Accounts Expense Unearned Rent Utilities Expense Vacation Pay Expenses Vacation Pay Payable Work In Process Account Classification Current asset Current asset/Cost of merchandise sold Current liability/Longterm liability Current asset/Investment Intangible asset Intangible asset Stockholders’ equity Normal Balance Debit Debit Credit Financial Statement Balance sheet Balance sheet/Income statement Balance sheet Debit Debit Debit Credit Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Stockholders’ equity Credit Balance sheet Operating expense Operating expense Current asset Long-term liability Current asset Current asset Stockholders’ equity Cost of merchandise sold Cost of merchandise sold Cost of merchandise sold Operating expense Other income Stockholders’ equity Debit Debit Debit Credit Debit Debit Credit Debit Income statement Income statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Income statement Credit Income statement Credit Income statement Debit Credit Credit Operating expense Current liability Revenue from sales Revenue from sales Revenue from sales Current liability Investment Investment Current liability Stockholders’ equity Stockholders’ equity Current asset Operating expense Cost of merchandise sold Stockholders’ equity Operating expense Current liability Operating expense Operating expense Current liability/longterm liability Current asset Debit Credit Credit Debit Debit Credit Debit Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Debit Debit Income statement Income statement Balance sheet/Retained earnings statement Income statement Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Income statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Balance sheet Retained earnings statement Balance sheet Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Debit Debit Credit Debit Debit Credit Balance sheet Income statement Balance sheet Income statement Income statement Balance sheet Debit Balance sheet STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS A summary of the cash receipts and cash payments of a business entity for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year. The Basics 1. Accounting Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity 2. T Account: Account Title Left Side debit Right Side credit 3. Rules of Debit and Credit: Balance Sheet Accounts ASSETS LIABILITIES Asset Accounts Liability Accounts Debit Credit Debit Credit for for for for increases decreases decreases increases OWNER’S EQUITY Owner’s Equity Accounts Debit Credit for for decreases increases Income Statement Accounts Debit for Credit for decreases in owner’s equity increases in owner’s equity Expense Accounts Debit for increases Credit for decreases Revenue Accounts Debit for decreases Credit for increases Normal Balance 4. To Analyze a Transaction: 1. Determine whether an asset, a liability, owner’s equality, revenue, or expense account is affected by the transaction. 2. For each account affected by the transaction, determine whether the account increases or decreases. 3. Determine whether each increase or decrease should be recorded as a debit or a credit. 5. Financial Statements: INCOME STATEMENT A summary of the revenue and the expense of a business entity for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year. RETAINED EARNINGS STATEMENT A summary of the changes in the earnings retained in a business entity for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year. BALANCE SHEET A list of the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity of a business entity as of a specific date, usually at the close of the last day of a month or a year. 6. Accounting Cycle: 1. Analyze and record transactions in journal. 2. Post transactions to ledger. 3. Prepare trial balance, assemble adjustment data, and complete worksheet. 4. Prepare financial statements. 5. Journalize and post adjusting entries. 6. Journalize and post closing entries. 7. Prepare post-closing trial balance. 7. Types of Adjusting Entries: 1. Deferred expense (prepaid expense) 2. Deferred revenue (unearned revenue) 3. Accrued expense (accrued liability) 4. Accrued revenue (accrued asset) 5. Depreciation expense Each entry will always affect both a balance sheet and an income statement account. 8. Closing Entries: 1. Transfer revenue account balances to Income Summary. 2. Transfer expense account balances to Income Summary. 3. Transfer Income Summary balance to Retained Earnings. 4. Transfer dividends account balance to Retained Earnings. 9. Special Journals Rendering of services on account recorded in Revenue (sales) journal Receipt of cash from any source recorded in Cash receipts journal Purchasing of items on account recorded in Purchases journal Payments of cash for any purpose recorded in Cash payments journal 10. Shipping Terms Ownership (title) passes to buyer when merchandise is ……. Transportation costs are paid by: FOB Shipping Point FOB Destination delivered to freight carrier delivered to buyer buyer seller 16. Contribution Margin Ratio = Sales-Variable Costs Sales 11. Format for Bank Reconciliation: Cash balance according to bank statement…. Add: Additions by depositor not on bank statement……………………… Bank errors………………………………... $xxx 17. Break-Even Sales (Units) = $xx xx Deduct: Deductions by depositor not on bank statement……………………. Bank errors………………………………. Adjusted balance……………………………. $xx xx Cash balance according to depositor’s records.. Add: Additions by bank not recorded by depositor………………………………………. Depositor errors…………………………….. $xx xx Deduct: Deductions by bank not recorded by depositor…………………………. Depositor errors…………………………….. Adjusted balance……………………………… 12. 1. 2. 3. $xx xx xx $xxx 18. Sales (Units) = Fixed Costs + Target Profit Unit Contribution Margin xx $xxx 19. Margin of Safety = Sales-Sales at Break-Even Point Sales $xxx 20. Operating Leverage = Contribution Margin Operating Income xx $xxx 21. Variances Direct Materials=Actual Price per Unit- x Actual Quantity Price Variance Standard Price Used xx $xxx Inventory Costing Methods First-in, First-out (fifo) Last-in, First-out (lifo) Average Cost Direct Materials=Actual Quantity Used- x Standard Price Quantity Variance Standard Rate per unit Direct Labor = Actual Rate Per Hour – x Actual Hours Rate Variance Standard Rate Worked Direct Labor = Actual Hours Worked- x Standard Rate Time Variance Standard Hours per Hour 13. Interest Computations: Interest = Face Amount (or Principal) x Rate x Time Variable Factory Actual Budged Variable Overhead Controllable=Variable Factory Factory Variance Overhead Overhead for Actual Amount Produced 14. Methods of Determining Annual Depreciation: STRAIGHT-LINE: Cost-Estimated Residual Value Estimated Life DECLINING-BALANCE: Rate*xBook Value at Beginning of Period Fixed Factory 100% of Normal Std. Fixed Overhead Volume = Capacity-Std. Capacity x Factory Variance for Amount Produced Overhead Rate *Rate is commonly twice the straight-line rate (1 Estimated Life). 15. Cash Provided by Operations on Statement of Cash Flows (indirect method): Net income, per income statement……………. Add: Depreciation of plant assets…………….. Amortization of bond payable discount and intangible assets…………………… Decreases in current assets (receivables, inventories, prepaid expenses)………… Increases in current liabilities (accounts and notes payable, accrued liabilities)… Losses on disposal of assets and retirement of debt………………………………….. Deduct: Amortization of bond payable premium…………………………… Increases in current assets (receivables, inventories, prepaid expenses)……... Decreases in current liabilities (accounts and notes payable, accrued liabilities).. Gains on disposal of assets and retirement of debt…………………….. Net cash flow from operating activities……….. Fixed Costs_______ Unit Contribution Margin $xx 22. Rate of Return on = Controllable Operating Income Investment (ROI) Invested Assets Alternative ROI Computation: $xx ROI = Controllable Operating Income x Sales____ Sales Invested Assets xx xx xx xx xx $xx 24. Average Rate = Estimated Average Annual Income of Return Average Investment xx xx xx 23. Capital Investment Analysis Methods: 1. Methods that Ignore Present Values: A. Average Rate of Return Method B. Cash Payback Method 2. Methods That Use Present Values: A. Net Present Value Method B. Internal Rate of Return Method xx $xx 25. Present Value Index = Total Present Value of Net Cash Flow Amount to be invested 26. Present Value Factor = Amount to Be Invested___ for an Annuity of $1 Equal Annual Net Cash Flows