Sponge Anatomy: Label the Cross Section Worksheet
advertisement
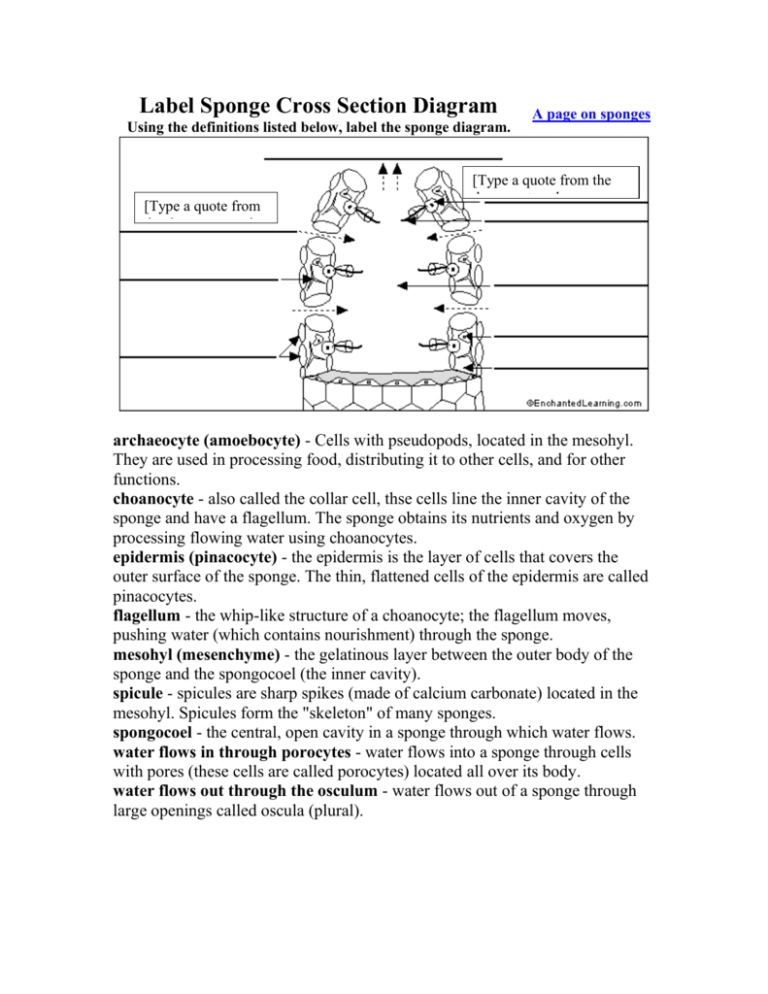
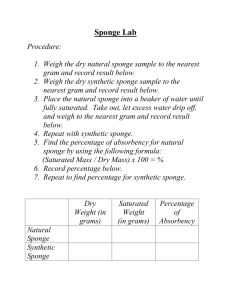
Label Sponge Cross Section Diagram Using the definitions listed below, label the sponge diagram. [Type a quote from the document or the summary of an interesting point. You can position the text box anywhere in the document. Use the Text Box Tools tab to change the formatting of the pull quote text box.] A page on sponges [Type a quote from the document or the summary of an interesting point. You can position the text box anywhere in the document. Use the Text Box Tools tab to change the formatting of the pull quote text box.] archaeocyte (amoebocyte) - Cells with pseudopods, located in the mesohyl. They are used in processing food, distributing it to other cells, and for other functions. choanocyte - also called the collar cell, thse cells line the inner cavity of the sponge and have a flagellum. The sponge obtains its nutrients and oxygen by processing flowing water using choanocytes. epidermis (pinacocyte) - the epidermis is the layer of cells that covers the outer surface of the sponge. The thin, flattened cells of the epidermis are called pinacocytes. flagellum - the whip-like structure of a choanocyte; the flagellum moves, pushing water (which contains nourishment) through the sponge. mesohyl (mesenchyme) - the gelatinous layer between the outer body of the sponge and the spongocoel (the inner cavity). spicule - spicules are sharp spikes (made of calcium carbonate) located in the mesohyl. Spicules form the "skeleton" of many sponges. spongocoel - the central, open cavity in a sponge through which water flows. water flows in through porocytes - water flows into a sponge through cells with pores (these cells are called porocytes) located all over its body. water flows out through the osculum - water flows out of a sponge through large openings called oscula (plural).