Biological Team
advertisement

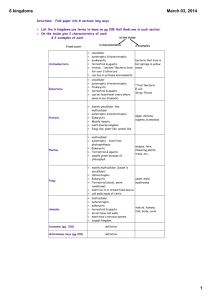
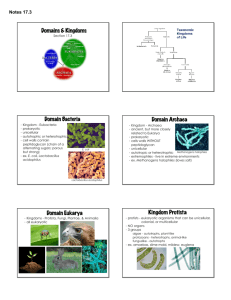
CLASSIFICATION NOTE BUDDY! Name: Per: Taxonomy Aristotle • first person to • classified living things as • grouped animals as – land dwellers – air dwellers – water dwellers • he groups plants into 3 groups based on their stems • his system was based on common names organisms or Why Doesn’t That System Work? • – for example: whales are classified with fish in the water and bats with birds in the air. Actually bats and whales are more closely related to each other as mammals • – for example: a dog in English is a chien in French, a cane in Italian and a perro in Spanish • – for example: jellyfish are not fish Linnaeus Linnaeus’ levels of classification K largest and most inclusive (there are 6 of them) P called division in plants Note: you need to memorize these 7 levels in order. Some people use memory aids like: C O F G S “King Philip Came Over For Great Soup.” smallest and most inclusive only one organism type/species (eg. dog) Binomial Nomenclature • • • • bi = nomial = nomen= cloture= • species name • • • • scientific name of an organism has two parts Writing the Name • • • • italicized (or underlined if hand written) genus is always species is always eg- Panthera leo is the scientific name of a lion Canis familiaris is the scientific name of a dog Canis lupus is the scientific name of a wolf (notice the close relationship between the dog and wolf-they are in the same Genus together) Six Kingdom System Important Vocabulary • • • • • • • • Prokaryotic – Eukaryotic – Autotrophic – Heterotrophic – Locomotion – Cell Wall – Multicellular – Unicellular – Archaebacteria are what cell type (prokaryotic / eukaryotic)? The number of cells in each (unicellular / multicellular)? Is the cell nucleus present or absent in Archaebacteria? Is the cell wall present or absent in Archaebacteria? How do Archaebacteria get nutrition (autotrophic / heterotrophic / both)? Do Archaebacteria have some form of locomotion? (present / absent)? Other information? Eubacteria are what cell type (prokaryotic / eukaryotic)? The number of cells in each (unicellular / multicellular)? Is the cell nucleus present or absent in Eubacteria? Is the cell wall present or absent in Eubacteria? How do Eubacteria get nutrition (autotrophic / heterotrophic / both)? Do Eubacteria have some form of locomotion? (present / absent)? Other information? Protista are what cell type (prokaryotic / eukaryotic)? The number of cells in each (unicellular / multicellular)? Is the cell nucleus present or absent in Protists? Is the cell wall present or absent in Protists? How do Protists get nutrition (autotrophic / heterotrophic / both)? Do Protists have some form of locomotion? (present / absent)? Other information? Fungi are what cell type (prokaryotic / eukaryotic)? The number of cells in each (unicellular / multicellular)? Is the cell nucleus present or absent in Fungi? Is the cell wall present or absent in Fungi? How do Fungi get nutrition (autotrophic / heterotrophic / both)? Do Fungi have some form of locomotion? (present / absent)? Other Information? Plantae are what cell type (prokaryotic / eukaryotic)? The number of cells in each (unicellular / multicellular)? Is the cell nucleus present or absent in Plants? Is the cell wall present or absent in Plants? How do Plants get nutrition (autotrophic / heterotrophic / both)? Do Plants have some form of locomotion? (present / absent)? Other Information? Animalia are what cell type (prokaryotic / eukaryotic)? The number of cells in each (unicellular / multicellular)? Is the cell nucleus present or absent in Animals? Is the cell wall present or absent in Animals? How do Animals get nutrition (autotrophic / heterotrophic / both)? Do Animals have some form of locomotion? (present / absent)? Other Information?