on account

Grade 11 Accounting Review
Chapter 1
Types of Business
Service business – does not make or sell a product as its main activity
Merchandising business – buys goods and resells them at a higher price
Manufacturing business – buys raw materials, converts them into a new product and sells that new product
Non-Profit Organization – carries on activities to meet social needs and not for financial profit
Types of Business Ownership
Sole Proprietorship – one owner
Partnership – two or more people share ownership
Corporation – owned by shareholders
Accounting Cycle
Transactions occur, recorded in journal, posted to ledger, trial balance, work sheet, formal financial statements, adjustments and closing entries, post-closing trial balance.
Professional Accounting Organizations
CPA – new designation in Canada merging CGA, CA and CMA
CGA – certified general accountants association
CMA – certified management accountant
CA – Chartered Accountant
CICA
– Canadian Institute of chartered accountants – CICA handbook – GAAPs
Duties of an Accounting Clerk
- ensure transactions are properly recorded
- record accounting entries in journal/ledger
- make payroll calculations
- make banking transactions
Duties of an Accountant
- developing accounting systems
- ensuring all GAAPs are followed
- interpreting data
- preparing reports
- going to management meetings
- supervising work of all accounting employees
Chapter 2 The Balance Sheet
Assets Things owned by an individual or firm, which have value
Debts Liabilities
Equity Difference between assets and liabilities, also called capital, or net worth
Fundamental Accounting Equation
Assets – Liabilities = Owner's Equity
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity
Know the parts of a balance sheet. Be familiar with the different accounts!
Creditor's Claims on Assets – liabilities
Owner's Claim on Assets – Equity
GAAPS
Business Entity Concept – accounting for a business organization must be kept separate form the personal affairs of its owner
Continuing Concern Concept
– business will continue to operate unless it is known that it will not
Chapter 3 Transactions
Source Document
A business paper which serves as the original record of a transaction.
Transaction
A change in financial position. A minimum of 2 accounts ALWAYS change in a transaction! After every transaction, the fundamental accounting equation will still equal.
GAAP – The Objectivity Principle
Accounting will be recorded on the basis of objective evidence.
Chapter 4 The Simple Ledger
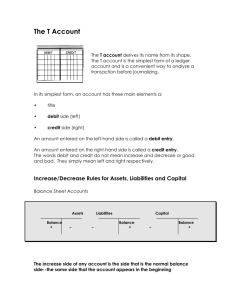
Account – a page specially designed to record the changes in each individual item affecting financial position
Ledger – group or file of accounts
Assets – have natural debit balances, increase on debit side
Liabilities – have natural credit balances, increase on the credit side
Equity – accounts which increase equity (revenue, owner's equity) have natural credit balances, and increase on the credit side – accounts which decrease equity (drawings, and expenses) have natural debit balances, and increase on the debit side
Know what to debit, and what to credit in various transactions!
1.
2.
3.
4.
Exceptional Balances
Occur when an account carries a balance opposite to its natural balance. (i.e. bank account has a credit balance)
4 Uses of the term "on account"
Purchase on account
Sale on account
Payment on account
Receipt on account debit an asset debit A/R debit A/P debit bank credit A/P credit revenue credit bank credit A/R
Trial Balance
The adding of all ledger balances. Debit balances added in dr column, Credit balances added in cr column.
Ledger is said to be in balance if dr column = cr column.
Called "taking off a trial balance"
Steps to take if trail balance is out of balance
1.
2.
3.
4. re-add columns check that all account balances transferred from ledger, and transferred properly recalculate each account balance in the ledger
Check that each accounting entry (transaction) is balanced
Chapter 5 The Expanded Ledger: Revenue, Expense and Drawings
Expanding of the Ledger
Equity – Revenues
Expenses
Drawings
1.
2.
Know the various parts of the income statement (and know how to date an income statement!)
Users of the Income Statement
Owners and managers
Bankers
– is it earning a profit? How much? What should our future plans be?
– should we lend money? Will they be able to repay a loan?
3. Income tax authorities (government) – How much tax should they pay?
Fiscal Period
Period of time over which earnings are measured. All fiscal periods for an individual business are of the same length. Also called the accounting period. Most companies have a 12 month (year) long fiscal period.
Chart of Accounts
Assets
Liabilities
100-199
200-299
Capital/Drawings
Revenues
Expenses
300-399
400-499
500-599
Chapter 6 The Journal and Source Documents
Journal
A book in which the accounting entries for all transactions are first recorded, in chronological (order that they happened) order. Also called the book of original entry.
Journal Entry
All accounting changes for one transaction in the form in which they are written up in the journal.
Journalizing
Process of recording accounting entries in the journal.
Know how to write the date properly in the journal. (pg. 159)
1.
2.
- debits come before credits
- credits should be indented
Opening Entry
Journal entry that starts the books off, or opens them.
Source Documents – 2 purposes
They serve as proof of a transaction.
Serve as reference for checking work, finding errors, etc.
Cash Sales Slip
- goods/services sold for cash
Dr bank, Cr sales
Sales Invoice
- goods/services sold on credit
Dr A/R, Cr sales
Purchase Invoice
- goods/services purchased on credit
Dr asset account, Cr A/P
Point of Sale Summary
- summary of revenues collected in the form of debit and credit card transactions
- use P.O.S. or point of sale terminal (electronic, computerized cash register)
Dr bank, Cr sales
Cheque Copies
- Document supporting the accounting entry for a payment by cheque
Dr A/P
Cr Bank
Cash Receipts Daily Summary
- lists money coming in from customers
- made by a mail-room clerk who opens the mail, checking for customer cheques
Dr Bank
Cr Accounts Receivable
Bank Advice
- document informing a business about an increase or decrease to their bank account
Bank Credit advice – Dr bank, Cr interest earned (revenue)
Bank Debit advice – Dr interest expense, Cr bank