Ion Symbol & Name Rules
advertisement

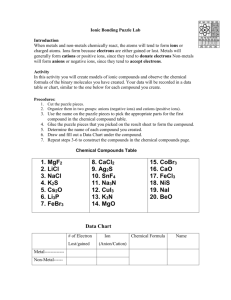
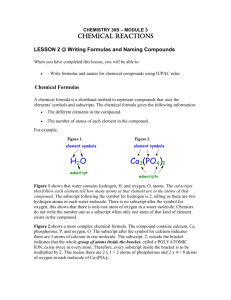
Ion Symbol & Name Rules 1. Ions are charged particles that have a symbol or formula and a name. 2. When an ion symbol is written you must include the charge of the ion. 3. When an ion name is written you do not include the charge of the ion. Cation (+) Ion Rules 1. 2. 3. 4. Elemental cation names look like the element names, so they must end in the word ion. Elemental cation charges are determined by their family on the Periodic Table. Ions that can hold more than one charge must have different names for each ion. There are two naming methods. Classical Names Suffix -ic means greater positive charge Suffix -ous means lesser positive charge Stock Names Roman Numerals indicate the positive charge Odd Ions That Do Not Follow Cation Rules As Stated NH41+ Anion (-) Ion Rules 1. Elemental anion names end in the suffix -ide. 2. Anion suffixes -ate & -ite mean that oxygen is present. Suffix -ate means the number of oxygens can be predicted by the Periodic Table. Suffix -ite means one less oxygen than -ate. Yet both hold the same charge. 3. Oxygen always acts as the Oxide ion with a (-2) charge, so almost anything that attaches to oxide to form an ion must be positive in charge. (Two negative things repel.) 4. Prefix bi- means that a Hydrogen Ion H1+ has attached to an anion and decreased its charge by one Odd Ions That Do Not Follow Anion Rules As Stated CN 1cyanide 1OH hydroxide C2H3O2 1acetate 1MnO4 permanganate ClO 1hypochlorite hypo- prefix means under, so one oxygen under chlorite 1ClO2 chlorite ClO31chlorate 1ClO4 perchlorate per- (hyper-) prefix means above, so one oxygen above chlorate Di- prefix means two H2PO41hydrogen biphosphate or dihydrogen phosphate Cr2O7 2dichromate C2O4 2- oxalate