Document
advertisement

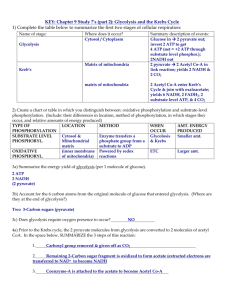
Biology 122, Quiz 3, 2012 Name: ______________________________ Directions: 1) Print your name LEGIBLY on BOTH the scantron form and this question sheet; 2) Fill in the scantron form appropriately – don’t mark on this question sheet; Turn both the scantron form and this answer sheet in. There are 10 questions, each worth 1 point plus one extra credit question. 1. The chemical 2,4 dinitrophenol (DNP) is used in the manufacturing of dyes, wood preservatives, explosives, and insect control substances, and as a photographic developer. Products containing DNP are TOXIC. In living cells, DNP acts as a proton ionophore, an agent that can shuttle protons (hydrogen ions) across biological membranes. It defeats the proton gradient across mitochondrial inner membranes, collapsing the proton motive force that the cell uses to produce most of its ATP chemical energy. Instead of producing ATP, the energy of the proton gradient is lost as heat. In a cell exposed to DNP, how many ATP molecules would be generated per molecule of glucose oxidized? A. 2 B. 4 C. 36 D. 38 2. Which of the following molecules does NOT need to cross the inner membrane of the mitochondria for cellular respiration to proceed normally? A. H+ ions (protons) B. acetyl-CoA C. pyruvate D. oxygen 3. If you were an ANAEROBIC bacterium and needed to harvest energy, which of the following would be your best option? A. glycolysis and fermentation B. fermentation and cellular respiration C. Krebs cycle and fermentation D. fermentation only 4. Select the correct sequence concerning glucose catabolism. A. glycolysis Pyruvate Acetyl CoA Electron Transport Chain Krebs Cycle B. glycolysis Pyruvate Acetyl CoA Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain C. glycolysis Acetyl CoA Pyruvate Electron Transport Chain Krebs Cycle D. glycolysis Acetyl CoA Pyruvate Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain 5. The energy released in the mitochondrial electron transport chain is used to pump (transport) protons into the A. matrix. B. cytoplasm. C. Endoplasmic Reticulum. D. inter-membrane space of mitochondria. E. enzyme complex of the Krebs cycle. 6. In cellular respiration, the decarboxylation (removal of a C and 2 O’s as CO2) step of pyruvate oxidation takes place in the A. cytoplasm. B. Golgi body. C. endoplasmic reticulum. D. matrix of the mitochondrion. E. nucleus. 7. The net end-products of glycolysis are A. 2 pyruvates, 2 ethanols, 2 ATP’s, 2 NADH’s. B. 2 ethanols, 2 ATP’s, 2 NADH’s. C. 2 pyruvates, 2 ATP’s, 2 NADH’s. D. 2 pyruvates, 4 ATP’s, 4 NADH’s. E. CO2, fructose, 2 ATP’s, 2 NADH’s. 8. In which of the following phases of glycolysis are two ATP molecules are required? A. cleavage and rearrangement (splitting) B. glucose priming (energy investment) C. conversion of a 6 carbon molecule into two 3 carbon molecules D. pyruvate formation E. acetyl-CoA formation 9. A process common to all living organisms, aerobic and anaerobic, is A. glycolysis. B. fermentation. C. the Krebs cycle. D. electron transport chain reactions. E. pyruvate oxidation. 10. A molecule that can gain and carry electrons and that is utilized in the CYTOPLASM during glucose oxidation is A. pyruvate. B. cyclic AMP. C. ATP. D. NAD+. E. FAD. Extra Credit: 11. The functions of the cytoskeleton include all of the following except A. providing the cell shape. B. providing scaffolding for the enzymes in certain areas of the cell. C. pulling chromosomes to opposite poles in mitosis. D. providing conduits for the movement of vesicles in the cell. E. ribosome assembly.