AutoRecovery save of Spanish Final Exam Format
advertisement

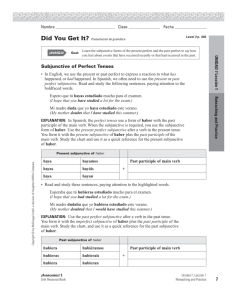
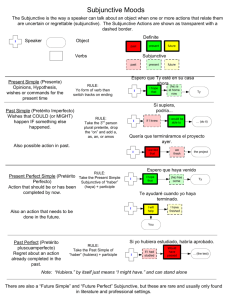
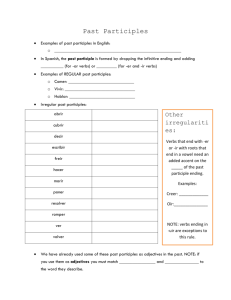
Spanish Final Exam Format Tuesday, June 15 (10:15 – 12:15) 160 Multiple Choice Questions – Should take an hour and a half o Listening Activity o Reading Comprehension Activity – T/F o Vocabulario - Vocabulary: (About 70) La Casa/Apartamento – House/Apartment – Parts, etc. (Dark Yellow Sheet - Under Sort: Build/Room) Might be pictures Quehaceres – Chores (Dark Yellow Sheet - under Sort: Chore/Chores) Example (in Spanish) – The doctor wrote a prescription for the patient. Expresionales Impersonales – See the 6-7 Impersonal Expressions (Part of pages of the Subjunctive Vocab) subjunctive “Verbos especiales” del subjuntivo – vocab Special Verbs for the Subjunctive (Subjunctive Vocab) Questions will be if it takes the subjunctive or not – see the sheet showing which are followed by subjunctive/indicative and the Wedding Sheet too Descripción – basic vocab such as color, etc. o Gramática – Grammar: Broken down into sections Pronombres Dobles – Double Object Pronouns Direct answers what/whom receives the action of the verb. Indirect answers to what/whom, for what/whom Position of double object prounouns o Before conjugate verb o Attach to the end of an infinitive or affirmative command Order of Pronoun Placement o Reflexive o Indirect o Direct Example 1: José compró la camisa para ella. a. José le la compró. b. José se la compró. c. José comprósela. Example 2: María quiere llevar la ropa para la iglesia. a. María se lo quiere llevar. b. María quiere se la llevar. c. María quiere llevársela. Example 3: Mario ha llevado la camisa a Juan. o Answer: María se la ha llevado Example 4: ¡Compra la camisa para él! a. ¡comprarlela! b. ¡comprársela! c. ¡cómprasela! Verbos Reflexivos – Reflexive Verbs Related to double object pronouns (RID) Presente Subjuntivo – Present Subjunctive Subjunctive vs. Indicative o Subjunctive – doubt/fantasy o Indicative – fact/no doubt See sheets and conjugations/irregulars (DISHES) below Conjugations -ar verbs -e -emos -es -éis -e -en The Irregulars (DISHES) dar - to give dé des dé demos deis den ir - to go vaya vayas vaya vayamos vayáis vayan ser - to be sea seas sea seamos seáis sean haber - to have (auxiliary verb) haya hayas haya hayamos hayáis hayan -er/-ir verbs -a -amos -as áis -a -an estar - to be esté estés esté estemos estéis estén saber - to know sepa sepas sepa sepamos sepáis sepan Presente Perfecto – Present Perfect: A compound tense that expresses an action that took place at no definite time in the past. It is called a compound tense because it is formed with an auxiliary or helping verb. Haber + past participle o The present perfect is the present tense of haber (have) plus the past participle of the verb. o The past participle in Spanish is formed by dropping the –ar, -er, or –ir of the infinitive and adding –ado to an –ar verb or -ido to an –er or –er verb. o Object pronouns (Direct, Indirect, or Reflexive) go before the conjugated form of HABER. o Nothing ever separates the form of Haber from the Past Participle. o Haber: Present Tense he hemos has ha habéis han o The Present Perfect is generally used for the following situations: o When events happened in a period of that includes the present (today, this morning, this week, this year, this century) o When past events are still relevant to the present o When summing up past actions, bring them up to the present Example 1: José ha comprado la gorra para Tomas. o Answer: José se la ha comprado. Participio Pasado (irregulares) – Past Participle (Irregulars) The irregular forms follow patterns. o Ex. abrir – abierto, cubrir cubierto Example 1: describir a. descrito b. describado c. describido Irregular Past Participles VERB PAST PARTICICIPLE ABRIR ABIERTO MEANINING-INFINITIVEPAST PARTICIPLE TO OPEN/OPENED CUBRIR DESCUBRIR CUBIERTO DESCUBIERTRO TO COVER/COVERED TO DISCOVER/DISCOVERED HACER DESHACER REHACER HECHO DESHECHO REHECHO TO DO, MAKE/DONE, MADE TO UNDO/UNDONE TO REDO, REMAKE/ REDONE, REMADE VOLVER VUELTO RESOLVER RESUELTO DEVOLVER DEVUELTO TO RETURN TO/RETURNED (PERSON) TO TO RESOLVE, SOLVE/ RESOLVED, SOLVED TO REURN/RETURNED (THING) PONER IMPONER PUESTO IMPUESTO TO PUT/PUT TO IMPOSE/IMPOSED ESCRIBIR DESCRIBIR ESCRITO DESCRITO TO WRITE/WRITTEN TO DESCRIBE/DESCRIBED IR DECIR MORIR VER ROMPER IDO DICHO MUERTO VISTO ROTO TO GO/GONE TO SAY, TELL/ SAID, TOLD TO DIE/ DIED TO SEE / SEEN TO BREAK/ BROKEN Double Vowels reír – reído leer – leído Futuro – Future Used to Express an action or a state of being that will take place at some time in the future In Spanish the future tense is also used to indicate other things. o Conjecture regarding the present ¿Qué hora será? (I wonder what time it is) ¿Quién será? (Who can that be? I wonder who that is) o Probability regarding the present Serán las cinco (it is probably five o’clock; it must be five o’clock) Tendrá muchos amigos (he probably has many friends; he must have many friends) Maria estará enferma (Mary is probably sick; Mary must be sick) o An indirect quotation Maria dice que ella vendrá mañana (Mary says that she will come tomorrow) The future tense is never used in Spanish after SI when SI means IF. é ás á emos éis án Condicional – Conditional ía ías íamos íais ía ían See sheets/ irregular sheet for future and condicional Irregular Future and Conditional Future Infinitiv o Yo Tú Ud./el/ ella Nosotros Vosotros Uds./ Ellos DECIR DIRÉ DIRÁS DIRÁ DIREMOS DIRÉIS DIRÁN HACER HARÉ HARÁS HARÁ HAREMOS HARÉIS HARÁN SABER SABRÉ SABRÁS SABRÁ SABREMOS SABRÉIS SABRÁN HABER HABRÉ HABRÁS HABRÁ HABREMOS HABRÉIS HABRÁN PODER PODRÉ PODRÁS PODRÁ PODREMOS PODRÉIS PODRÁN CABER CABRÉ CABRÁS CABRÁ CABREMOS CABRÉIS CABRÁN QUERER QUERRÉ QUERRÁS QUERRÁ QUERREMOS QUERRÉIS QUERRÁN PONER PONDRÉ PONDRÁS PONDRÁ PONDREMOS PONDRÉIS PONDRÁN SALIR SALDRÉ SALDRÁS SALDRÁ SALDREMOS SALDRÉIS SALDRÁN TENER TENDRÉ TENDRÁS TENDRÁ TENDREMOS TENDRÉIS TENDRÁN VALER VALDRÉ VALDRÁS VALDRÁ VALDREMOS VALDRÉIS VALDRÁN VENIR VENDRÉ VENDRÁS VENDRÁ VENDREMOS VENDRÉIS VENDRÁN DECIR DIRÍA DIRÍAS DIRÍA DIRÍAMOS DIRÍAIS DIRÍAN HACER HARÍA HARÍAS HARÍA HARÍAMOS HARÍAIS HARÍAN SABER SABRÍA SABRÍAS SABRÍA SABRÍAMOS SABRÍAIS SABRÍAN HABER HABRÍA HABRÍAS HABRÍA HABRÍAMOS HABRÍAIS HABRÍAN PODER PODRÍA PODRÍAS PODRÍA PODRÍAMOS PODRÍAIS PODRÍAN CABER CABRÍA CABRÍAS CABRÍA CABRÍAMOS CABRÍAIS CABRÍAN QUERER QUERRÍA QUERRÍAS QUERRÍA QUERRÍAMOS QUERRÍAIS QUERRÍAN PONER PONDRÍA PONDRÍAS PONDRÍA PONDRÍAMOS PONDRÍAIS PONDRÍAN SALIR SALDRÍA SALDRÍAS SALDRÍA SALDRÍAMOS SALDRÍAIS SALDRÍAN TENER TENDRÍA TENDRÍAS TENDRÍA TENDRÍAMOS TENDRÍAIS TENDRÍAN VALER VALDRÍA VALDRÍAS VALDRÍA VALDRÍAMOS VALDRÍAIS VALDRÍAN VENIR VENDRÍA VENDRÍAS VENDRÍA VENDRÍAMOS VENDRÍAIS VENDRÍAN Conditional Por o para – Por or para Para – think of it as an arrow as it tells us where something is going/going somewhere Por – think of it as a balance sclae as you can often feel the balance on both sides of the term (Exchange) See Por y Para Sheet for more details Mandatos - Commands: Comes into play w/ object pronouns, since double object pronouns attach to the end of an infinitive/affirmative command. o Cultura – Culture: 10-15 Questions at end Artistas (nombre, país): General info Example: Which artista is from Spain? Picasso Mapa de España – Like the test we took with numbers Comunidades autónomas de España – General info about Spain Ex. Eat seafood Ex. Galicia is in south of Spain. Yes or No? Ex. The following artists are from Spain – 1 isn’t from Spain Comidas, etc. de España