Cell Respiration Key
advertisement
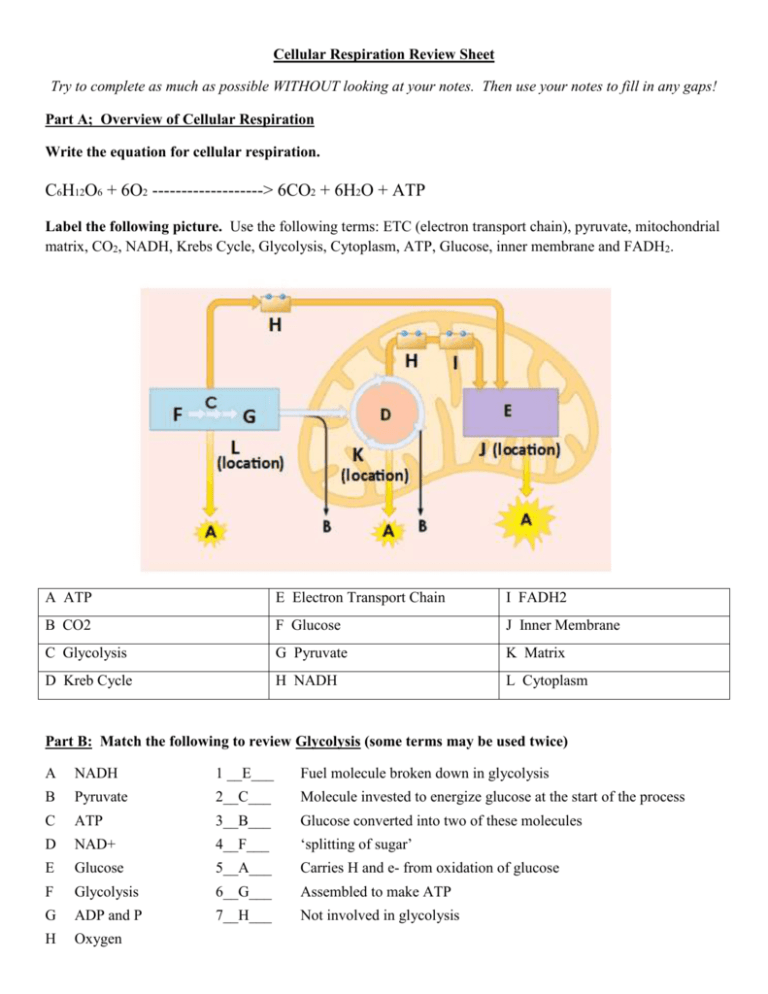
Cellular Respiration Review Sheet Try to complete as much as possible WITHOUT looking at your notes. Then use your notes to fill in any gaps! Part A; Overview of Cellular Respiration Write the equation for cellular respiration. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -------------------> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Label the following picture. Use the following terms: ETC (electron transport chain), pyruvate, mitochondrial matrix, CO2, NADH, Krebs Cycle, Glycolysis, Cytoplasm, ATP, Glucose, inner membrane and FADH2. A ATP E Electron Transport Chain I FADH2 B CO2 F Glucose J Inner Membrane C Glycolysis G Pyruvate K Matrix D Kreb Cycle H NADH L Cytoplasm Part B: Match the following to review Glycolysis (some terms may be used twice) A NADH 1 __E___ Fuel molecule broken down in glycolysis B Pyruvate 2__C___ Molecule invested to energize glucose at the start of the process C ATP 3__B___ Glucose converted into two of these molecules D NAD+ 4__F___ ‘splitting of sugar’ E Glucose 5__A___ Carries H and e- from oxidation of glucose F Glycolysis 6__G___ Assembled to make ATP G ADP and P 7__H___ Not involved in glycolysis H Oxygen Part C: Fill in the blanks to review the grooming of Acetyl CoA and the Kreb Cycle 1. Glycolysis occurs in the (matrix) cytoplasm . while the Kreb cycle in the 2. While the pyruvate passes into the mitochondria it is converted into 3. As glucose is broken down, bonds are broken and energy is acetyl CoA released 4. During these stages of cellular respiration the Carbon in glucose is released as 5. Some of the energy is released as ATP 6. The high energy electrons are carried by inner membrane of the mitochondria. mitochondria . . CO2 gas. but most of it is in high energy electrons. NADH and FADH2 to the Part E: Next to each statement write a G for Glycolysis, KC for Kreb Cycle or ETC for Electron Transport Chain / Chemiosmosis & Oxidative Phosphorylation 1 __ETC___ Generates most of the ATP formed by cellular respiration. 2__KC___ Reduces NAD+ and FAD, producing NADH and FADH2 3__G___ Occurs outside the mitochondrion. 4__G___ Requires 2 ATP and produces 4 for a net gain of 2 ATP. 5__ETC___ Here e- and H+ combine with O2 to make water. 6__ETC___ Occurs along the inner mitochondrial membrane. 7__KC___ Generates most of the CO2 produced by cellular respiration. 8__ETC___ ATP synthase makes ATP. Part F: Fill in the blank to review anaerobic respiration. 1. When oxygen is scarce, human muscle cells can make ATP by lactic acid fermentation. 2. Fermentation enables cells to make ATP in the absence of Oxygen. 3. For every molecule of glucose consumed, glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and NADH. 4. The products of alcoholic fermentation are alcohol and CO2. 5. Lactic Acid fermentation is used to make cheese and yogurt. 6. A cell can use glycolysis supply of NAD+. to generate a small amount of ATP, but it must somehow recycle its 7. Like aerobic respiration, alcoholic fermentation produces CO2 8. The ATP yield of fermentation is much 9. The buildup of lactic acid less gas as a waste product. than that of aerobic respiration. from strenuous exercise can cause muscle fatigue and soreness. Part G: Complete the following. 1. Create a Venn diagram comparing aerobic and anaerobic respiration. 2. Complete the following table to review aerobic respiration Out Purpose Glucose Pyruvate ATP NADH Begin the process of cellular respiration, release energy from glucose. Pyruvate O2 CO2 NADH ATP FADH2 To continue releasing energy from glucose. NADH FADH2 O2 ATP H2O To use the movement of e- and build up of H+ to fuel the production of ATP. ETC Kreb Cycle Glycolysis In 3. Label the following diagram to review the connection between cellular respiration and photosynthesis. WORD BANK Chloroplast Mitochondria Glucose O2 CO2 H2O ATP Solar Energy







