choosing a specialty
advertisement

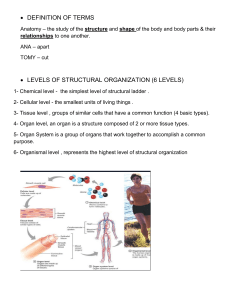
Exercise 1 CHOOSING A SPECIALTY Jill Mathews studied ______ the faculty of medicine and she has just graduated ______ medical school and is talking about her future: ‘I haven’t decided what to specialize ______ yet. I need more experience before I decide, but I’m quite attracted ______ the idea of paediatrics because I like working ______ children. I’d certainly prefer to work with children than, say, elderly patients – so I don’t fancy geriatrics. I was never very interested ______ detailed anatomy, so the surgical specialties like neurosurgery don’t really appeal. You have to be good ______ your hands, which I don’t think is a problem for me – I’ve assisted ______ operations several times, and I’ve even done some minor ops by myself – but surgeons have to be able to do the same thing again and again without getting bored, like tying off cut arteries and so on. I don’t think that would be a problem for me, but they need to make decisions fast and I’m not too good ______ that. I like to have time to think, which means surgery’s probably not right for me. I considered becoming a general practitioner but to get your own consulting room (doctor’s office) is so difficult nowadays.’ HUMAN ANATOMY Ex.2: Fill in the correct name of the system. Choose from the box below. 1.__________ system – the system that carries blood to various parts of the body. It is also called circulatory. 2.__________ system – all the organs and glands involved in the ingestion and digestion of food. 3.__________ system – the ductless gland that produce internal secretions and secrete these directly into the blood or lymph and circulates it to all body parts. 4.__________ system – the skin (the largest organ in the body) and its associated structures. 5.__________ system – a system of nerve cells. It regulates and co-ordinates bodily activities and enables the body to adjust to external and internal changes. 6.__________ system – the system that enables human beings to have offspring. 7.__________ system – the system that brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide. This process, called breathing, involves two acts: inspiration and expiration. 8.__________ system – the system that protects and supports the internal organs and also helps the body move. The skeleton has 206 named bones. Surrounding the bones and soft organs of the body are more than 605 muscles. 9.__________ system – the system that removes urea and other waste materials from the body in a liquid called urine. RESPIRATORY NERVOUS CARDIOVASCULAR URINARY REPRODUCTIVE INTEGUMENTARY ENDOCRINE DIGESTIVE MUSCULOSKELETAL Ex. 3.: Complete the respective system to the individual organs. skeletal system bones liver lungs blood spine thyroid gland stomach genitals heart kidneys 1 intestines skin brain vessels adrenal glands gullet gallbladder bladder skull bronchi spinal cord muscles hair lymph nodes sweat glands spleen 1. How many major cavities are there in the body? Name them. 2. Complete the sentences: The __________ cavity contains the digestive, excretory, and reproductive organs. The __________ cavity contains the spinal cord. The __________ cavity contains the heart, lungs, and associated structures. The __________ cavity contains the brain. 3. Complete the sentences: The __________ plane divides the body into a right and left half. The __________ plane divides the body/organs into upper and lower portions. The __________ plane divides the body into an unequal right and left side. The __________ plane divides the body into an anterior and posterior portion. 4. Match the corresponding terms and their directions. 1. medial a. direction close to the surface of the body 2. lateral b. similar to anterior 3. proximal c. direction towards the back of the body 4. distal d. direction towards a joint/the trunk 5. inferior e. similar to posterior 6. superior f. lower / below a structure located above 7. anterior g. direction away from a joint/the trunk 8. posterior h. direction towards the right / left body side 9. dorsal i. direction towards the front of the body 10. ventral j. upper / above a structure located underneath 11. deep k. direction away from the surface of the body 12. superficial l. direction towards the midline of the body 5. Match the terms with their respective adjective. 1. wrist a. otic 1. 2. ear b. occipital 2. 3. spinal column c. sternal 3. 4. back of head d. mental 4. 5. breastbone e. carpal 5. 6. finger f. vertebral 6. 7. chin g. digital 7. 2 thigh navel lower back neck instep chest abdomen a. b. c. d. e. f. g. lumbar pectoral umbilical femoral tarsal abdominal cervical ANATOMICAL PLANES AND DIRECTIONS - TERMINOLOGY Ex. 4.: Fill in the gaps using the words in the box. feet head upper and lower arms equivalent position front and back fingers planes palms anatomical When discussing the anatomy of the human body, it is useful to consider the body in a standard ___________. This allows the relative position of parts of the body to be described accurately and with less confusion. This is the _____________ position. A person in the anatomical position is standing up straight, with _________ at the sides and ____________ facing forwards (this is known as 'supine') with the __________ extended. The toes of the ____________ are facing forwards, as are the head and eyes. There are three __________ cutting through the body that are used to describe the position and orientation of parts of the body. Median or sagittal plane runs through the body from the __________ to the feet, and divides the body into left and right halves. Midsagittal plane splits the body down in two ____________ portions. Coronal or frontal plane runs through the body from the head to the feet, this time dividing the body into ___________ and ____________ halves. Transverse or horizontal plane is any plane that runs left to right through the body and divides it into _____________ and ___________ sections. Ex. 5: Read the text about diagnosis and try to fill in one word into each gap DIAGNOSIS Medical diagnosis, the determination of the nature and cause of an illness, begins _______(1) a patient history. This includes a history of the present illness with a __________ (2) of symptoms, a past medical history, and a family and a social history. A physical examination, which includes a __________ (3) of all systems and observation of any signs of illness, follows the history taking. Practitioners use the following _____________ (4) in performing physicals: • _____________ (5): visual examination. • _____________ (6): touching the surface of the body with the hands or fingers. • _____________ (7): tapping the body and listening to the sounds produced. • _____________ (8): listening to body sounds with a stethoscope. Vital signs (VS) are also recorded for comparison with normal ranges. Vital signs are _____________ (9) that reflect basic functions necessary to maintain life and include: • Temperature (T). • Pulse rate, measured in _____________ (10) per minute (bpm). • Respiration rate (R), measured in _____________ (11) per minute. • Blood pressure (BP), measured in millimeters _____________ (12) (mm Hg) and recorded when the heart is contracting ( _____________ (13) pressure) and relaxing ( _____________ (14) pressure). 3