Conclusion (20 minutes)
advertisement

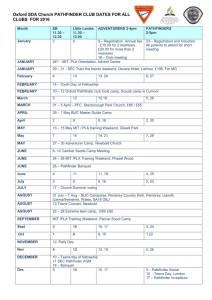
APRIL 2014 SCIENCE LESSON PLAN SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS PATHFINDER PERIOD/TIME 2 Periods/80 minutes THEME Interactions TOPIC Interaction within the Environment LEARNING OBJECTIVES The theme introduces pupils to: Interactions between organisms and the environment. How Man interacts with his environment and the consequences of his actions. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students are able to: Recognise the interactions between Man, living and non-living things in the environment. Comprehend Man’s positive impacts to his environment. Understand the role of Man in conservation to ensure the continuity of life and availability of resources. INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIAL Introduction: NG Picture Slides. Main Lesson : Science textbook. Conclusion : NGX Pathfinder magazine, NGX Pathfinder Projectable Edition, NGX Pathfinder Science Worksheet. SKILLS AND PROCESSES Communicating and creative problem- solving. ETHICS AND VALUES Responsibility and curiosity. Introduction (10 minutes) Show the class picture slides of green innovative buildings, found at the link: http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2012/07/pictures/120726-green-tech-city-buildingsolutions-urban-heat-island/#/city-solutions-green-buildings-floating-laboratory_57161_600x450.jpg. Next, discuss these architectural wonders and their impact on the environment. Ask questions such as: What is the common characteristic or purpose of the construction of these buildings? Why do you think it is important to build such buildings? What impact do you think these buildings have on future constructions and development of a city or country? 1 Introduce the topic of the lesson: In today’s lesson, we will learn about Man’s Positive Impact on His Environment. Main Lesson (50 minutes) Man’s Positive Impact on His Environment Man stands at the top of the ecological pyramid. He is an omnivore, a tertiary consumer, consuming both plants and animals. The human race may have had many negative impacts on the environment, however we have also made an equal number of positive impacts. We have not yet made our environment the best it can be, but we are working hard to fix the problems. Here are just a few of the ways we are giving back: Captive Breeding and Release of Endangered Animals Nearly extinct animals are bred in protected environs. When the numbers are sufficient, they are reintroduced in to the wild. One example is the Arabian Oryx. These animals were captive bred in the Phoenix, San Diego and Los Angeles zoos and later released in the Middle East. California condors, Mauritius kestrels, and black-footed ferrets are some of the other species that have been captive bred and released. Selective Removal Invasive Species Some plants and animals deliberately or accidentally introduced into new areas often thrive there. They wind up replacing indigenous plants and the ecosystems that have been supported by them for thousands of years. One example is Australian gum trees, which have become invasive in California. Efforts are being made to replace them with indigenous trees like the coast live oak. Protecting Native Species Chinese giant pandas are notorious for their poor breeding rate in the wild. The Indian tiger is under threat from illegal poaching. Slow-moving, shallow-water-dwelling manatees are also under threat. All of these animals and others are afforded protection by declaring certain areas of their native habitat as protected reserves. This may help increase their numbers. Controlling Wildfires Every year, wildfires that start spontaneously in Australia, California and other dry areas destroy large areas of forest and the animals living in them. Human efforts often help contain the damage to some extent. Cleaning Waterways Waterways get clogged up with the accumulation of natural debris and excessive plant growth, and also by waste dumping. Periodical clearing prevents flooding of the banks and protects many ecosystems. Reforestation Efforts Large areas that underwent deforestation for cultivation, grazing and for human settlements are reforested with native plant species to restore ecological balance. Finding Renewable Energy Sources Bio-fuels made from plant-derived ethanol and oils are used to reduce our dependence on fast depleting oil 2 reserves. Wind turbines and solar energy generators can help meet local electricity needs and take some of the load off the power grid. The Development of Local Food Sources Local food systems rely upon a network of small, usually family-run farms. Supporting local farmer's markets and community support agriculture (CSA) programs cuts down on individual carbon footprints and encourages the development of a healthy local economy. More people are also growing their own food due to rising costs and a renewed interest in health and sustainability. Using Technology to Reduce Pollution Technological advances are being used to help control and remediate pollution. This includes Nanotechnology filtration systems that purify water, absorbent materials and oil-digesting bacterial cultures to clean up oil spills, and low-sulfur fuels and efficient carbon filters to reduce air pollution. For more information, go to: http://greenliving.lovetoknow.com/How_Do_Humans_Affect_the_Environment Note: Discuss the topic of Man’s Impact on His Environment further with reference to the science textbook. Conclusion (20 minutes) Reproduce the NGX Pathfinder Science Worksheet and discuss the questions to further reinforce students’ understanding of the topic. Afterwards, have the students read the article ‘Feed the World’ from the National Geographic Explorer Pathfinder magazine. Then, divide the class into pairs. Have them do research and write a report about new developments and ways to grow food which is beneficial to both Man and nature. The students should include pictures and proven research in their report. Have them share their findings in the next lesson. 3