allosteric control of glyc
advertisement

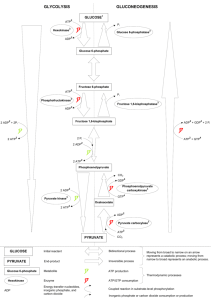
Chem 356 Structure and Function in Biochemistry Lecture Oct 27-30 Allosteric Control of Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis glycolytic pathway degrades glucose ATP provides building blocks rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these two cellular needs In metabolic pathways, enzymes catalyzing irreversible reactions are potential sites of control Glycolysis—irreversible reactions hexokinase phosphofructokinase pyruvate kinase each reaction serves as a control site activities are controlled by allosteric effectors, or by covalent modification, or by transcriptional control 1 Regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis glucose hexokinase G6phosphatase Glucose 6-phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate PFK F1,6bisPase Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate phosphoenolpyruvate PEP carboxykinase Pyruvate kinase oxaloacetate Pyruvate carboxylase pyruvate 2 Phosphofructokinase (PFK) Fructose 6P + ATP PFK fructose 1,6-bisP + ADP most important control element in glycolytic pathway 340 kDa tetrameric enzyme, allosteric inhibited by high levels of ATP negative heterotropic effector 2 conformational states T R in equilibrium each subunit has 2 binding sites for ATP substrate site regulatory site substrate site binds ATP in either state inhibitor site binds ATP in T state other substrate, fructose 6P, binds to R state 3 inhibitory action of ATP is reversed by AMP ATP PFK activity increases when AMP Glycolysis stimulated as energy charge falls Citrate enhances inhibitory effect of ATP High citrate levels indicate abundance of biosynthetic precursors Stop glucose degradation via glycolysis Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (F1,6BPase) Inhibited by AMP Activated by citrate Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate Potent allosteric regulator of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis 4 1980 – F2,6-bisP activator of PFK 1981 –F2,6-bisP inhibitor of F1,6-BPase [F2,6-bisP] in the cell depends on rate of synthesis by phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2) rate of degradation by fructose2,6bisphosphatase (FBPase-2) in starved rat, <1M in liver in well-fed rat, 20M in liver PFK-2 fructose 6P fructose 2,6-bisP FBPase-2 5 the 2 enzymatic activities on one protein bifunctional (or tandem) enzyme the opposing activities of this bifunctional enzyme are regulated in 2 ways phosphorylation vs dephosphorylation 1. F6P (substrate of PFK and product of F1,6BPase) allosterically activates PFK-2 and inhibits FBP-2ase 6 [F6P] [F2,6bisP] PFK feedforward stimulation 2. covalent modification phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) at Ser residue dephosphorylation by phosphoprotein phosphatase phosphorylation inhibits PFK-2 activity and activates FBPase-2 activity dephosphorylation PFK-2 FBPase-2 7 Hexokinase inhibited by G6P if PFK inactive then F6P F6P then G6P inhibition of PFK inhibits hexokinase However liver possesses glucokinase an isoform of hexokinase glucokinase not inhibited by G6P phosphorylates glucose only when it is abundant because >> KM than hexokinase 5 mM glucokinase; 0.1 mM hexokinase role of glucokinase is to provide G6P for the synthesis of glycogen high KM of glucokinase in liver gives brain and muscle priority for glucose when limited 8 Pyruvate kinase (PyK) tetramer of 57 KDa subunits (228 KDa) catalyzes the third irreversible step in glycolysis controls product outflow from pathway pyruvate building block or oxidized (ATP) exists as isoforms L-type: liver M-type: muscle and brain allosterically inhibited by ATP Alanine Acetyl CoA allosterically activated by F1,6-bisP 9 Catalytic properties of L type (but not M) controlled by reversible phosphorylation [glucose] glucagon cAMP cascade phosphorylation of pyruvate kinase PK activity GYLCOLYSIS 10 Pyruvate carboxylase Activated by acetyl CoA Inhibited by ADP Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase Inhibited by ADP 11 12