Exam #3 Study Supplement
advertisement

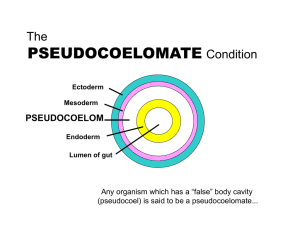
Short answer questions for Zoology Exam #3 Pseudocoelomates 1. Describe the characteristics of the pseudocoelomates and the evolutionary advantages of a pseudocoel. 2. Describe the characteristics of the Phylum Rotifera and Phylum Nematoda. 3. Describe the life cycle of Ascaris Lumbricoides pinworms Trichinella spiralis Filarial Worms (Wuchereria bancrofti). Molluscs 1. Describe the two hypothesis that explains the development of the coelom and which would best fit the Flatworm as its predecessor. 2. Describe the characteristics of the Phylum Mollusca and components of its 3-part body plan. 3. Describe the general characteristics of the class Gastropoda, and compare it to the class Bivalvia. 4. Descrbe the characteristics of the class Cephalopoda and its interesting copulation (reproductive) process. Annelids 1. Describe the characteristics of the Phylum Annelida and the advantages of metamerism and tagmatization. And describe the characteristics of the Class Polychaeta and explain the gas exchange and circulation. 2. Describe the characteristics of the Class Clitellata and describe the reproductive structures and copulation, also describe the Subclass Oligochaeta and Hirudinea and there benefits. 1 Key Terms Pseudocoelomate- Aschelminthes Triploblastic, Aschelminthes, corona, cuticle, elephantiasis, eutely, pseudocoel, cuticle, mastax, , molting, ecdysis, ecdysozoa, lophotrochozoa, Pseudocoelomate, protonephridia, Phylum Rotifera, head, trunk, foot, proboscis, renettes, genital pore, Nematoda, ascaris lumbricoides, roundworm, pinworm, enterobius vermicularis, trichinella spiralis, porkworm, trichinosis, Filarial worm, elephantiasis, lymphatic system, Hookworm, Necaor americanus Molluscan Aceolomate, flatworm, triploblastic, schizocoel hypothesis, protostome, enterocoel hypothosis, diploblastic, Molluscan, head-foot, visceral mass, mantle, mantle cavity, radula, gills, operculum, statocysts, osphradia, nephridium, pericardial cavity, trochophore larva, veligar larva, Class Gastropoda, Torsion, proboscis, siphon, open circulatory system, hydraulic skeleton, Class Bivalvia, umbo, incurrent opening, excurrent opening, anterior end, posterior end, Class Cephalopoda, closed circulatory sytems, hectocotylus, Class Polyplacophora, Class Scaphopoda, Annelida Annelid, metamerism,tagmatization, schizocoelous coelom formation, protostomium, peristomium, parapodia, cuticle, setae, chaetae, closed circulatory system, ganglia, metanephridium, nephridia, clitellum, annuli, pharynx, crop, gizzard, seminal receptacle, ventral nerve, ganglion, Class Polychaeta, Class Clitella, Subclass Oligochaeta, Subclass Hirudinea 2