Nematodes
advertisement
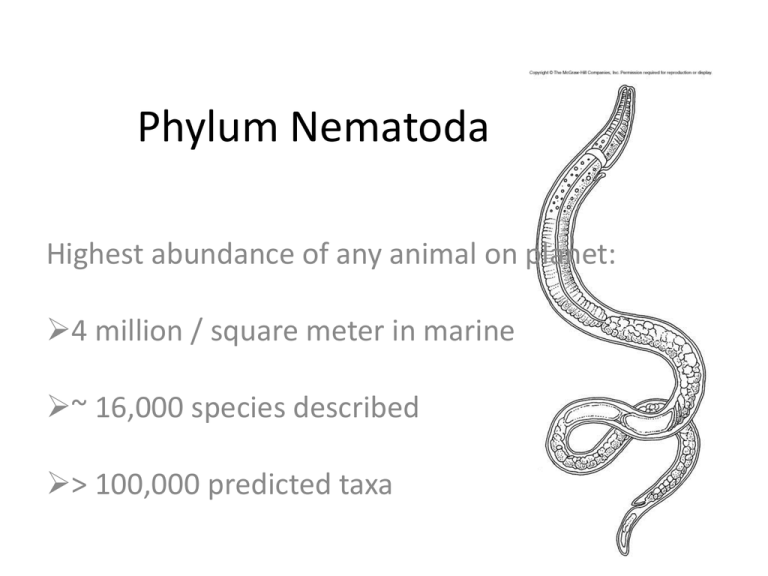
Phylum Nematoda Highest abundance of any animal on planet: 4 million / square meter in marine ~ 16,000 species described > 100,000 predicted taxa Phylum Nematoda • • • • Triploblastic, bilateral, vermiform, unsegmented Complete gut No circulatory or gas exchange structures Longitudinal muscles ONLY Dioecious - males have “hooked” posterior Marine, freshwater, terrestrial some free-living, some parasitic Nematoda body wall • Cuticle secreted by epidermis • Epidermis: syncytial = nuclei not separated by complete cell membranes • Longitudinal nerve cords Support and Locomotion • • • • • Longitudinal muscles No circular muscle layer (burrowing impossible) Body cavity not spacious, filled with organs Cuticle provides support = hydrostatic Whiplike undulatory motion Nematodes feeding on termite Feeding • Detritivores, microscavengers: consume bacteria/fungi on decomposing organic matter • Free-living taxa can be carnivores Digestion Complete digestive tract: mouth, pharynx, intestine, anus Pharynx adds enzymes Digestion extracellular Circulation, Gas Exchange, Excretion, Osmoregulation • Circulation and gas exchange by diffusion and movement of body cavity fluids • Excretory system: renette? • Cuticle differentially permeable to water (H2O in but not out) Nervous System and Sense Organs • Cerebral ganglion = nerve ring and ganglia • Nerves extend from nerve ring • Abundant sense organs = papillae and setae (tactile receptors) • Amphids - paired organs on head = chemosensory Reproduction and Development • Mostly dioecious: sperm amoeboid • Few hermaphroditic (sperm and egg production in same gonad = ovitestis) • Few parthenogenetic • Female: ovary, oviduct, uterus, vagina, gonopore Female nematode x-sec Male – Smaller, curved body – Threadlike tubular testes – Sperm stored in seminal vesicle Male x-sec Hookworm: Necator americanus > 1 billion infected worldwide egg Pinworm = Enterobius vermicularis ~ 20 % US children infected Cool Nematodes! Guinea worm: female can be 1 m long, just under skin, produces ulcer that causes opening, release young (to intermediate copepod host) Chapter 17 Pechenik Cycloneuralia: Nematomorpha and others Phylum Nematomorpha • “thread body” = Hair Worms • 2 orders – marine – freshwater and terrestrial Hair worms • ~ 320 species described •5 are marine •Adults all free-living •Adults do not feed = nonfunctional digestive tracts •Juveniles are internal parasites •Lack digestive tract •Mostly insect hosts •Details of life cycles unknown for most species











