ISE312 Chapter 8 Notes (Sule)
advertisement

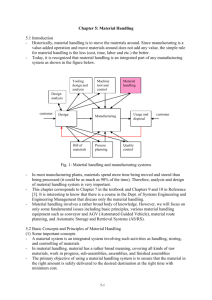
ISE 312 Chapter 8 (Sule) Material Handling: Principles & Equipment Description Spring Semester Two Primary Reasons for study & careful planning of a material-handling system (MHS) 1. Material Handling costs are a large portion of production costs 2. Material Handling costs impacts the operation & design of a facility Objectives > Increase Throughput > Decrease Inventory > Decrease Operating Expense Reducing Production Costs through efficient handling > To increase the efficiency of material flow by ensuring the availability of material when & where they are needed. > To reduce the material handling cost. > To improve facility utilization. > To improve safety and working conditions > To facilitate the manufacturing process. > To increase productivity Principles Of Material Handling: 1. Planning Plan all material-handling & storage activities to obtain maximum overall operating efficiency. 2. System Flow Integrate as many handling activities as is practical into a coordinated system of operations covering vendor, receiving, storage, production, inspection, packaging, warehousing, shipping, transportation, & customer. 3. Material Flow Provide an operation sequence & equipment layout optimizing material flow. 4. Simplification 5. Gravity 6. Space Utilization Simplify handling by reducing, eliminating, or combining unnecessary movements and/or equipment. Use gravity to move material whenever practical. Make optimum utilization of the building cube. 7. Unit size 8. Mechanization Increase the quantity, size, or weight of unit loads or flow rate. Mechanize handling operations. 9. Automation 10. Equipment Provide automation to include production, handling, and storage functions. In selecting handling equipment, consider all aspects of the material handled, the movement, and the method to be used. Standardize handling methods as well as type and sizes of handling equipment. 11. Standardization 12. Adaptability 13. Dead Weight Use methods & equipment that can best perform a variety of tasks & applications when special-purpose equipment is not justified. Reduce the ratio of dead weight of mobile handling equipment to load carried. 1 ISE 312 Chapter 8 (Sule) Material Handling: Principles & Equipment Description Spring Semester 14. Utilization Plan for optimum utilization of handling equipment & manpower. 15. Maintenance 16. Obsolescence Plan for preventive maintenance & scheduled repairs of all handling equipment. Replace obsolete handling methods & equipment when more efficient methods of equipment will improve operations. Use material-handling activities to improve control of production, inventory, and order handling. Use handling equipment to help achieve the desired production capacity. Determine the effectiveness of handling performance in terms of expense per unit handled. Provide suitable methods & equipment for safe handling. 17. Control 18. Capacity 19. Performance 20. Safety Degrees of Mechanization: 1. Manual and dependent on physical effort (includes hand trucks) 2. Mechanized (power is used for driving) 3. Mechanized complemented with computers (extension of above with computers generating directions) 4. Automated (Minimal human intervention) 5. Fully Automated (computers perform on-line control) Unit Load Concept: Definition – a unit load the number of items arranged such that they can be handled as a single object. Advantages: > Move large quantities > Cost per piece for movement is low > Reduced frequency of moves > Supports stacking of materials – better cubic space utilization > Greater speed in loading and unloading the unit load > Protection against damage Disadvantages: > Conflict with large unit loads and JIT > Container handling – return, recycle, or waste > Extra effort to load container and unload Main Material-Handling Costs For Design & Operating MH Systems: > Equipment: cost to purchase equipment & to install. > Operating: cost to maintain, fuel, and operate. (Includes labor wages & injury compensation). > Unit purchase: cost associated with purchasing the pallets & containers. > Packaging > Damage > Money Invested > Computer support systems 2 ISE 312 Chapter 8 (Sule) Spring Semester Material Handling: Principles & Equipment Description Productivity Ratios: Material-Handling-Labor Ratio MHL = Personnel assigned to MH / Total operating personnel Aisle Space Percentage ASP = Space occupied by aisles / Total space Movement/Operation Ratio MO = number of moves / number of productive operations Damaged Loads Ratio DL = number of damaged loads / Total number of loads Relationship between Material Handling & Plant Layout Common Objectives: 1. Effect on space 2. Flow pattern Plant Layout analyzes the equipment & associated costs in order to locate the departments that will minimize the total material handling cost. MHS design analyses the plant layout for move length & move time. Source & Destinations. Equipment ordered to meet these conditions. (Solve & modify until satisfactory design is found that meets objectives). Material-Handling Equipment Main Types: > Conveyors > Cranes > Trucks Equipment Types: Conveyors: Belt, Roller, Chute, Slat, Screw, Chain, Overhead Monorail, Trolley, Wheel, Tow, Bucket, Cart-on-track, Pneumatic tube Cranes: Hoists, Overhead Cranes, Hydraulic Scissors lift Trucks: Handcart, Tier platform, Hand lift, pallet jack, Power Driven hand truck, Forklift, Material lift, Narrow-aisle, Tractor-trailer train, Drum lifter, Dolly, Automated Guided Vehicle System (Advantages/Disadvantages): Conveyors: Moves large number of items, Combine operations (inspection), Temp storage, Fixed path, breakdowns stop system, hinder movement of mobile equipment Cranes Hoists: Space is saved, Heavy load, lifted High investment, limited area, straight line, operator to run Trucks/Carts: Serve different areas, lift, load, unload Cannot handle real heavy loads, limited capacity, aisles, most driven, no combining Screw Conveyor: Large spiral or screw contained in a channel or tube. Rotation moves part along path. Slat Conveyor: Moving surface made up of slats Chute Conveyor: Slide (metal) guides materials Chain conveyor: endless chain directly carrying loads Monorail: overhead track with trolleys & hooks (can be closed loop) 3 4