Part A - spicehotel
advertisement

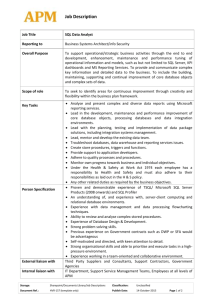
PART A: 1. a) The current system used by Spice Hotel is a manual system. This current system does take a vast amount of time to search, fill out and update employee details due to this manual pen and paper method. Whilst the new employee database system for Spice Hotel will be easy to access employee information as well as searching, changing and updating employee information will be quicker and easier to maintain over the currently manual system. b) As the payroll manager it will be quicker to calculate employee’s wages. Currently this process would be done manually going through each employee file to calculate an employee’s award wage rate level. The new employee database system will have employee information is listed in a clear and easy to access manner. 2. “A prototype is a working model of an information system” Powers, G.K. (2000) pg 13. Spice hotel would advantage from producing prototypes for the new employee database system as this new electronic system can better reflect the participants needs where they can better understand the new prototype with a ‘hands on’ approach and therefore participants have the opportunity to be involved earlier and more directly in developing this new system. Another advantage would be that the Spice Hotel employee files created and used for the prototypes can be used to develop the new system making the new system easier to create. 3. Prototypes are used in developing information systems as they: are created in aid of defining the problem. determine how an information system might solve the problem. are created in order to understand the requirements of the system. test information system features (good and bad features). allow participants to be involved in the process of developing prototypes: a) participants evaluate the model b) participants suggest improvements c) another prototype is built. The three steps are repetitive until a successful prototype successfully solves the problem. Then from here when a prototype has clarified requirements for the problem it will be adapted for more permanent use. 4. Types of prototypes that can be used: data entry screens small sample database formulas that provide approximate results 5. Feasibility Study Feasibility Study Two options have been identified as being suitable candidates for the Spice Hotel database solution. The first solution option involves a Microsoft Access based database running on a Windows 2003 server platform, while the second solution option involves a PostGre SQL based database running on an Ubuntu Linux platform. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages in the contexts of technical, economic, schedule and operational feasibility. A summary of the feasibility study is shown in the table below. Technical Feasibility Microsoft Access PostGre SQL (+) Software is ubiquitous, readily available (-) Readily available but smaller install base (+) Software is routinely upgraded (-) Updates and upgrades are sporadic (+) Widely available technical support and consultancy (-) Relatively difficult to obtain technical support (+) Works on common hardware (+) Works on common hardware (-) Difficult to customise being proprietary software (+) Easy to customise, source code available (+) Integrates with MS Office and other popular software (-) Stand alone, difficult to integrate (+) Shallow learning curve (-) Relatively unstable compared to PostGre SQL (-) Steep learning curve (+) Superior system stability Economic Feasibility Microsoft Access PostGre SQL (-) High ongoing license fees (+) No ongoing license fees (-) Proprietary software, expensive to purchase (+) Open source software, legally free of charge (+) Cheaper technical support and consultancy (-) Expensive technical support and consultancy (+) Cheaper to train participants on Windows systems (-) Difficult to train participants on Linux systems (+) Low hardware maintenance costs, runs on PC’s (+) Low hardware maintenance costs, runs on PC’s (+) Increases staff efficiency = increased profits (+) Increases staff efficiency = increased profits (-) More prone to virus attack, higher chance of downtime (-) Virus attacks far less common (-) Not as stable as PostGre SQL, downtime costs (+) Easier to install and commission = cheaper (+) Extremely stable when set up correctly = less downtime (-) Relatively difficult to install = more costly Schedule Feasibility Microsoft Access (+) Faster to implement compared with Postgre SQL (+)Hardware readily available (+) Shorter training time for existing or new staff (+) Shorter wait times for technical support (+) Less likely to run over time during PostGre SQL (-) Slower to implement (+)Hardware readily available (-) Longer to train existing or new staff (-) Longer wait time for technical support (-) More likely to run over time during implementation implementation (-) Software and licenses may take time to obtain (+) Software instantly available/downloadable Operational Feasibility Microsoft Access PostGre SQL (-) Possible staff resistance to the use of computers (-) Possible staff resistance to the use of computers (+)Greater likelihood of staff acceptance vs. Linux/PostGre (-) Less chance of being accepted by staff (+) Staff most likely have preexperience with Windows (-) Most staff haven’t even heard of Linux/PostGre (-) Possible resistance of management to ongoing license fees (+) No software on-costs once implemented = higher management acceptance (+) Management will value the increase in efficiency (+) Management will value the increase in efficiency Based on the results of the feasibility study, the Microsoft Access based solution was decided upon as the most viable solution for Spice Hotel. The decision to adopt a computer based solution to the current paper based system was based on two main factors; the first factor is that the current paper-based system precludes any future significant growth of the company, and the second factor is to improve operational efficiency in line with modern standards. The adoption of computer based logistics is well and truly overdue for Spice Hotel in this day and age. The major advantages identified with the Microsoft Access solution is the ease of installation, availability of technical support, speed at which the solution can be implemented and the higher level of staff acceptance. The major disadvantage is the initial financial costs of the software and on-going license fees. The decision was made however, that the financial investment in the cost of the software and license fees would be compensated by the shorter training times, cheaper consultancy fees and reduced time to implement the solution. The major advantages identified with the Linux/PostGre SQL solution is the zero financial outlay for the software product and no ongoing licensing fees and proven system stability. However, these advantages would be negated by the relative difficulty in obtaining technical support, higher costs for technical support, longer time required for design and implementation, steeper learning curve for staff and ultimately just would not be a solution that staff would be willing to accept. 6. Design tools: i) Context diagram: ii) Data flow diagram: iii) Data dictionary: Data employee details: Data item Staff id Surname Given name Address Suburb Postcode Department Wage grade level Description Employee’s staff identification number Employee’s surname Employee’s first name Employee’s address Employee’s residing suburb Employee’s residing suburb postcode Employee’s area of work Employee’s wage grade level Employee award grade wage level: Data item Description Surname, Given Name Employee’s surname and given name Department Employee’s area of work Wage grade level Employee’s wage grade level Example 100101 Cahill Michael 65 Kerry Street Newtown 2201 Food and beverage 5 Example Cahill, Michael Food and beverage 5 7. Network Designer Steps A network designer can follow the following steps: 1. Understanding the problem: This step involves identifying the problem and its elements. A requirement report will need to be conducted and prototypes would need to be built. After that decisions would need to be made by conducting a feasibility study. 2. Designing the solution: After understanding the problem, design solutions would need to be constructed such as Context diagrams and data flow diagrams with data dictionaries describing the data within the system. 3. Implementation: After designing the solution you need to decide on a conversion method from the following: - Direct Conversion - Parallel Conversion - Phased Conversion - Pilot Conversion 4. Testing and Evaluation: Finally testing and evaluation the system involves assessing it against technological changes and upgrades in software. Regular maintenance and surveys to the client are part of the evaluation process. 8. Gantt chart: 1. Development of the system qualifications TASK 2. Development, customisation and testing 3. Ordering and installing the equipment 4. Software installation and system testing 5. Training of managers 1 2 3 4 5 TIME (WEEKS) 6 7 8