Al-Andalus Notes
advertisement

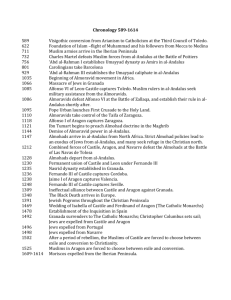
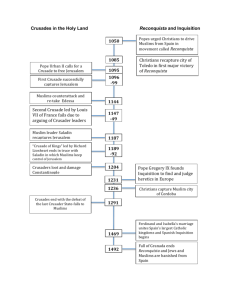
Al- Andalus- Notes- The Rise of Moorish Spain Climate and Geographic Factors o Coordinates of Spain- 40º North and 4º West. Area- 504, 782km (though not all conquered by Muslims, 1.04% water covered) (Wiki, Geography). o Close bodies of water: Cantabrian Sea (Bay of Biscay) North, Mediterranean and Balearic Sea- SouthEast, North Atlantic Ocean- West. South- Strait of Gibraltar, connects North Atlantic Ocean with Mediterranean Sea, separates Morocco and Spain by 13 km apx. (Possible method of travel for conquest of Muslims). o Climate- Continental Region (Meseta Central): → Annual rainfall from 30- 64cm. Winter chilly -1ºCapx, strong wind currents, high humidity, low precipitation. Summer’s warm at 21ºC in North area and 24-27ºC in South area. Night temperatures reach 7-10ºC. o Mediterranean Area→ Higher temps in Winter- 10-13ºC in January. Summer temperatures on coast are 22-27ºC and 2931ºC farther from bodies of water, high humidity (Modern, temperatures known to not have changed greatly since then). o Topography→ Meseta Central (Inner Plateau)- centre of Spain, elevations from 610- 760m, surrounded with mountains Sierra Morena (highest point slightly higher than 1300m), Cordillera Cantábrica (near Bay of Biscay, around areas of Christian rule, ranging from 1500m to 2600m+), and Sistema Iberco (2500m+ highest point of elevation). → Sistema Central- Mountain range splitting Meseta into 2 regions along Castile and Leon. Highest peak at 2592m. South- Montes de Toledo and Sierra de Guadelupe (highest at 1500m). Split by Tagus River, longest in both Spain and Portugal (1038km). → Pyrenees Mountain Range- Highest point at 3404m, separating the peninsula from France and other European Countries. Extends 430km from Bay of Biscay to Mediterranean Sea. Low terrain in east and west part of range. Events and Leaders Umayyad Conquest of Hispania → (Wiki, Conquest) Led by Tariq ibn Ziyad with mostly Berber Soldiers, Muslims+ Syrians. 711-718. Ability from Caliph Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik (Umayyad Caliphate). → Iberian Peninsula dominated by Christian Visigoths, invasion held in 8 years. Series of attacks held, civil war in peninsula at time. → Spain had no governor; Tariq left to Morocco, Musa ibn Nusair (N. African Gov.) brought Arab troops to reside. Captured Seville, Medina, Merida, Sidonia and Saragossa. Battle of Guadalete –(Wiki, Guadalete) → Approx. July 19-23 in 711/712, armies fought at Guadalete River (Cádiz, Spain). Ratio of Visigoths to Umayyads was approx. 100,000: 9,500-12,000 (1st supposed to be much smaller). → King Roderic + other Visigoth nobility believed to have died in Battle of Guadalete. Christian Visigoths defeated, Muslims won. Start of capture in Spain+ Portugal. → Opened Toledo (capital) and Cordoba for conquest; Muslims and Berbers able to control “AlAndalus”- given name for modern Spain and Portugal. Visigoths fled to Eeija. Battle of Covadonga→ (Wiki, Covadonga) Summer, 722, 1st major Christian victory in Al- Andalus after Conquest of Hispania. 718- Visigoth refugees made Don Pelayo leader, forming Asturias and small army. Little threat at first. → Moors defeated by Kingdom of Franks (modern France) in Battle of Toulouse; decided to put down rebellion in Asturias for raising morale. → Commanders: Al-Kama and Munuza. Force of 800 men to Picos de Europa, Pelayo managing strength of 300. Tried influencing Pelayo to surrender; he declined, ordered troops to slaughter. Moors fled, Al-Kama dead. → Later Munuza confronted Pelayo with another force, again failed- 600 moors and 289 Asturias dead. Assured independence of Asturias, Beginning of “Reconquista” (recapturing peninsula from the Moors). Battle of Tours→ (Koeller, Tours) Oct. 10, 732. Spain governed by Abdul Rahman Al Ghafiqi, sent 60,000- 400,000 to Loire River for more land (France) and end of Christian Religion. Army stopped outside Tours, by Franks and leader Charles Martel. → Franks used phalanx style fighting (rectangular group form), with swords, shields, axes, javels, etc. Muslims used many horsemen with big swords and lances. French resisted, battle lasted 2-7 days and ended with French victory, Abd- er Rahman dead and swift flee of Muslims. Emir Abd- al Rahman I- (Bookrags, Abd- al Rahman, I) → Ruled from 756- 788, was entitled “the immigrant”. Formed Emirate of Cordoba, rule of the Umayyad Dynasty. → Escaped murder from Abbasid Dynasty, came to Spain. Blind in one eye, expert with poetry and military. → Dealt with revolt of al- Ala ibn Mugith with beheading, and another from 768- 776 led by Berber Shakya. Al- Mansur Ibn Abi Aamir (Wiki, Al-Mansur) → Ruled Al- Andalus in late 900’s (981) to early 1000’s at peak of peninsula’s power. Title as victorious by grace of God. Organized 57 military campaigns (Leon and Castile, Barcelona, etc.). Very religious, criticised and rejected astronomy and logic, burnt texts on topics in the community (Wiki, Al- Andalus). → Santiago de Compostela- 997- destroyed this city and took doors + bells from shrine of St. James the Apostile (Christian figure) and placed in Mosque of Cordoba for Christian humiliation; Consequence resulted in alliance of Christian rulers in peninsula against him. Died 1002 (spanishfiestas, Moorish Spain). Socio-Political Structure Moorish Spain run by Umayyad Caliphate of Islam until 750’s- symbolizes unity of politics and control in Muslim district. Caliphs ruled empire, at first appointed governors, usually governed there for 3 years (Wiki, Umayyad). 756- Established Emirate and later Caliphate of Cordoba after Muslim wars- Monarchy: One governs entire land. First ruler- Abd al- Rahman. Al- Andalus had Christians/ Mozorabs, Jews, and Muslims (Arabs, Berbers, and Syrians). Muslims, though dominated, never had biggest population (AnneKristina, Moorish Spain). The 10th century had much Christian conversion into Muslim faith, customs, etc. (Mozorabs) (Wiki, AlAndalus). The end of 900’s held many Muslims of Iberian Origin (A.K.A. Muladies). Non- Muslims had status as protected peoples (dhimmis). Adult men had to pay a “Jizya” tax (= to one dinar) annually to stay. Jewish and Christians there had less rights than Muslims. Though better treatment + conditions there than in other parts of Christian Europe. Allowed to practice their religion (privately). Arabic language used in Jewish prayers, when going into synagogues would ceremoniously clean hands and feet (Islamic custom) (Marks, The Jews in Islamic Spain). Jews were 5%+ of pop. Worked mostly as tax collectors, doctors, traders, ambassadors, etc. Treated with dignity and tolerance for most part. Up to apx. 976 A. D. Jews lived well. 750’s- 800’s- Jews worked in translating program, Arabic text converted into languages of love, Greek and Hebrew texts (including science+ philosophy) into Arabic. Similar fashions to Muslims taken, could not wear fur and silk though, nor white and green robes (Islamic colours). Some Christians in Cordoba, however, were beheaded for acts against Muslim faith (martyrdom- dying for good beliefs/causes). Small unrest at beginning, later grand children protested (Wiki, Al- Andalus). Pogroms (raids) in Moorish Spain held- riots against non- Muslims with usual destruction of homes, businesses, and religious buildings. One occurred at Cordoba in 1011. Dec. 30, 1066, Jews banished from Granada, Spain. 1,500 families slaughtered due to their stay. Agriculture and the Economy Irrigation started with hydraulics and hydrostatics to raise water (floodgates, wheels and pumps). Constructed water channels for travel to cities (AnneKristina, Moorish Spain). Several hydraulic practices, including use of Shaduf- (A.K.A- jattara or cigüeñal) tool to move up water from wells, rivers, lakes, etc. Bucket joined to bucket on wooden pole, with fulcrum and counterweight to bring bucket out of water (Covington, Art of science and water). Today’s irrigated lands similar to Al- Andalus- used irrigation in dry summers, improved profit. Albolafia Noria- water wheel- last trace of mills and dams made on Guadalquivir (great) River between 700’s and 900’s, big part of irrigation then (Covington, Art of science and water). Gutters, pipes and aqueducts used to get water, put in cisterns (containers for liquids). Alcazar- Palace in Cordoba- traces of aqueduct at approx. 800’s in reign of Abd- al Rahman II- brought fresh water from Sierra Morena Range, 80km approx. far! Mills used for pounding paper pulp, rice and sugar cane with trip-hammers (powerful, for pounding), process obtained from China. Uni. Of Cordoba and School of Arabic Studies find info tulip coming to Europe through Al- Andalus in the 1000’s. Texts attained from botanist Abu I-Jay’s Umda, + Ibn al-‘Awwam’s Kitab al-Filaba. (Plataforma SINC, Tulips) Crops introduced: Sugar Cane and cotton (most important), Rice, lemons, oranges, asparagus, barley, cinnamon, mustard, ginger, apricots, cloves, nutmeg, artichokes, aubergines, saffron, mulberries, and cumin. Muslims brought over almonds, figs, bananas, etc. Bettered produce of olive trees and oil (AnneKristina, Water Secrets). Spices found in (sub) tropical regions- used for trading, heightening taste in Al-Andalus, disguising sourness of food in dark period (other parts) of Europe, high value. Usage of herbs to better wellbeing. Mulberry trees- planted mostly for leaves- big source of food for silkworms. Spanish silk had high value, booming silk industry. Founded Mediterranean diet: consists of eating olives, cereals, grapes mainly, also eat fruit, nuts, fish, dairy, chicken and lamb, “healing foods”, believed to prevent disease. Organic Farming: Moors studied soil- type and plants reactions to them, applied different types of manure, tried making similar environment, increased productivity. Used Crop Rotation- Land placed with diverse crops, controlled soil fertility (AnneKristina, Moorish Spain). Honey gathered in February, June + September; put fake golden bees in honeycombs for better production (Imamuddin, 92). Valued forest; produced pine, box-wood, teak and oak woods, made utensils, pots, gum, resin (in inks, paints, medicine, etc.), rosin, tar, oil, etc. (Imamuddin, 94). Sheep, cattle, chickens, ducks, hens, geese, doves kept. Rulers raised exotic animals (ex. Peacocks) in gardens as “royal gifts”. Falcons used for hunting, pigeons for messages (UPF, Zoology). Farmers on Spain’s borders kept sheep and cattle- easy escape in case of battle or emergency. In mountains would raise cows and goats also, only Christians raised pigs (Imamuddin, 95). Seas: sardines, al burah, al- shulah, al- shabil, tunny and turjata fished along Spanish rivers, seals found on cost of Mediterranean Sea, skin used for creating coats. (Imamuddin, 99). Breeding- especially horses- large. Andalusian breed perfected during times of Islamic Spain, most modern horses have descent from Andalusia. Creation of finding ancestry of a horse. Used mostly for battling, fed with barley (UPF, Zoology). Mules raised often- used for travel around and carrying carts, large items, etc. (Imamuddin, 96). Raised camels; same use as mules, not as common though, difficult to breed with climate and land (Imamuddin, 97). Cordoba- sheep farming worked well, high importance, wool sent off to textile factories up north, trading use, for winter clothing (AnneKristina, Water Secrets). Raisin industry booming. Linen Exported. Flax heavily grown. Esparto grass made into articles (AnneKristina, Moorish Spain). Al- Andalus farmed extensively, led to low yield of wealth later on, worsening effect on land. Science and Mathematical Contributions In 800’s, Abd- ar Rahman II conscripted many scholars, poets, historians, etc. by offering bribes for the benefit of knowledge in Moorish Spain (Lunde, Science in Al-Andalus). One of first scholars- Abbas ibn Firnas, coming to instruct music and mathematics in Cordoba. Became fascinated in flight; he created wings made of wooden frame and feathers + tried flying. He survived, but began making planetarium where planets on solar system orbited and simulated thunder + lightning; it went well. He bettered mathematical formula for development of synthetic crystals and looked into problems with normality of crystal’s surfaces. Died in 888 A.D. Al- Khwarizmi- wrote book obtained by early period of Al- Andalus, called The Calculation of Integration and Equation, dealt with multiplying and dividing algebraic equations, measuring surfaces of different shapes and other equations. Also introduced “Arabic” figures that symbolized numbers, as well as number zero. Al- Khwarizmi’s tables corrected for astronomic purposes by Maslama al- Kajriti in 900’s. Wrote literature on math and astronomy. Made conversion tables to match Persian dates with Hijran for precise recording of history and past science/ math. Abu al- Quasim- Most famous surgeon (936- 1013), worked for al Hakam II, wrote Tasrif, medical encyclopaedia. 30 volumes including pictures of surgical tools, descriptions of amputations, dental surgeries, treatment of wounds, etc. Invented many medical devices, such as forceps (for extracting dead fetus), surgical needles, the specula (for inspecting of urethra), the scalpel (surgery, dissection usage) and curette (scrapes biological tissue). Used catgut for internal stitching (still used today) (Abu al-Quasim, wiki). Math used for industrial purposes and business, calculating inheritance, measuring, etc. Astronomy used for finding time of prayer and adjusting the calendar. Medicine used for better and faster healing, keeping humans healthy and living longer (Lunde, Science in Al-Andalus). Art, Literature and Music Stone, stucco + plaster used for covering outer surface of buildings, bricks replaced stones later (Beig, Legacy of Al- Andalus). Mosques- places of worship for Muslims. Began as a house and later similar to a temple. Great Mosque (Mezquita) of Cordoba- (wiki, Mosque of Cordoba) → In Cordoba, Spain, contains about 1000 columns and arcs, made by Abd al-Ramán I+ II, Al haken II and Al manzor. Once second biggest Muslim mosque. First called Aljama Mosque. → Made in 600’s as Christian church of St. Vincent; Abd- al- Rahman bought and demolished it and made as mosque. Project began in 784 and named to honour his wife and join with his palace. → Many changes on the mihrab, and creation of a new minaret. Contained a different orientation, facing south possibly from borrowed constructions from Romans and Visigoths. Made of jasper, onyx, marble and granite, from fragments of the old shrine. → Double Arches introduced to Mosque; concept fairly new to architecture and found to support the weight of the large ceilings. Dome contains blue tiles with stars. Gardens = immense ritual and spiritual value to Muslims in Moorish Spain. Has supply of water, shade, flowers and fruit trees. Represents heaven on world and tries to leave an open surrounding, though bringing less emphasis on the sky. Two significant gardens of this time- Alhambra and Generalife (School of Architecture Planning Landscape, Islamic gardens). Geometry used greatly in art and design- little difficulty, applies repetition, balance and symmetry to bring harmonious effect. Appeals more to mind than feeling (Hispanoarabe, To the Andalus). Uses the circle (perfect form), rhombuses, zig zag drawings, star shaped bows, etc. as designs. Artists not allowed to make art of living beings, had to focus on uniqueness of god. Trees + flowers allowed, and anything non-living (Beig, Legacy of Al- Andalus). Calligraphy made into art, floral designs used as well in paintings, drawings on architecture, etc. Hispano- Moresque ware- type of pottery, different from Islamic decoration. Introduction to two new techniques: glazing with opaque white tin finish or metallic lustres (Wiki, Al- Andalus). Arabic calligraphy large and respected. Many would write poetry and other books on science and mathematics through the art of paper making. Ibn Abd Rabbih- Moorish writer and poet, born in 860 in Cordoba. Known for great anthology, called “The Unique Necklace”, divided in 25 parts. Chapters named after jewels and includes poem “Urjuza” which tells story of Abd- ar Rahman’s war use and abuse (Wiki, Ibn, Abd Rabbih). In the 900’s, Cordoba, Spain had about 60,000 palaces, 700 mosques, and 70 libraries. The biggest library held 600,000 books, huge compared to 400 manuscripts in Christian European library. Annually, 60,000 poems, treatises (expositions, more detailed than essay), polemics (similar) and compilations written. Literature more sophisticated than in other parts of Europe (Wiki, Al- Andalus). Today’s musical instruments believed to originate from Moorish ones: the lute from the oud, the guitar from the quetara, the rebec from the rebab (similar to violin), etc. Zyryab- (Abu I- Husan, “Blackbird”) - Musician, astronomer, geographer, botanist, fashion designer and more, played for the court of Abd al- Rahman II from 822- 852. Said to have improved the oud by adding an extra string and established one of first music schools (Wiki, Ziryab). Rhymes made from Arab poetry into European music, specifically muwashshah, and zajal types (Eyre, Andalusian Music). No music to accompany the poetry ever written, hard for musicologists to know how they played. Written By Marko Ilic → The area of Spain, with its areas of varied climate. → A map depicting the Conquest of Muslims, Berbers and Syrians. With this conquest would drive many Visigoths to the northern area. An illustration of Hasdai Ibn Shaprut, a Jewish physician from the 10th century who contributed to the Rise of Moorish Spain. The current state of the Albolafia noria (waterwheel), made in Cordoba, Spain along with other dams and mills on the Guadalquivir River. Illustration of Abu al-Qasim’s innovative surgical tools. Brought much advance in the medical field of Moorish intellect. The famous musician Ziryab, credited for the introduction of Asparagus to Toothpaste. He had revolutionized musical history in Al- Andalus.